Analysis of Diverse Microbial Strains in Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus
10 likes | 130 Views
This study investigates various strains of Escherichia coli, Synechococcus, and Prochlorococcus, focusing on their genetic diversity and ecological roles. With an emphasis on growth conditions, metabolic pathways, and environmental interactions, we explore the adaptability and significance of strains like Synechococcus WH7803, Prochlorococcus MIT9312, and Roseovarius species. Understanding these microbial communities enhances our knowledge of aquatic ecosystems and their responses to climate change.

Analysis of Diverse Microbial Strains in Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus
E N D
Presentation Transcript
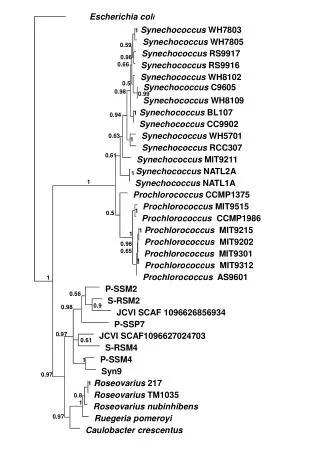
Escherichia coli Synechococcus WH7803 1 Synechococcus WH7805 0.59 Synechococcus RS9917 0.96 Synechococcus RS9916 0.66 Synechococcus WH8102 0.5 Synechococcus C9605 0.98 0.99 Synechococcus WH8109 Synechococcus BL107 1 0.94 Synechococcus CC9902 Synechococcus WH5701 0.63 1 Synechococcus RCC307 0.61 Synechococcus MIT9211 Synechococcus NATL2A 1 Synechococcus NATL1A 1 Prochlorococcus CCMP1375 Prochlorococcus MIT9515 1 0.5 Prochlorococcus CCMP1986 Prochlorococcus MIT9215 1 1 Prochlorococcus MIT9202 0.98 0.65 Prochlorococcus MIT9301 1 Prochlorococcus MIT9312 Prochlorococcus AS9601 1 P-SSM2 0.56 S-RSM2 0.9 0.98 JCVI SCAF 1096626856934 P-SSP7 0.97 JCVI SCAF1096627024703 0.61 S-RSM4 P-SSM4 1 Syn9 0.97 Roseovarius 217 1 Roseovarius TM1035 0.8 1 Roseovarius nubinhibens 0.97 Ruegeria pomeroyi Caulobacter crescentus