Understanding Energy Flow in Ecosystems
240 likes | 376 Views
Learn about producers, consumers, decomposers, food chains, food webs, ecological pyramids, and chemical cycles in ecosystems.

Understanding Energy Flow in Ecosystems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
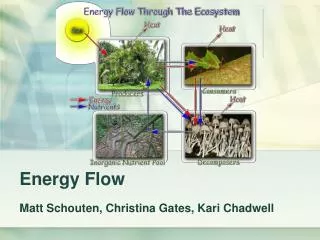
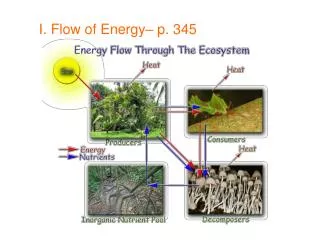
I. Energy Flow A. Producers • Make their own food through photosynthesis using sun, water, and carbon dioxide • Plants, algae
B. Consumers • Feed on other organisms, cannot make their own food • Example: humans, bear, fox, cow, insects
C. Decomposers • Break down dead organisms, recycling chemicals to soil, water, & air • Example: fungi, bacteria, certain insects like earthworms, centipedes, sow bugs
D. Energy enters ecosystems as LIGHT is converted to CHEMICAL ENERGY by producers and exits the ecosystem as HEAT.
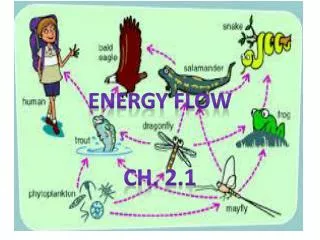
II. Food Chain • Trophic levels Feeding level, represents position in food chain/food web
Food Chain pathway of food transfer from one trophic level to another You always start with PRODUCERS on the left/bottom of a food chain.
Producer --> Primary Consumer--> Secondary Consumer--> Tertiary Consumer D. Decomposers are found at EACH trophic level.
III. Food Web • Definition: pattern of feeding represented by interconnected branching food chains- more realistic representation of feeding relationships.
IV. Three Kinds of Ecological Pyramids A. Energy pyramid • Description: diagram representing energy loss from one trophic level to the next
10% Rule- an average of 10% of the available energy at a trophic level is converted to biomass in the next higher trophic level.
B. Biomass Pyramid • Description: represents the actual dry mass of organisms at each trophic level
Pyramid of Numbers • Description: the number of individual organisms in each trophic level of an ecosystem
V. Chemical Cycles A. Basic plan Producers Consumers Decomposers
B. Carbon-Oxygen Cycle • CO2 Used for photosynthesis • Product of photosynthesis is sugar and oxygen • During cellular respiration, sugar is broken down in presence of oxygen, and CO2 is release into air
C. NITROGEN CYCLE • Nitrogen found in amino acids, make proteins • 80% of it is in atmosphere • Nitrogen Fixation- certain bacteria “fix” nitrogen gas into ammonium • Found near peas, beans, alfalfa
Nitrification- other bacteria convert ammonium into nitrate • Plants can USE nitrate