Isotopes: Key Concepts & Practice
210 likes | 229 Views
Learn about isotopes, mass numbers, and atomic properties. Practice calculating average atomic mass. Understand the relationship between protons, neutrons, and electrons. Access guided notes and worksheets. Improve your grade calculations.

Isotopes: Key Concepts & Practice
E N D
Presentation Transcript
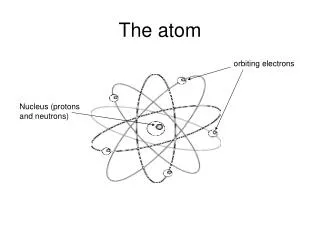
The Atom Isotopes
Drill • You completed problem #2 on the Structure of the Atom WS yesterday. • Pull out that worksheet. • We will go over #2.
Objectives • iWBAT • determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons for isotopes • Explain how isotopes are different from neutral atoms and ions.
Guided Notes • Pick up a copy of the “Isotopes” Guided Notes WS
ISOTOPES • atoms that have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons • the chemical properties of an element depend primarily on its electrons and protons • isotopes of the same element, with different numbers of neutrons have essentially the same chemical properties
ISOTOPES the major difference between 2 isotopes is their mass • isotopes with more neutrons have higher mass than those with fewer neutrons • mass # = (isotope’s # of p+) + (isotope’s # of n0) • to identify an isotope you add the mass number after the element’s name (i.e. chlorine -37) • number of neutrons = mass # - atomic #
On Your Notes • Chlorine is used as an example. • We will look at two chlorine isotopes • Chlorine – 35 • Chlorine - 37 • The “35” and “37” represent mass numbers. • Do you remember how to determine a mass number?
Determine the # of neutrons for each isotope of chlorine • Chlorine – 35 has 18 neutrons • Chlorine – 37 has 20 neutrons • Both isotopes have the same number of protons and electrons, but different numbers of neutrons.
Carbon-12 • The entire periodic table is based on the carbon-12 isotope. • You can write the isotope as: carbon-12 (the line is a dash not minus sign) or 12 C (notice how the mass # is written at the top of the symbol)
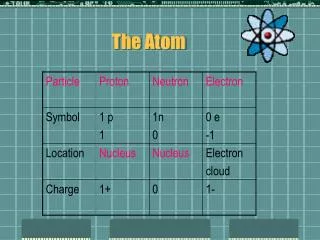
Example Protons don’t change Mass number p+ e- nº Carbon-12 6 6 6 Carbon-14 6 6 8 2 extra neutrons Electrons don’t change
Iodine-125 • What is the difference between this isotope of iodine and the iodine shown on the periodic table? • How many neutrons does iodine-125 have?
Practice • Pick up a copy of the “Structure of the Atom” WS • Answer question “5” only
Average Atomic Mass • Take a look at the Periodic Table. • Notice that the atomic mass for most of the elements is not a whole number. • This is because there are various isotopes for each element. • The average atomic mass of the element is calculated and that is what you see as the mass on the periodic table.
Avg Atomic Mass • Pick up a copy of the Isotopes and Average Atomic Mass WS. • Let’s look at the example in the box at the top of the page.
Example • A sample of cesium is 75% 133 Cs, 20% 132 Cs and 5% 134 Cs. What is its average atomic mass? • Change the % into a decimal. • Multiply the decimal times the mass #. • Add all of the answers. 0.75 x 133 = 99.75 0.20 x 132 = 26.4 0.05 x 134 = 6.7 132.85 amu You will sometimessee the mass withunits of amu “atomic mass units”
Your Grade • We use a math process like Average Atomic Mass to calculate your grade. • 50% assessments • 30% labs • 20% home/classwork
Your Grade • If you currently have… 89.4 % for assessments 73.7 % for labs 84.1 % for home/classwork What is your overall grade for the marking period?
Your Grade • Assessments 50% becomes 0.50 • Labs 30% becomes 0.30 • home/classwork 20% becomes 0.20 Assessments 89.4 % x 0.50 = 44.7 Labs 73.7 % x 0.30 = 22.11 home/classwork 84.1 % x 0.20 = 16.82 83.63
Summary • Explain the difference between a neutral atom, ion and isotope.
Summary Protons: An atom’s identity is determined by the number of protons. If you change the number of protons, you change the element. Neutrons: Neutrons maintain stability. If you change the number of neutrons, you have an ISOTOPE. Electrons: Electrons determine an atom’s behavior. If you change the number of electrons, then you have an ION.