COE: Who we are
340 likes | 469 Views
COE: Who we are. We are a US Center for Excellence directed to educate, train, research and assist in disaster management and humanitarian assistance operations: Department of Defense organization Direct Reporting Unit to U.S. Pacific Command and geographic Combatant Commands

COE: Who we are
E N D
Presentation Transcript
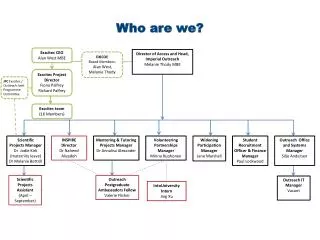
COE: Who we are We are a US Center for Excellence directed to educate, train, research and assist in disaster management and humanitarian assistance operations: • Department of Defense organization • Direct Reporting Unit to U.S. Pacific Command and geographic Combatant Commands • Established in 1994 Government Funded: · Ability to accept interdepartmental and international contributions · Partner with inter-agencies and DoD components · Partner with foundations, institutes, universities, and corporations Establishing field offices at each U.S. Regional Combatant Command Staff: ~ 42 staff, augmented with consultants
COE Mission Educate, train, conduct research and assist in international disaster preparedness, disaster mitigation, disaster management, disaster response, health security, humanitarian assistance and societal resiliency. COE Vision A community of nations prepared to respond, collaborate, and manage natural and man-made disasters. Nations with disaster management plans, prepared to respond to plausible contingencies, and willing to participate in a regional collaborative framework.
Threats and Challenges COE’s Perspective • Poverty • Ethnic Tensions • Natural Disasters • Terrorism • Conflict • Disfunctional Societies U.S Military Responses to Situations, 1990-2002 Evac’s Peace/Relief Contingency Positioning Show of Force Combat Natural Disaster
Samoa 2001: Cyclone Worst Flooding in 50 years 2004: Cyclone Whole towns destroyed India/Pakistan Micronesia Oct. 2005: Earthquake 73,000 dead (Pakistan) 1,400 dead (India) 2002: Cyclone affected 2,000 Papua New Guinea 2007: Cyclone affected 145.000 2002: Earthquake Historical DM/HA Honshu Japan Earthquake, July 2008 “Ring of Fire” Bangladesh, Cyclone Sidr November 2007 3,000 dead China, Sichuan Province, May 2008, 68,000 dead Burma, Cyclone Nargis May 2008, 121,000 dead Philippines June 2008: Typhoon Fengshen, 2004, 2006 Mudslides Luzon 2004 Flood Luzon Indian Ocean, Tsunami Dec 2004 230,000 dead Earthquake Solomon Islands 2007 Tsunami, affected 9,000 Earthquake Feb 2008, Simeulue, Indonesia 2005, Sumatra, Indonesia Central Java Earthquake 2006, 6,000 dead Tsunami Volcano “Ring of Fire” Cyclone Indonesian Volcano Soputan, Nov 2007 Other Natural Disaster
Forecast for DM/HA • Natural Disaster • Flooding – annual occurrence (2 Major events annually) • Earthquake – 2 major events every 5 years • MED,PI,HIV/AIDS • Increasing AIDS cases - PNG, IN, ID, PRC • Cyclonic Storms – annual occurrence(10 major events annually)
COE Disaster Risk Assessment & Research Disaster Preparedness Risk Assessment Assist in Disaster Forecasting
HA/DR Preparedness/Response Observations • How Prepared Do We Need to Be – (Not if – but when) • Scenarios – Most likely, moderate • Measures Capacity & Capability • Test Preparedness • Promotes Understanding: when an event will exceed capabilities • How prepared are we • To Coordinate – To Communicate – To C2 • Roles – Responsibilities • Within – Between Levels of Government • Public – Private - Community Response – Recovery and Revitalization
HA/DR Preparedness/Response Observations • How prepared are we (Cont) • Coordinate With External Support: • UN – NGO – International • Communicate: • Focus (Now-Where are we?) • Requirements (Next-Where are we going?) • Template of Response & Recovery efforts • Method to guide Recovery Redevelopment sequencing • Results: Protracted Recovery - Limited Revitalization • Not just what you do but how you do it
National HA/DR Design Method Design Frame Build Supporting Concept Foster Resilient Societies • Enabling Functions: • Interagency Coordination • Civil-Military Coordination Functional Concepts Humanitarian Assistance & Resiliency Response, Recovery & Transition Disaster Management Disaster Mitigation Revitalization Strategic Outcomes Socially responsible, sporting Individuals Inspired & committed youth Strong and stable families Human dignity upheld Safe and durable society 10
Emergency Relief Phase Recovery / Development Transition Point Need for Assistance Show up early or don’t bother coming International Military and Civil Defence Relief International Civilian Relief UN OCHA, Modified Local / National Response Disaster
Social Resiliency: Characteristics of Success Resistance Recovery Revitalization Predict Absorb Improvise Anticipate Respond Innovate Recover “Revive, not just Restore.” Level of functioning Level of functioning Level of functioning Goal Goal Goal resistance threshold Time Time Time Sources: “Disasters and Communities: understanding social resilience”, Australian Journal of Emergency Management; ICLEI Local Governments for Sustainability, http://www.iclei.org
Front End Assessment On-HadStores andsupply stores Private Sector Capacity HAZARD EVENT CommunityGrids ExternalSupplies andServicesRequired EmergencyResponseCapacity NGO’s Displacedand Homeless CriticalServices CommunitySystemsFunctioning ExternalDistributionCapacityRequired InfrastructureCapacity IncidentManagementCapacity Gap Analysis = Response Capability and Capacity Disaster threshold Recovery Revitalization Emergency Response Time
Understand the Characteristics and Hierarchy of Societal Development Liberty Disruption Identity Creativity Learning Community Protection Subsistence Shelter Water Food Clothing Resist Respond Recover Revitalize Nurturing Services Critical Services Essential Services Promoting Services
Know the HA/DR framework Affected State UN County Team NGO Military Forces Disaster Strikes NGO Donor Nat’l NGOs NGO Nat’l Red Cross/ Red Crescent “Fog of Relief” Donor Donor Donor NGO NGO Affected State Agencies NGO NGO NGO NGO NGOs
Disaster Response: Coordination Mechanisms Government Response State/ Province GovernmentCoordination Mechanism Private/ Public Do No Harm Messages & Outcomes Roles & Responsibilities Community/ Village Early Recovery Emergency Shelter International Military/ Bilateral Camp Coordination & Management Emergency Telecommunications International/ Regional Clusters Coordination Water, Sanitation and Hygiene Health Int’l / RegionalCoordination Mechanism Protection Logistics Nutrition UN/NGOs
Overarching International HA/DR Principles • “Affected State” is a sovereign nation responsible for: • Care of all persons within its territory • Coordination, implementation & monitoring all DR assistance • Request of international disaster relief
Know the HA/DR Framework • Coordination Guidelines & Mechanisms: • International: • Oslo Guidelines • New Humanitarian Architecture (Cluster Approach) • Regional: • APC MADRO • ARF Strategic Guidance for HA/DR • ASEAN Agreement on Disaster Management and Emergency Response (AADMER) • MNF-SOP (Multi-National Forces) • National: • Int’l Disaster Response Laws (IDRL) - Int’l Federation of the Red Cross (IFRC) • Regional Actors involved in Initiatives (Asia-Pacific): • ASEAN • SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) • PIF (Pacific Islands Forum) / SOPAC (Pacific Islands Applied Geoscience Commission)
Overarching International HA/DR Principles • Assisting States/Orgs to coordinate DRO w/ Affected State • Assisting States and their personnel shall abide by the domestic laws • Assisting States self-fund their disaster relief assistance • Assisting States provide disaster relief without seeking: • To further a political or religious standpoint • To Intervene in the internal affairs • Gain a commercial advantage • Gather sensitive political, economic, or military information
Overarching International HA/DR Principles The Principle of Do No Harm: • Not all aid is good aid: • Improperly delivered aid can divide communities and fuel conflicts • Improperly delivered aid can force displacement of populations • Improperly monitored aid can build cultures of dependency • Humanitarian aid • Provides for basic human needs • Lays the foundation for recovery and development
Linking in International HA/DR Response National Enduring Interests Crisis Assessment Identify Disaster Region National Strategy What Happened? Gap Analysis National Response • Affected Region • Infrastructure • Population • Stability • - Political - Economic • - Social - Security How Resilient Are They? Policy Limitations Capability Capacity Activities Messages Outcomes Outcomes Outcomes Long Term Development Effort
ResilientNationFramework Governance Economy Infrastructure Social Structure/Systems Security/Defense Rule of Law Financial Sector Transportation Health Military Participation Trade &Investment Energy Education Police Phases Response Recovery Preparation Mitigation Revitalization Strategic Outcomes Effective and Responsible Governance Sustainable & Broad-based Growth Effective Support of Social Capacity Strengthened Vibrant Society Robust Defense & Law Enforcement
ResilientCommunityFramework Enhance Societal Capacity Develop Intellectual Capital Enhance Resource Independence Create Social Cohesion Foster Good Governance Humanitarian Assistance Education Economy Cultures, attitudes & motivations Leadership Public Health Communication& Information Sustainable Development Social Parity Security Phases Response Recovery Preparation Mitigation Revitalization Strategic Outcomes Safe and durable society Socially responsible, sporting individuals Strong and stable families Human dignity upheld Inspired and committed youth
Village COP Local placeof worship Health clinic Cellulartower Early warning tower Research/ Demonstration nursery Bridge toother markets Community bank Enclosedlatrines Recycling center Communityhall Water storagetanks Earthendam Bridge tocapital city Terracingof crops Women’sco-op center Animalhusbandry Policestation School Granary Seed bank Reforestation Marketplace Borehole well Early warningsirens Fish farm Resilient Village Concepts Societal Capacity(Public health, infrastructure, disaster preparedness, response) Intellectual Capital(Education, communication, information, research, innovation) Resource Independence(Economy, resource management, sustainable livelihoods) Social Cohesion(Gender parity, social protection, community involvement) Good Governance(Leadership, integration, policy & planning) Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment Assessment
Planning Coordination Status of Forces Agreement? Contracting? With whom are we working? When should we respond?0 What is required for landing rights? What are the customs requirements? What are the fuel arrangements and needs? What are the considerations regarding weapons? What fees are Involved? When should we transition?
Disaster Response Framework Host Nation Activity Host Nation Activity Host Nation Activity International Military Activity Effect International Military Activity Effect Host Nation Response & Recovery Effort Effect Int’l Military Activity Foster Resilient Societies Revitalization Recover Response Effect Effect Effect International Military Activity Year 1 Year 10 or longer
Civilian Humanitarian Responders - NGOs • Not an agencies of a government or UN; • Private humanitarian organizations established by individual charters; • Diverse in size, organization, motive, resources, function and mission; • Funded by grants or private donations; • National or international; • Essential to humanitarian operations: • Implementing partners for UN and donor government projects • First responders to arrive, last to leave • Primary “on-the-ground” humanitarian actors
Civilian agencies’ view on military HA/DR assistance Varies greatly amongst agencies: Negative views & concerns: Concern over politicization / militarization of aid; Militaries lack expertise in HADR operations. Lack of proper transition / military HADR operations not sustainable. Military HA/DR operations blur the lines of distinction, lessening staff / beneficiary security. Militaries take over operations, ordering aid agencies. Positive views: • Militaries bring needed logistics & material in the emergency phase. • Militaries bring in needed manpower in the emergency phase. • Militaries fill HA/DR gaps during the emergency phase. • Militaries help provide security. • Militaries help coordinate response activities.
Societal Structure National/ Federal Regional State/Provincial County/District First Responders Community Families
Coordination & Integration: Preparedness and Support National/ Federal Regional Organizations International Organizations Regional Assistance International Assistance OC Funding OC Provide Assistance Regional EOC EOC State/Provincial • Subject Matter Experts • Resources • Equipment • Facilities • Training • Communications Request Assistance EOC EOC County/District First Responders OC OC OC OC Community CC CC CC CC CC CC Families CW CW CW CW CW CW
Preparedness: Seams, gaps & capacities National/ Federal AL AZ KS KY LA NM NY NC AR NJ Seams Regional Regional NW NE SW SE State/Provincial Seams CA CO CT DE FL GA ID IL IN MD MA OH State/Provincial WV SD TN TX UT VT VA WA WY WI MI MN MS MO MT NE NV NH OR PA RI SC IA OK ME ND Gaps County/District C County/District C D D D C C C C D D D C C C D Gaps First Responders Hwy Patrol Sheriff St. Police St. Police City Fire First Responders City Fire Paramedics Hwy Patrol Co. Fire Paramedics City Fire State Fire Sheriff Hwy Patrol State Fire Paramedics Sheriff Co. Fire State Fire Community St. Police Co. Fire Seams churches supplies doctors hospitals energy Community stores churches restaurants business energy schools schools hospitals restaurants hospitals stores schools churches restaurants business supplies supplies doctors stores doctors business energy Gaps Family F F F F F F F Family F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F F