Protists
360 likes | 596 Views
Protists. Using words. What does the word cryptic mean? What is a cryptic message? What is a pseudonym ? Why might a writer use a pseudonym ? What is a pseudopod ? What do you think a pseudopod helps an organism do?. Samuel Clemens wrote under the pseudonym Mark Twain.

Protists
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Using words • What does the word cryptic mean? • What is a cryptic message? • What is a pseudonym? • Why might a writer use a pseudonym? • What is a pseudopod? • What do you think a pseudopod helps an organism do? Samuel Clemens wrote under the pseudonym Mark Twain
Key Ideas • What types of organisms are classified as Protists? • What methods of reproduction do protists use? • Why is the classification of protists likely to change in the future?
A Visual of Protists • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RI-Aa2Uf0B8&feature=related • You need to wear headphones for this. • Draw at least 7 different types of protists that you see.
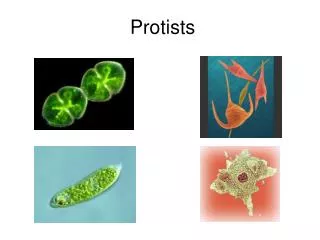
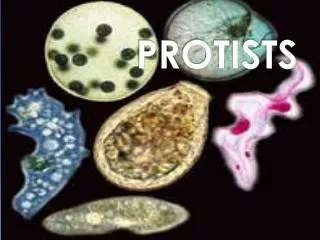
What are protists? • From tiny glass stars that float in the ocean to slimy green fuzz that carpets rocks on the shore, a wide variety of organisms make up the group we call protists. • The kingdom Protista is made up of organisms that do not belong in any of the other kingdoms – the members of this kingdom are quite diverse. • All protists have one thing in common – they are eukaryotic • Protists are eukaryotic organisms that cannot be classified as fungi, plants or animals.
Asexual Results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent Binary fission – a unicellular organism replicates its DNA and splits in half Budding – a part of the parent organisms pinches off and forms a new organism Fragmentation – part of a multicellular organism breaks off and forms a new organism Sexual Results in offspring that are genetically different from the parents Occurs as a result to environmental stress, such as a period of drought Unicellular organisms – see diagrams that follow Multicellular organisms – see diagrams that follow Reproduction
Classifying Protists • The classification of organisms currently grouped in the kingdom Protista is likely to change as scientists learn more about how these organisms are related to each other and to members of other kingoms.
Define the following words: • protist • Protista • prokaryote • eukaryote
Bell Ringer • Complete the Venn Diagram on the back of your paper. • Use pages 502, 504, 505, and 506 to help you.
Amoebas The amoeba is a tiny, one-celled organism. You need a microscope to see most amoebas - the largest are only about 1 mm across. Amoebas live in fresh water (like puddle and ponds), in salt water, in wet soil, and in animals (including people). There are many different types of amoebas. The name amoeba comes from the Greek word amoibe, which means change. (Amoeba is sometimes spelled ameba.)
Amoebas Amoebas use chlorophyll and accessory pigments to harvest (collect) and use the energy from the sunlight. Amoebas are considered one of the most important groups of organisms on our planet because they produce much of Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis.
Amoebas- Diet Amoebas eat algae, bacteria, plant cells, and microscopic protozoa and metazoa - some amoebas are parasites. They eat by surrounding tiny particles of food with pseudopods, forming a bubble-like food vacuole. The food vacuole digests the food. Wastes and excess water are transported outside the cell by contractile vacuoles.
Amoebas- Locomotion Amoebas move by changing the shape of their body, forming pseudopods (temporary foot-like structures). The word pseudopod means "false foot."
Amoebas- Reproduction Amoebas reproduce asexually by binary fission. A parent cell divides (the nucleus also divides in a process called fission) and produces two smaller copies of itself.
Amoebas- Classification • Eukaryota (organisms with nucleated cells) • Kingdom Protista (flagellates, amoebae, algae, and parasitic protists) • Phylum Protozoa (single-celled organisms) • Class Sarcodina (having pseudopods).
Amoebas Nucleus-central organelle, controls reproduction and other functions. cell membrane - thin layer that surrounds the amoeba; it allows some substances to pass into the cell, and blocks other substances. contractile vacuole – sends out excess water and waste Food being engulfed by pseudopods food vacuole - a cavity where food is stored and digested (broken down) pseudopods - temporary "feet" that the amoeba uses to move around and to swallow up food. cytoplasm - a jelly-like material that fills most of the cell and “holds” the organelles.
Malaria • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iwAEsOpvHn0 • You will need headphones for this. • Please X out of the video when it is done.
Malaria • Malaria is spread by the bite of the Anopheles mosquito • The infected mosquito bites a human and injects saliva containing the parasite. [A] Anopheles mosquito • First Stage: the sporozoite infects the liver. [B] • Second Stage: merozoite infects red blood cells. [C] • Inside the red blood cell, the parasite divides, producing 8-24 merozoites [D] • The merozoites burst from the red blood cell and destroy the blood cell [E]
Oxygen Production Plant-like protists, along with photosynthetic cyanobacteria, produce at least half of Earth’s oxygen.
Nutrient Cycling During photosynthesis, these protists also consume carbon dioxide (CO2), a greenhouse gas. By taking up CO2, protists may play an important role in reducing global warming. Other protists are important decomposers. They contribute to the recycling of nutrients, such as carbon, nitrogen, and other minerals.
Food Webs Photosynthetic protists, with cyanobacteria, and tiny arthropods form the base of almost all aquatic food chains. For example, protists make up a large percentage of the plankton in the oceans. Plankton are eaten by anchovies. Anchovies are eaten by sea lions. Sea lions are eaten by orcas.
Algal Blooms During warm seasons, when nutrients in ocean water are abundant, algae population can rise significantly. An algal bloom is a rapid increase in the population of algae in an aquatic ecosystem. During a bloom, there may be as many as 20 million protists per liter of sea water. A red tide is caused by a bloom of dinoflagellates. Dinoflagellates cause toxins. Humans can become ill if they eat fish or shellfish during a red tide. When an algal bloom dies, the bacteria that consume and decompose the algae reduce the oxygen levels in the water. As a result, large numbers of fish and other marine animals may die.
Algal Blooms • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B4IAAa667EM&feature=related • You will need headphones for this. • Please X out of the video when you are done.
Protist Symbioses Symbiotic protists, including the ones that cause disease, make up about 15% of all the species on Earth. Some photosynthetic protists live with corals. The protists supply the coral with nutrients and give the coral its color. The coral provides the protists with a stable environment, nitrogen, and minerals. Many protists live in the digestive tract of humans and other animals. Cattle could not digest hay and grass without their protists symbionts. Photosynthetic single-celled algae form an association with fungi that we call lichen.
A protist is any organism that is not a plant, an animal, a fungus, or a (an)… A. archaebacterium B. eubacterium C. eukaryote D. prokaryote
In an amoeba, what is the small cavity within the cytoplasm that stores and digests food? • gullet • pseudopod • food vacuole • contractile vacuole
How does a person come down with malaria? • contaminated water supplies • Infection by the animal-like Giardia • The bite of the Anopheles mosquito • The bite of the tse-tse fly
Which substances allow algae to harvest and use the energy from sunlight? • cilium and fucoxanthin • chlorophyll and accessory pigments • phycobilin and flagellum • oogonium and antheridium
What is a bloom? • the clouding of water by sewage. • an enormous mass of algae. • a symbiotic relationship between algae and coral. • none of the above
Why are algae considered one of the most important groups of organisms on our planet? • They are rich in vitamin C. • They produce chemicals that are used to treat health problems. • They produce much of Earth’s oxygen through photosynthesis. • They produce chemicals that are used to make plastics, waxes, and paints.