DNA : REPLICATION
140 likes | 391 Views
DNA : REPLICATION. SOAR Charter Academy Mr. Najera. DNA?. Stands for : DEOXYRIBONUCLEAIC ACID. Structure of DNA. Discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 with the help of Rosalind Franlin’s x-ray photography. DNA: Structure.

DNA : REPLICATION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DNA : REPLICATION SOAR Charter Academy Mr. Najera
DNA? • Stands for : DEOXYRIBONUCLEAIC ACID
Structure of DNA • Discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953 with the help of Rosalind Franlin’s x-ray photography.
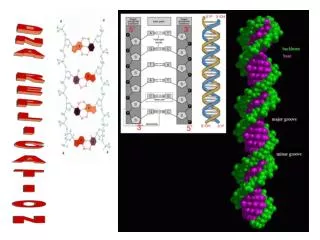
DNA: Structure • DNA strands are tightly wound around proteins. These proteins support the structure. • Looks like a twisted ladder.
“Sides of the Ladder” • Molecules of sugar called Deoxyribose alternating with molecules called phosphates. (salts)
“Steps of the ladder” • Made up of four different nitrogen bases. (molecule paired with nitrogen) which pair up with a partner base. • ADENINE • THYMINE • GUANINE • CYTOSINE
“Partner bases”-the steps of the ladder • ADENINE only with THYMINE • GUANINE only with CYTOSINE A-T and G-C
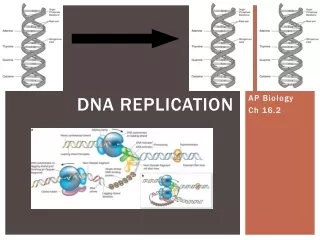
REPLICATION-copying DNA • DNA unwinds like a zipper. • Nitrogen bases pair with their partners backwards. • Results in two exact copies of the original.