DEVELOPMENT AND Economic geography
360 likes | 551 Views
DEVELOPMENT AND Economic geography. RESOURCES. What are the kinds of resources available?. Natural Resources. Renewable resources will replace themselves over time. Soil, water, and forests. Nonrenewable resources. Will not replace themselves. Once they are used, they are gone.

DEVELOPMENT AND Economic geography
E N D
Presentation Transcript
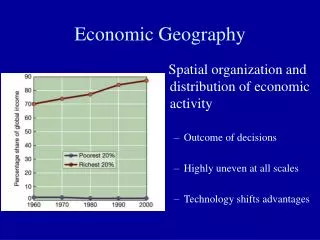
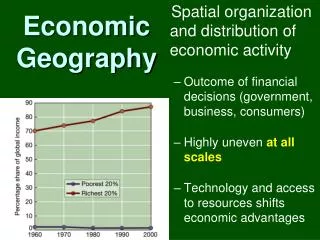
RESOURCES What are the kinds of resources available?
Natural Resources • Renewable resources will replace themselves over time. • Soil, water, and forests
Nonrenewable resources • Will not replace themselves. Once they are used, they are gone. • Fossil fuels (oil, coal, natural gas), and metals (gold, iron, copper, and bauxite)
Human Resources • Human resources are man and his mind, and they depend on: • Level of education • Is labor skilled or unskilled? • Are entrepreneurial or managerial abilities needed?
Capital Resources • Resources that can be used to make more, like money or tools • the availability of money for lending • the level of infrastructure, • the availability and use of tools, machines, and technologies
What are the effects of unequal distribution of resources? • 1. Causes countries to specialize in the goods and services they produce. • 2. Interdependence of nations -- they must trade with each other to acquire the goods they do not possess • 3. Uneven economic development (rich and poor countries)
The effects of unequal distribution of resources cont. • 4. Energy producers and consumers • 5. Imperialism (one country dominating another) • 6. Conflicts over control of resources
How is development measured? • Gross Domestic Product Per Capita • aka GDP per capita • value of goods and services produced within a country within a given year • Other similar measures include • GNP (broader value), • PPP (purchasing power parity) which considers what money actually buys in each country • Usually calculated in US dollars to allow comparisons between countries
Two other ways of Measuring Development Gross National Product (GNP) Measure of the total value of the officially recorded goods and services produced by the citizens and corporations of a country in a given year. Includes things produced inside and outside a country’s territory. Gross National Income (GNI) Measure of the monetary worth of what is produced within a country plus income received from investments outside the country. Now also includes remittances. ** Most common measurement used today.
Issues with Measuring Economic Development • All measurements count the: • Formal Economy – the legal economy that governments tax and monitor. • All measurements do not count the: • Informal Economy – the illegal or uncounted economy that governments do not tax or keep track of.
High human development 35000 Medium human development 6000 Low human development 358 Measuring Development • Gross Domestic Product per Capita
Other Measures of Development --Unemployment • The number of people who (in a given year) were not working but were available for work and had taken steps to seek work. • In some circumstances where employment opportunities are particularly limited in a country, the last criteria ("had taken steps to seek work") may be relaxed.
Other Measures of Development Telephone Lines • Number of subscriber lines (business and residential) plus public telephones per 100 inhabitants.
Other Measures of Development Undernourished peopleThe percentage of the population whose food intake falls below the minimum requirement needed to meet dietary energy requirements on a regular
Other Measures of Development • Television Receivers Number of television receivers and/or number of licenses issued per thousand inhabitants. • Water Resources per CapitaAverage amount of water that is available per person from rivers and groundwater each year.
Dependency Ratio by Country, 2005 A measure of the number of people under the age of 15 and over the age of 65 that depends on each working-age adult.
Types of Economic Systems • Subsistence economies : goods and services are created for the use of the kinship group. • Commercial economies : producers or their agents freely market their goods and services, following the law of supply and demand. • Planned economies: associated with communist societies, when governments controlled the economies.
Categories of Activities/Jobs • Occupational Structure of the Workforce: Ranges along a continuum of both increasing complexity of product or service and distance from the natural environment. • PRIMARY (agriculture) • SECONDARY (industry) • TERTIARY (services) • QUATERNARY (information)
Occupational Structure of Various Countries United States GDP $41,890 • Agriculture 2%, Industry 21%, Services 78% China GDP $6,757 • Agriculture 44%, Industry 18%, Services 16%
Occupational Structure Tanzania GDP $1,213 • Agriculture 82%, Industry 3%, Services 15% Brazil GDP $8,402 • Agriculture 21%, Industry 21%, Services 58%
Primary Activities Direct removal of natural resources from the earth: mining, forestry, and agriculture. These are most important in the LDCs. • Subsistence Agriculture • Fishing and Forestry • Mining and Quarrying
Primary Products The percentage of people working in agriculture exceeds 75% in many LDC’s of Africa and Asia. In Anglo-America and Western Europe the figure is <5%
Trade in Primary Products • Important to Developing Economies • Danger of Commodity Trade Dependence Puerto Rico Coffee Plantation
Secondary Activities: Manufacturing Secondary - Processing and transforming natural resources: steel, textiles, auto assembly. These used to be most important in MDCs, but are increasingly important in the semi-periphery (Korea, Mexico, Brazil, Singapore)
Tertiary and Beyond: Services Provision of services in exchange for payment. Includes retailing, banking, law, education, and government. Education, R & D, and information technology becoming most important in the postindustrial core regions. Less-developed countries often focus on tourism. Services historically were clustered into settlements. Increasingly the most important service centers are massive world cities.
Tertiary and Beyond: Services Less-developed countries often focus on tourism. Vendors, Bali Club Med, The Bahamas