Ch 9 Seed Plants
400 likes | 645 Views
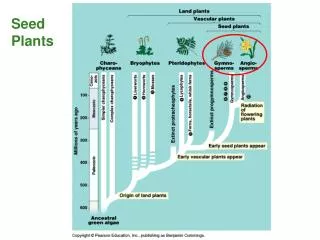
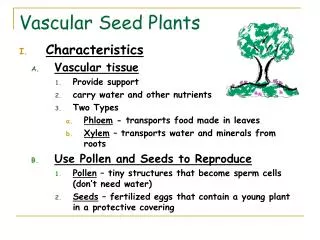
Ch 9 Seed Plants. Pp. 274-300. Notes 9-1. All seed plants share 2 characteristics. They have vascular tissue and use seeds to reproduce. They all have body plans that include leaves, stems, and roots. Water, food, and nutrients are transported throughout the plant’s vascular tissue.

Ch 9 Seed Plants
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ch 9 Seed Plants Pp. 274-300
Notes 9-1 • All seed plants share 2 characteristics. • They have vascular tissue and use seeds to reproduce. • They all have body plans that include leaves, stems, and roots.
Water, food, and nutrients are transported throughout the plant’s vascular tissue. • Phloem- vascular tissue through which food moves. • When food is made in the leaves, it enters the phloem and travels to the stems and roots.
Xylem-water and nutrients travel in this vascular tissue from the soil. • Seeds are structures that contain a young plant inside a protective covering. • Seeds have 3 parts- embryo, stored food, seed coat
The young plant that develops from the zygote, or fertilized egg, is called the embryo and has the beginnings of roots, stems and leaves • in some plants food is stored inside 1 or 2 seed leaves, called cotyledon.
The outer covering of a seed is called the seed coat. • Germination is the early growth stage of the embryo. • Germination begins when the seed absorbs water from the environment
Germination continues as the embryo uses its stored food to begin to grow. • Leaves capture the sun’s energy and carry out the food-making process of photosynthesis. • The underside of the leaf has small openings or pores, called stoma.
These open and close to control when gases enter and leave the leaf. • The process by which water evaporates from the stomata in a plant’s leaves is called transpiration.
The stem carries substances between the plant’s roots and leaves. • The stem also provides support for the plant and holds up the leaves so they are exposed to the sun.
Inside the stem is a layer of cells called the cambium. • The cells of the cambium divide to produce new phloem and xylem and to increase the stem’s width.
Roots anchor a plant in the ground and absorb water and nutrients from the soil. • The tip of the root is rounded and is covered by a root cap. • The root cap protects the root from injury from rocks as the root grows through the soil.
Vocabulary#1-9 • Transpiration, cambium, root cap, Phloem, xylem, seed, embryo, cotyledon, germination
Notes 9-2 Gymnosperms • A __________ is a seed plant that produces naked seeds, seeds that have no protective covering. • All gymnosperms produce “_____” seeds.
Many gymnosperms have ________ or scalelike leaves and deep-growing root systems. • Gymnosperms are classified into __ groups-cycads, ginkgo, gametophytes, conifers.
Most reproduce with ______. • Two types of cones: male and female • male cones produce tiny grains of _______ which contain microscopic cells that later become sperm cells.
Female cones contain at least 1 at the base of each scale, it contains an ________ cell. • After being fertilized, the ovule develops into a ______. • The cone closes and seals in pollen.
To reproduce pollen falls from a ____ cone onto a ______ cone. • In time a sperms cell and egg cell joint together in an ovule on the female cone.
The transfer of pollen from a male to a female cone or structure is called __________. • Conifers produce many useful products like paper and the lumber to build homes.
The rayon fibers in clothes are also from conifers. • Conifers are grown in large forests. • _______________ is one method to obtain lumber, when all the trees in a large area of forest are cut down.
This practice can destroy animals’ homes and cause the soil to be washed away by rains.
Vocabulary#10-14 • Gymnosperm, cones, pollen, ovule, pollination
Notes 9-3 Angiosperms • An __________ is a plant that produces seeds that are enclosed in a fruit. • Seeds develop in a protective structure called an _________.
The ovary is located within an angiosperm’s ________. • 2 characteristics that all angiosperms share: all produce _______ and ______. • Not all flowers appear the same.
Some flowers do not have ________, colorful structures that you see when flowers open. • The flower bud is enclosed by leaflike structures called ______ that protect the flower.
Within the petals are the male and female reproductive parts. • Thin stalks topped by small knobs inside the flower are _________, this is the male part. • The stalk is called the filament.
The knob at the end of the filament is the anther, this is where the pollen is produced. • The ______ is the female part, usually found in the center of the flower. • The sticky tip of the pistil is called the stigma.
A slender tube down the center of the pistil is called the _______, connecting the stigma to the ovary. • The ovary contains 1 or more ovules.
In reproduction pollen falls on a stigma, over time the sperm and egg cell join together in the ovule. • The _______ develops into the _______ part of the seed.
As the seed develops, the ovary changes and eventually becomes a _______, a ripened ovary. • Angiosperms divide into __ groups: _______ and _______
Monocots • __ seed leaf,cotyledon • ________ veins • scattered bundles in veins • flower parts in ______ • EX: grasses, corn, wheat,rice, lilies, tulips
Dicots • __ seed leaves, cotyledons • ________ veins • circle of veins • flower parts in _____ or _____ • EX: roses, violets, dandelions
Vocabulary#15-23 • Angiosperm, ovary, flower, petal, sepal, stamen, pistil, monocot, dicot
Notes 9-4 Plant Growth • A plant’s growth response toward or away from a stimulus is called a ______. • ______, ______, and _____ are important stimuli to which plants respond.
__________ produced by a plant are chemicals that affect how the plant grows and develops. • Plant hormones control tropisms; germination,_______ _________, ______, and ______, shedding of _______, _______ of and ripening of ______.
________ is an important plant hormone that speeds up the rate at which a plant’s cells grow. • Auxin controls a plant’s response to _____ by making some cells grow faster than others so the plant bends toward the light.
Flowering plants that flower and die in the same year are called annuals. • Ex: marigolds, petunias, pansies, wheat, tomatoes, cucumbers.
Flowering plants that live 2 years are ___________. • Ex: parsley, celery • plants that live for more than 2 years are ________. • Ex: oak trees and honeysuckle
Vocabulary #24-28 • Tropism, auxin, annual, biennial, perennials
Good Luck on the quiz! • Mr. Callahan is teaching ___ Grade Science next year.