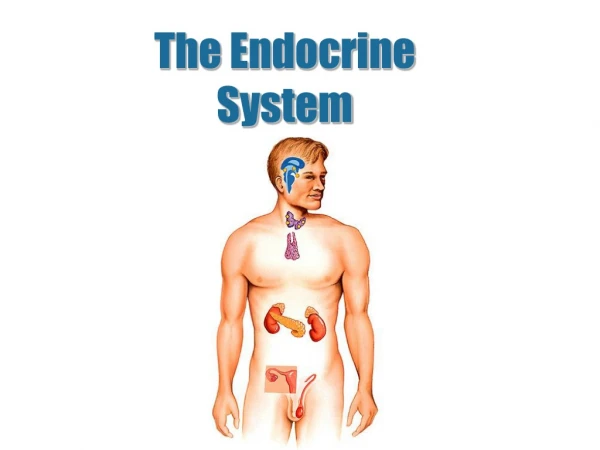
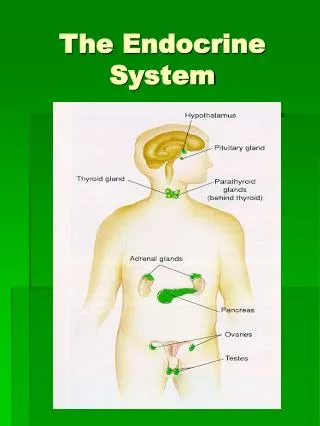
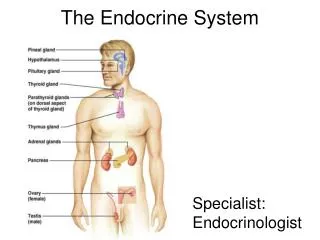
The Endocrine System
370 likes | 382 Views
Learn about key endocrine organs like pineal and pituitary gland, hormones they produce, and disorders like acromegaly and Cushing’s syndrome.

The Endocrine System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
pineal gland hypothalamus pituitary gland Endocrine Organs of the Brain
Pineal Gland • Produces melatonin • High levels at night make us sleepy; low level during day • Pineal gland is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light • Function in regulating circadian rhythms (sleep, body temp, appetite) biological clock
Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary • Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) • Oxytocin
Oxytocin (+ feedback) loop oxytocin
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary • Growth Hormone (GH) • Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) • Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) • Gonadotropins (FSH, LH) • Prolactin (PRL) • Melanocyte-stimulating Hormone (MSH)
Growth Hormone (GH) • Stimulates protein building • Stimulates cell growth (cell size and number), especially in muscle and bone. • Also stimulates fat breakdown.
strenuous exercise GH Levels sleep awake
Dwarfism hyposecretion of GH Little People Big World Kenadie - worlds smallest girl due to primordial dwarfism
Gigantism hypersecretion of GH Bao Xishun, a 7ft 8.95in herdsman from Inner Mongolia
Acromegaly hypersecretion of GH 7 ft 1 ¼ inches
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) • Acts on the thyroid gland, stimulating it to release T3 & T4 • These thyroid hormones increase glucose catabolism and body heat production. • Regulated via negative feedback
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) • Acts on the adrenal cortex, stimulating it to secrete glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol). • Helps make glucose from amino acids and fatty acids
The Thyroid Gland larynx thyroid trachea
Thyroid Hormones Thyroid gland selectively uptakes iodine to produce T3 & T4 • Thyroxine (T4) • Triiodothyronine (T3) Both control metabolic rate and cellular oxidation • Calcitonin - lowers blood Ca2+ levels and causes Ca2+ reabsorption in bone
Goiter Lack of iodine in diet hyposecretion of T3 & T4
hyposecretion of T3 & T4 Cretinism
Myxedemahyposecretion of T3 & T4 After thyroid treatment myxedema
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) • PTH release: • stimulates osteoclasts to reabsorb bone
Pancreas: • Regulates glucose uptake by cells • Controlled via negative feedback: insulin & glucagon • Blood sugar level: 90 mg/mL
Cushing’s Syndrome Hypersecretion of cortisone; may be caused by a releasing tumor in pituitary Symptoms: trunkal obesity and moon face, emotional instability Treatment: removal of adrenal gland and hormone replacement
Addison’s Disease Hyposecretion of glucocorticoids and mineral corticoids; Symptoms- wt loss, fatigue, dizziness, changes in mood and personality, low levels of plasma glucose and Na+ levels, high levels of K+ Treatment- corticosteroid replacement therapy
Thymus Located anterior to the heart Produces- thymopoetin and thymosin helps direct maturation and specialization of T-lymphocytes (immunity)
Gonads Ovaries- produce estrogen and progesteroneresponsible for maturation of the reproductive organs and 2ndary sex characteristics in girls at puberty ovary
Gonads Testes- produce sperm and testosterone (initiates maturation of male repro organs and 2ndary sex characteristics in boys at puberty)
INQUIRY • A disease in which too much T3 and T4 are produced. • The posterior pituitary produces which two hormones and what is their function? • What is acromegaly? • What organ does glucagon target? • The target tissue for gonadotropins is ____. • Where are epinephrine and norepinephrine produced? • What effect does parathyroid hormone have on your bones?