The Stage Model of Memory
90 likes | 252 Views
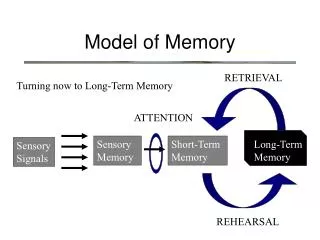
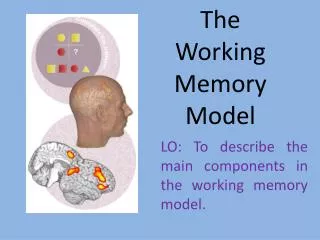
The Stage Model of Memory. What is memory?. Memory : mental processes that enable us to acquire, retain, and retrieve information. Stage Model of Memory. sensory memory : info from senses. large capacity for info. Lasts ¼ sec. --3 sec.

The Stage Model of Memory
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is memory? • Memory: mental processes that enable us to acquire, retain, and retrieve information Cristen Klute 10/05
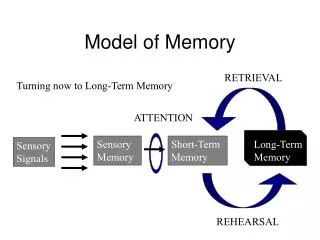
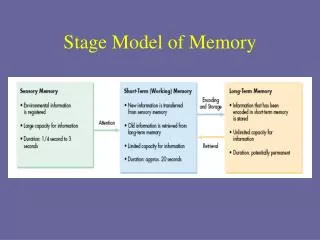
Stage Model of Memory • sensory memory: info from senses. large capacity for info. Lasts ¼ sec. --3 sec. • short term memory: info from sensory memory and long term memory. limited capacity for info. Lasts 30 sec. • long term memory: info from short term memory. Unlimited capacity. Potentially permanent. Cristen Klute 10/05
Ways to remember… • Maintenance Rehearsal: Consciously rehearsing information • Chunking: grouping of related items together into a single unit • Elaborative rehearsal: focus on the meaning of information to encode it into long term memory. Cristen Klute 10/05
Levels of Processing Framework • information processed at a deeper level is more likely to be remembered than information processed at a shallower level Cristen Klute 10/05
Types of Information • Procedural Information: long term memory of how to perform different skills (ex. bike riding, typing) • Episodic Information: long term memories of events in your life (your wedding, prom, going to the grocery store) • Semantic Information: general knowledge that includes facts, names, concepts, ideas Cristen Klute 10/05
Types of Memory • Explicit Memory: consciously recollected information • Implicit memory: memory without awareness (ex. Telephone dialing, typing) Cristen Klute 10/05
Semantic Network Model • making associations between concepts concept map created by J. Lansing
References • Lansing, J. (1997). Concept mapping homepage. Retrieved October 11, 2005, from http://users.edte.utwente.nl/lanzing/cm_home.htm • Tavris, C. (2000). Psychology in perspective (3rd ed.). Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Cristen Klute 10/05