Understanding Basic Units of Matter and Physical Properties of Substances
160 likes | 281 Views
This educational resource focuses on the fundamental concepts of matter, including atoms, molecules, and the difference between mass and weight. It outlines objectives that help students recognize that all matter consists of atoms and understand the properties of matter through directed readings and questions. The Bellwork and word wall sections provide definitions and encourage active learning. Additionally, students will engage with physical changes versus chemical changes, enhancing their understanding of scientific principles through practical examples.

Understanding Basic Units of Matter and Physical Properties of Substances
E N D
Presentation Transcript
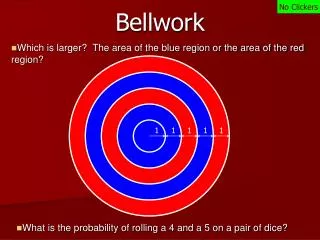
Bellwork 10/13/14 1. The most basic unit of matter in the composition of a dog is...? A. a molecule. B. a tissue. C. an atom. D. a compound. Write the question and answer. Justify your answer.
Bellwork answer • 1. The most basic unit of matter in the composition of a dog is...? • A. a molecule. B. a tissue. • C. an atom. D. a compound. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element.
Objectives • SPI 0807.9.1 – Do I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? • SPI 0807.9.2 - What is the common outcome of all chemical changes? • SPI 0807.9.6 – How can I discover if a chemical or physical change has occurred? • SNB – 2nd 9 weeks word wall - Write the following words and definitions in the back of your Scientific Notebook.
2nd 9 Weeks Word Wall • 1. Weight - measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object • 2. Matter - anything that has mass and takes up space • 3. Inertia - tendency of an object to resist change • 4. Density - the amount of matter in a given space or volume • 5. Composition - the type of matter that makes up the object and the way the matter is arranged
Word Wall • Glue the 2nd 9 Weeks Word Wall Words in the back of your SNB. • We will work on 5 each week. • We will have a quiz over the 5 words at the end of each week.
Chapter 7 Directed ReadingRead Section 1 then answer the following questions on a piece of paper to be turned in. • For each description, write whether it applies to mass or to weight. • ________________1. is a measure of the amount of matter in the object • ________________2. is always constant no matter where the object is located • ________________3. is a measure of the gravitational force on an object • ________________4. is measured using a spring scale • ________________5. is expressed in grams (g), kilograms (kg), or milligrams (mg) • ________________6. is expressed in Newtons (N) • ________________7. is less on the moon than on Earth
Chapter 7 Directed Reading • For each description, write whether it applies to mass or to weight. • ___Mass_________1. is a measure of the amount of matter in the object • ___Mass_________2. is always constant no matter where the object is located • ___Weight_______3. is a measure of the gravitational force on an object • ___Weight_______4. is measured using a spring scale • ___Mass_________5. is expressed in grams (g), kilograms (kg), or milligrams (mg) • ___Weight_______6. is expressed in Newtons (N) • ___Weight_______7. is less on the moon than on Earth
Read Section 2 then answer the following questions.Match the correct example with the correct physical property. • ____8. Aluminum can be flattened into sheets of foil. • ____9. An ice cube floats in a glass of water. • ____10. Copper can be pulled into thin wires. • ____11. Plastic foam protects you from hot liquid. • ____12. Flavored drink mix dissolves in water. • ____13. An onion gives off a very distinctive smell. • ____14. A golf ball has more mass than a table tennis ball. • A. State E. odor • B. Solubility F. ductility • C. thermal conductivity G. density • D. Malleability
Match the correct example with the correct physical property. • _D__8. Aluminum can be flattened into sheets of foil. _A__9. An ice cube floats in a glass of water. • _F__10. Copper can be pulled into thin wires. • _C__11. Plastic foam protects you from hot liquid. • _B__12. Flavored drink mix dissolves in water. • _E__13. An onion gives off a very distinctive smell. • _G__14. A golf ball has more mass than a table tennis ball. • A. State E. odor • B. Solubility F. ductility • C. thermal conductivity G. density • D. Malleability
15. What is the equation for density? • 16. If you pour different liquids into a graduated cylinder, the liquids will form layers based upon differences in the ______________________ of each liquid.
15. What is the equation for density? • D=M/V • 16. If you pour different liquids into a graduated cylinder, the liquids will form layers based upon differences in the __density_________ of each liquid.
Read section 3. Identify whether the following changes are physical changes or chemical changes. Label each change either PC for physical change or CC for chemical change. • _____17. sanding a piece of wood • _____18. baking bread • _____19. crushing an aluminum can • _____20. melting an ice cube • _____21. dissolving sugar in water • _____22. molding a piece of silver • _____23. mixing vinegar and baking soda
Read section 3. Identify whether the following changes are physical changes or chemical changes. Label each change either PC for physical change or CC for chemical change. • _____24. grinding baking soda into a powder • _____25. souring milk • _____26. melting an ice cream bar • _____27. burning a wooden match • _____28. shooting off fireworks • _____29. mixing drink mix • _____30. bending an iron nail
Read section 3. Identify whether the following changes are physical changes or chemical changes. Label each change either PC for physical change or CC for chemical change. • _PC__17. sanding a piece of wood • _CC__18. baking bread • _PC__19. crushing an aluminum can • _PC__20. melting an ice cube • _PC__21. dissolving sugar in water • _PC__22. molding a piece of silver • _CC__23. mixing vinegar and baking soda
Label each change either PC for physical change or CC for chemical change • _PC__24. grinding baking soda into a powder • _CC__25. souring milk • _PC__26. melting an ice cream bar • _CC__27. burning a wooden match • _CC__28. shooting off fireworks • _PC__29. mixing drink mix • _PC__30. bending an iron nail
Exit Ticket • What is the mass of a car that weighs 13,620 N?