Chemical Reactions
230 likes | 462 Views
Chemical Reactions. 6.2. Chemical Reactions allow living things to grow, develop, reproduce, and adapt. Is this a chemical reaction?. What makes it a chemical reaction?. Atoms or groups of atoms in substances are reorganized into different substances. Fe + O 2 -> Fe 2 O 3 Iron Oxide.

Chemical Reactions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemical Reactions allow living things to grow, develop, reproduce, and adapt
What makes it a chemical reaction? • Atoms or groups of atoms in substances are reorganized into different substances. • Fe + O2 -> Fe2O3 • Iron Oxide
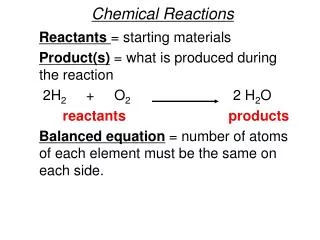
Reactants and Products • Reactants -> Products • C6H12O6 + 602 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O • What biological process does this chemical equation explain?
Why do we have to balance equations? • Conservation of Mass- Matter cannot be created or destroyed. • The amount you put in is the amount you should get out. • We use coefficients to balance equations
Is this equation balanced? • C6H12O6 + 02-> CO2+ H2O • How do we balance it? • C6H12O6 + 602-> 6CO2+ 6H2O
Let’s Practice • K + B2O3 -> K2O + B • 6K + B2O3 -> 3K2O + 2B • CH4 + O2 -> CO2 + H2O • CH4 + 2O2-> CO2 + 2H2O • Al + S8 -> Al2S3 • 16Al + 3S8-> 8Al2S3
How do we get reactions started? • Activation Energy! • Minimum amount of energy needed from reactants to form products in chemical reactions.
Endothermic vs. Exothermic • Endothermic -> Energy of products is higher than the energy of the reactants • Exothermic -> Energy of the products is lower than the reactants.
Enzymes • Enzymes are catalyst • Catalyst lowers the activation energy • A Catalyst doesn’t increase the amount of product or get used up in the reaction • Enzymes are biological catalyst
Chicken Liver and Peroxide • Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a harmful by- product that some of our cells give off. • The enzyme catalase (shown here in the chicken liver) breaks the H2O2 into H2O and O. • After the reaction is complete we can pour more peroxide onto the livers and the reaction will happen again because enzymes are not used up.
Endothermic and Exothermic Endothermic Reactions Exothermic Reactions Burning a Candle Combustion of fuels Nuclear Fission • Photosynthesis • Water evaporation • Emergency Cold Packs
Draw a graph of an endothermic reaction. • Draw a graph of an exothermic reaction. • Chemical reactions need ________ to begin. • A __________ lowers the activation energy in chemical reactions. • A _________ is a biological catalyst. • What type of electron is available to form bonds? __________
Two or more elements joined in a definite amount is called ___________. • What is the atomic number for an element composed of? • Carbon-14 is considered a what? • Is salt water a homogeneous or heterogeneous mixture? • Give an example of a suspension.
Give an example of a monomer. • Why is phosphorus important? • What 3 elements compose carbohydrates? • Lipids are hydrophobic or hydrophilic? • What are the two types of nucleic acids? • What are proteins composed of?
How an Enzyme works • The substrates (reactants) bind to the active sites on the enzyme. • Active site changes and the enzyme- substrate complex is formed. • Substrates (reactants) react to form products • Enzyme releases the product.
Important things to remember • Enzymes are not used up in a chemical reaction. • An enzyme’s name describes what it does. • The active site and substrates have complementary shapes. Think lock and key model • pH and temperature can affect enzymes