Unveiling the Secrets of DNA - History, Replication, and Repair
150 likes | 250 Views
Explore the intriguing journey of DNA discovery, replication process, and repair mechanisms in this informative guide. From early misconceptions to groundbreaking experiments, delve into the intricate world of genetic material.

Unveiling the Secrets of DNA - History, Replication, and Repair
E N D
Presentation Transcript
History of DNA • Early scientists thought protein was the hereditary material • Protein is more complex than DNA • Proteins are composed of 20 different amino acids in long polypeptide chains
Transformation • Fred Griffith worked with virulent “S” and nonvirulent “R” strains of Pneumoccocus bacteria • He found • R strain becomes virulent when it absorbs DNA from killed S strain bacteria • Transformation- bacteria gets DNA from a dead bacteria and aquires new traits • Study suggested that DNA was probably the genetic material
History of DNA • Viruses are made of DNA and protein • Hershey & Chase used radioactively tagged bacteriophage viruses to prove DNA is the genetic material • Tag DNA with 32P • Tag protein with 35S • 32P shows up in the bacteria, 35S doesn’t
Replication Facts • DNA must be copied before a cell divides • DNA is copied during S (synthesis) phase of interphase • New cells need identical DNA strands
S phase DNA replication takes place in the S phase. G1 G2 interphase Mitosis -prophase -metaphase -anaphase -telophase Synthesis Phase (S phase) • S phase during interphase of the cell cycle • Nucleus of eukaryotes
3’ Parental DNA Molecule 5’ Replication Fork 3’ 5’ DNA Replication • Enzyme Helicase unwinds& separates the 2 DNA strands by breaking weak hydrogen bonds • Begins atOrigins of Replication • Two strands open forming Replication Forks (Y-shaped region)
Bubbles Bubbles DNA Replication • DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides • Replication Bubbles form as the DNA strands open at the origin • Eukaryotic chromosomes have Multiple bubbles • Prokaryotes (bacteria) have one Single bubble
Proofreading New DNA • DNA polymerase makes about 1 in 10,000 base pairing errors • Enzymes proofread and correct mistakes • Error rate for proofread DNA is 1 in 1 billion base pairing errors
DNA Damage & Repair • Chemicals & ultraviolet radiation damage DNA in our cells • Cells continuously repair DAMAGED DNA • Excision repair- one of over 50 different repair enzymes removes damaged DNA • DNA polymerase and DNA ligase replace and tie in (bond) new, correct nucleotides
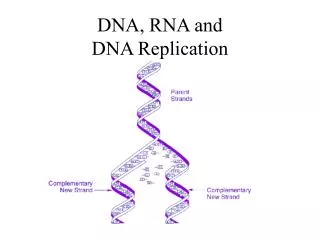
DNA Template Parental DNA New DNA Replication is Semiconservative Watson & Crick suggested: • The parental DNA acts a template for a new complementary strand • Final, new DNA molecules consist of 1 Parental (original) strand and 1 New strand of DNA
Question: • What would be the complementary DNA strand for the following DNA sequence? DNA 5’-CGTATG-3’
Answer: DNA 5’-GCGTATG-3’ DNA 3’-CGCATAC-5’