Respiratory System Essentials: Functions, Organs, and Conditions
60 likes | 136 Views
Discover the vital functions of the respiratory system and the key organs involved, from the upper respiratory tract to the alveoli. Learn about conditions like hypoxia, COPD, bronchitis, and asthma that affect respiratory health.

Respiratory System Essentials: Functions, Organs, and Conditions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Functions of the Respiratory System • Brings Oxygen into the blood. • Removes Carbon Dioxide from the blood stream. • Pulmonary Ventilation: Exchange of air between external environment and the air sacs of the lungs. • External Respiration: Exchange of gases between the lungs and the blood stream. • Internal Respiration: Exchange of gases between the blood stream and the body cells. • Respiration: All three of the above put together.
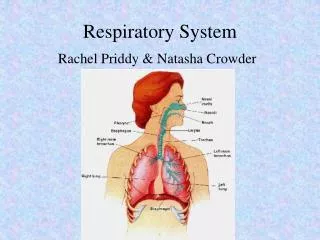
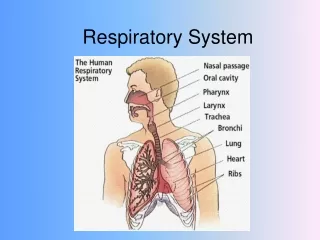
Organs of the Respiratory System • Upper Respiratory Tract • Nose: Initial receiving chamber for inhaled air. • Vestibule: Small chamber of nose (nasal cavity) • Nasal Cavity: Larger chamber of nose (nasal cavity) • Nasal Septum: Divides the nose (nasal cavity) in half • Nasal Conches: 3 boney projection in the nasal cavity that increase airflow. • Pharynx: (AKA the throat) • Runs from the nasal cavity to the larynx • Carries the oxygenated air to the larynx • Carries food to the esophagus
Organs of the Respiratory System Cont… • Larynx: Connects the pharynx to the trachea • Adam’s Apple: Enlargement of Larynx in males. • Voice Box: • Vocal Cords: are folds of elastic fibers that vibrate when air rushes past them. • Doesn’t contain cilia ( why you must clear your throat) • Epiglottis: Flap that covers the trachea when you are swallowing food to prevent food from passing into the lungs. • When you swallow the Larynx moves up and the Epiglottis moves down.
Organs of the Respiratory System Cont.. • Lower Respiratory Tract • Trachea: ( 4 ½ inches long) • AKA the wind pipe • Divides in the thoracic cavity to form the right and left bronchi. • Lined with mucous membranes and cilia which are used to move dust particles and bacteria towards the pharynx. • Bronchial Tree: • Primary Bronchi-Distal end of bronchial tree (where trachea splits in two) • Bronchioles-Subdivisions of primary bronchi (more branching) • Alveolar Ducts- Smallest tubes of the bronchial tree. • Alveoli- Small round sacs at the end of each alveolar ducts. • 300-500 million in each lung • Location of gas exchange( between blood and the air of the lungs) • One cell thick • Have the surface area of a tennis court • Allow for the diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide
Conditions of the Respiratory System • Hypoxia: A deficiency in the amount of oxygen being delivered to the tissues of the body (often used in reference to the supply of oxygen to the brain) • COPD: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder, a group of disorders that result in difficulty expelling air from the lungs. • Bronchitis: Inflammation of the tissue lining the bronchial tubes. • Asthma: Disorder of respiration(often allergenic), characterized by bronchio-spasm, wheezing, and difficulty in expiration, often accompanied by coughing and a feeling of constriction in the chest.