The Ankle and Foot
670 likes | 1.73k Views
The Ankle and Foot. ESAT 3600 Fundamentals of Athletic Training. Joints of the Ankle and Foot. Tibiofibular joint Ankle ( Talocrural ) joint Distal end of tibia fibula & Talus Subtalar joint Divisions of foot. Ankle Joint (Mortise -and- Tenon Joint). Mortise Recess or hole

The Ankle and Foot
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Ankle and Foot ESAT 3600 Fundamentals of Athletic Training
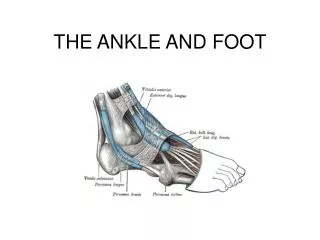
Joints of the Ankle and Foot • Tibiofibular joint • Ankle (Talocrural) joint • Distal end of tibia fibula & Talus • Subtalar joint • Divisions of foot
Ankle Joint (Mortise-and-TenonJoint) • Mortise • Recess or hole • Lateral and medial malleolus • Tenon • Peg • Talus • Tenon fits into mortise
Skeletal Review (Lower Leg) • Tibia • Medial malleolus • Fibula • Lateral Malleolus
Skeletal Review (Foot) • Talus • Calcaneus • Navicular • Cuneiform 1-3 • Cuboid • Metatarsals • Phalanges
Medial/Lateral View of Foot • Sustentaculumtali • Sinus tarsi • Neck of talus • Head of talus • Body of talus
Ligaments of Ankle and Foot • Distal Tibiofibular • Interosseous membrane • Anterior tibiofibular ligament • Posterior tibiofibular ligament • Posterior • Talocalcaneals • Lateral • Posterior • medial
Medial Ligaments • Deltoid • Tibionavicular • Tibiocalcaneal • Tibiotatalar • Calcaneonavicular • Spring ligament
Deltoid Ligament • Very strong • Prevents eversion • Difficult to rupture • Usually involves either avulsion fracture or spiral fracture of tibia
Lateral Ligaments • Anterior Talofibular • Inversion and plantar flexion • Calcaneofibular • inversion • Posterior talofibular
Retinaculum • Hold tendons in place • Extensor • superior • Inferior • Flexor • Peroneal • Superior • inferior
Ankle Stability • Strong bony stability • Strong ligaments
“Ankle” Movements • Talocrural • Plantar flexion • Dorsiflexion • Subtaler • Inversion • Eversion • Abduction • Adduction
Axis of Rotation for Ankle • Axis not truly horizontal • Tilt causes movement to not be truly in sagittal plane
Axis of Rotation For Subtalar • Axis not truly horizontal • Arthrokinematics • Sliding
Ankle & Subtalar • Oblique nature of joints causes movements to occur together • P-flexion with inversion and adduction • Supination • D-flexion with eversion and abduction • Pronation of foot
Stability/Mobility of Subtalar Joint • Subtalar joint is main connection between mobility and stability of ankle complex • Allows adaptive movements of foot • Shape of talus contributes to stability • Wedge shape • Ligaments of ankle/subtalar joint play significant role in stability
Function of the Foot • Transmit loads between lower leg and ground • Static • Dynamic • Shock absorption • Propulsion
Transverse Tarsal Joint • AKA • Mid-tarsal joint • Chopart’s joint • 2 articulations • Talonavicular joint • Calcaneocuboid joint
Axis of Rotation for Transverse Tarsal Joint • Oblique • Abduction and dorsiflexion • Adduction and plantarflexion • Longitudinal • Eversion • Inversion
Transverse Tarsal Joint • Adds to: • Pronation of foot • Supination of foot • Especially on uneven and unstable surfaces
Medial Longitudinal Arch • Shock absorber • Load-bearing structure • Load distribution • Rearfoot = 60% • Midfoot = 8% • Forefoot = 28%
Abnormal Shape of Medial Longitudinal Arch • PesPlanus • PesCavus
Distal Intertarsal Joints • Cuneonavicular joints • Cuboideonavicular joint • Intercuneiform joint complex • Cuneocuboid joint complex
Additional Joints • Intermetatarsal joints • Metatarsophalangeal joints • Interphalangeal joints
Muscles of the Anterior Compartment • Tibialis anterior • Extensor digitorumlongus • Extensor hallucislongus • Peroneustertius • Innervation • Deep Peroneal nerve
Muscles of the Lateral Compartment of the leg • PeroneusLongus • PeroneusBrevis • Innervation • Superficial peroneal nerve
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Leg • Superficial (P-Flexors) • Gastrocnemius • Soleus • Plantaris • Deep (Invertors) • Tibialis Posterior • Flexor digitorumlongus • Flexor hallucislongus • Innervation • Tibial
Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot • Layer 1 • Flexor digitorumbrevis • Abductor hallucis • Abductor digitiminimi
Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot • Layer 2 • Quadratusplantae • Lumbricals
Intrinsic Muscles of the Foot • Layer 3 • Adductor hallucis • Flexor hallucisbrevis • Flexor digitiminimi • Layer 4 • Plantar interossei • Dorsal interossei
Tibialis Anterior • O: lateral condyle of tibia, proximal 2/3 of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane, deep fascia and lateral intermuscular septum • I: plantar surface of base of 1st metatarsal and medial plantar surface of 1st cuneiform • A: dorsiflexes and inverts foot at ankle • RO-IA: active in standing balance mechanism (A/P sway)
Extensor Digitorum Longus • O: lateral condyle of tibia, head and proximal ¾ of anterior surface on body of fibula, proximal portion of the interosseous membrane, deep fascia and intermuscular septa • I: divides into 4 tendons, inserts on dorsal surfaces of the bases of the middle and distal phalanges of the 2nd-5th toes. • A: extends lateral 4 toes, dorsiflexes and everts foot at ankle
Extensor Hallucis Longus • O: middle ½ of anterior surface of the fibula and the adjacent interosseus membrane • I: dorsal surface of base of distal phalanx of big toe • A: extends distal phalanx of big toe; extends proximal phalanx, dorsiflexes and inverts foot at ankle
Peroneus Tertius • O: distal 1/3 of anterior surface of fibula, interosseous membrane and adjacent intermuscular septum • I: dorsal surface of the base of the 5th metatarsal • A: dorsiflexes and everts foot at the ankle
Peroneus Longus • O: head and proximal 2/3 of lateral surface of fibula, intermuscular septa and adjacent fascia • I: lateral margin of plantar surface of 1st cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal • A: eversion and plantar flexion of the foot at ankle; lateral stability to ankle
Peroneus Brevis • O: distal 2/3 of lateral surface of the body of fibula and adjacent intermuscular septa • I: tuberosity on lateral side of base of 5th metatarsal • A: eversion and plantar flexion of foot at the ankle; lateral stability to ankle
Gastrocnemius • O: lateral condyle and posterior surface of femur, capsule of knee joint. Medial condyle and adjacent part of femur • I: posterior surface of calcaneus by means of Achilles tendon • A: plantar flexion and inversion of foot, flexes leg at knee (especially when foot is dorsiflexed)
Soleus • O: posterior surface of head and upper 1/3 of shaft of fibula, soleal line and middle 1/3 of medial border of tibia, tendinous arch between tibia and fibula • I: posterior surface of calcaneus by means of Achilles tendon • A: plantar flexion and inversion of foot at the ankle • RO-IA: active in standing balance mechanism (forward sway)
Plantaris • O: lower part of lateral supracondylar line of femur and from oblique popliteal ligament of knee joint • I: posterior part of calcaneus medial to Achilles tendon • A: plantar flexes and inverts foot at ankle, flexes leg at knee
Flexor Digitorum Longus • O: posterior surface of middle 3/5 of tibia • I: divides into 4 tendons, insert on the plantar surfaces of bases of distal phalanges of the 2nd-5th toes • A: flexes phalanges at all interphalangeal and metatarsophalangeal articulations of 2nd-5th toes, plantar flexes and inverts foot at ankle
Flexor Hallucis Longus • O: distal 2/3 of posterior surface of fibula, interosseous membrane and adjacent intermuscular septa and fascia • I: plantar surface of base of distal phalanx of big toe • A: flexes big toe, aids in plantar flexion and inversion of foot at ankle, gives medial ankle stabilization
Tibialis Posterior • O: lateral part of posterior surface of tibia, proximal 2/3 of medial surface of fibula, interosseous membrane, intermuscular septa and deep fascia • I: tuberosity of navicular bone w/ branches to sustentaculum tali of calcaneus, plantar surfaces of all 3 cuneiforms and cuboid and bases of 2nd, 3rd, & 4th metatarsals • A: inverts and plantar flexes foot at ankle, medial ankle stabilizer