Overview of the Endocrine System: Functions, Anatomy, and Hormonal Processes
200 likes | 323 Views
The endocrine system is a complex control system that maintains homeostasis through slow, long-lasting effects via chemical secretions. It contrasts with the fast-acting nervous system. The system relies on hormones, which can be peptide (water-soluble) or steroid (lipid-soluble). Key components include the hypothalamic-pituitary axis, thyroid and parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, and pancreas. The system plays a crucial role in growth, metabolism, stress responses, and regulating electrolytes and nutrients. Understanding its anatomy and functions is essential for grasping overall human physiology.

Overview of the Endocrine System: Functions, Anatomy, and Hormonal Processes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
I. General Features • A. Control System 1. Maintains homeostasis 2. Contrast with the nervous system a. nervous system = fast, short- lived effects b. endocrine system = slow, long-lasting effects
General Features (cont.) B. Glandular System 1. Effects via chemical secretions 2. Contrast with exocrine glands a. exocrine = ducts, secrete into body cavities b. endocrine = ductless, secrete into bloodstream
General Features (cont.) • C. Types of Secretions (Hormones) • 1. Chemistry • a. Peptide hormones • i. Water-soluble • ii. Bind to receptors on cell surface • iii. Require cAMP within cell to cause effect • b. Steroid hormones • i. Lipid-soluble • ii. Pass directly into target cells to cause effect
Types of Hormones (cont.) • 2. Location of effects • a. Circulating Hormones • i. Secreted into bloodstream • ii. Effects occur after entry into blood • iii. Effects occur distal from secreting gland • b. Local Hormones (Paracrine) • i. Eventually enter blood • ii. Effects occur prior to entry into blood • iii. Effects occur in close proximity to secreting gland
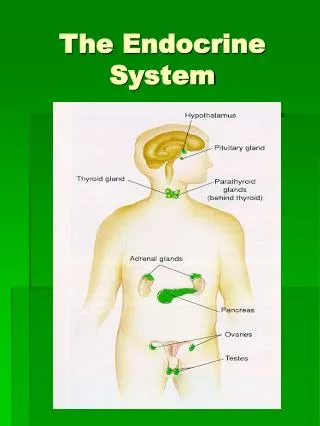
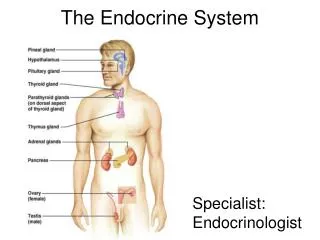
II. Anatomy of the Endocrine System • A. Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis • 1. Hypothalamus = neural tissue • a. Releasing/Inhibitory Hormones control anterior pituitary • b. Direct neural stimulation via hypothalamohypophysealtract controls posterior pituitary
Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis (cont.) 2. Pituitary (“master” gland) a. Anterior Pituitary - true gland i. Human Growth Hormone (hGH) -increased growth/metabolism -via production of insulin-like growth factors (IGF’s) ii. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) -stimulates hormone secretion (primarily thyroxine) from thyroid gland
Anterior Pituitary (cont.) iii. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) males - initiates increased sperm production females - stimulates egg maturation iv. Leutinizing Hormone (LH) males - maintains increased sperm production females - stimulates ovulation v. Prolactin stimulates milk production in mammary glands
Anterior Pituitary (cont.) • vi. Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH) - stimulates hormone secretion from adrenal cortex • Primarily of cortisol
b. Posterior Pituitary • i. Not a true gland, but extension of hypothalamus • ii. Hormones made in hypothalamus and stored in posterior pituitary • iii. Hormones: • Oxytocin - stimulates: • Milk release from mammary glands • Uterine contractions during childbirth
Posterior Pituitary (cont.) • Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH; also known as vasopressin) • Stimulates increased water reabsorption (primarily from urine back into blood) • Released when dehydrated or low blood pressure
Endocrine Anatomy (cont.) • B. Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands • 1. Thyroid - controlled by TSH • a. Thyroxine (T3/T4) • i. increases metabolic rate • b. Calcitonin – regulation of electrolytes • i. stimulates storage of Ca+2 and PO4-2 in bones and teeth • 2. Parathyroid • a. Parathryroid Hormone (PTH) • i. stimulates release of Ca+2 and PO4-2 from bones and teeth
Endocrine Anatomy (cont.) • C. Adrenal Glands • 1. Adrenal Cortex - controlled by ACTH • a. Aldosterone • i. Regulation of electrolyte concentrations • via control of release/retention in urine • b. Cortisol (glucocorticoids) • i. Long-term coping with stress • c. Androgens • i. secondary sexual traits in both sexes and sex drive (females)
Adrenal Glands (cont.) • 2. Adrenal Medulla - controlled by sympathetic nervous system • a. Epinephrine/Norepinephrine • i. short-lived, immediate response to stress • ii. Both secretions collectively referred to as “adrenalin”
Endocrine Anatomy (cont.) • D. Pancreas • 1. Islet cells • a. Insulin (Beta cells) • i. promotes storage of nutrients in body tissues • b. Glucagon (Alpha cells) • i. promotes release of nutrients from body tissues