Protein Synthesis
190 likes | 335 Views
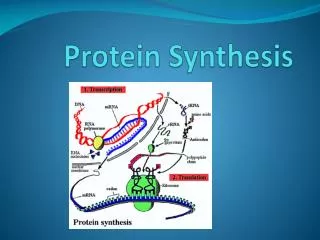
Protein Synthesis. Summary. Gene (DNA) RNA Protein Each gene codes for one protein. 2 Stages of Protein Synthesis. Transcription Translation. Transcription. DNA is coded (transcribed) into mRNA A DNA sequence is copied into a complementary RNA sequence G C C G

Protein Synthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Summary Gene (DNA) RNA Protein Each gene codes for one protein
2 Stages of Protein Synthesis • Transcription • Translation
Transcription • DNA is coded (transcribed) into mRNA • A DNA sequence is copied into a complementary RNA sequence • G C • C G • T A • A U
Transcription con’t. The completed mRNA moves into cytoplasm—to the ribosomes
Why is transcription necessary? (why do we need RNA at all?) • DNA is too big to fit through nuclear pores • DNA is too precious to allow it to leave the safety of the nucleus
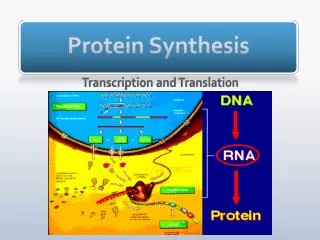
Translation (Stage 2 of protein synthesis) DNA RNA protein
The Genetic Code • Each gene codes for one protein. • Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains. • So the genetic code tells how to put the amino acids together.
The genetic code is read 3 “letters” (nucleotides) at a time. Each 3 letter “word” is called a codon. Each codon stands for a specific amino acid
Example of triplet code • UUU = phenylalanine • GGU = glycine • ACU = threonine UUU – GGU – ACU = ? phe-gly-thr
The Genetic Code • There are 64 different codons. • Some amino acids have more than one codon. (protection against errors) • The START codon is AUG. It occurs at the beginning of EVERY protein. • There are 3 STOP codons—UAA, UAG, and UGA.
Translation 1. mRNA attaches itself to ribosome to be read
Reading means linking amino acids together— where do the amino acids come from?
Translation con’t. • tRNA molecules with amino acids attached are floating in cytoplasm
Translation con’t. 2. tRNA molecules bring the correct amino acids to the mRNA strand on the ribosome
How do they know what to bring? • Each tRNA molecule has an amino acid attached to one end and 3 nucleotide bases at the other end. Those 3 bases = anticodon
Codon-Anticodon match • tRNA anticodon attaches to mRNA codon Example: mRNA codon = AAG tRNAanticodon = UUC (AAG codes for Lysine)
Translation 3. The ribosome attaches the amino acids together to make the protein.
Translation con’t. 4. Completed protein goes to where it is needed in the cell