Software Design Principles and Techniques for Efficient Development Process
130 likes | 230 Views
Dive into the world of software design with a focus on detailed DFDs, flowcharts, N-S charts, PDL, and component-level designing. Learn about structural components, procedural descriptions, layout for human-machine Interaction, and internal-external interfaces. Explore relationships, patterns/styles, domain models, and scenario-based diagrams. Understand the significance of UML class hierarchies, data design, and architectural principles. Discover concepts like abstraction, modularity, information hiding, and refactoring in software design.

Software Design Principles and Techniques for Efficient Development Process
E N D
Presentation Transcript
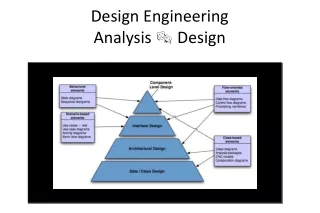
Analysis -> Design Detailed DFDs; Flowchart; N-S chart; pdl; component level designs Structural components and procedural description of software Layout and interaction mechanisms for human-machine interaction; Internal and external interfaces Relationships among major structural components of program; Patterns and styles Information domain model created during analysis data structures and database model Procedural design Scenario-based diagrams Interface design Structure Chart UML class hierarchy Architectural design Class diagrams Data design
Design Principles • Design not equal to coding!!! • Design should: • Consider alternative approaches • Be traceable to analysis model • Be structured to accommodate change • Degrade gently • Assess for quality while creating design • Be reviewed • Design derived from repeatable method driven by information in req. analysis phase.
Fundamental Concepts of Good Design • Abstraction • Solution stated in problem environment • Data, procedure, control • Refinement:Top-down design strategy • Software Architecture • Hierarchical structure of procedural components
Concepts of Good Design • Modularity • Easier to solve problems when broken up (logical partition) • “size” based on independent functional characteristics (high cohesion and low coupling) • Lead to interfaces with reduced complexity
Concepts of Good Design cont. • Information Hiding • Controlled interfaces • Use of patterns that convey essence of a proven design solution • Refactoring – a reorganization technique that simplifies the design
Refactoring • Fowler [FOW99] defines refactoring as: "Refactoring is the process of changing a software system in such a way that it does not alter the external behavior of the code [design] yet improves its internal structure.” • When software is refactored, the existing design is examined for • redundancy • unused design elements • inefficient or unnecessary algorithms • poorly constructed or inappropriate data structures • or any other design failure that can be corrected to yield a better design.
Design Patterns • Best designers have an uncanny ability to see patterns and combine them to create a solution • A description of a design pattern may also consider Design forces describe non-functional requirements (e.g., ease of maintainability, portability) associated with the software • The pattern characteristics (classes, responsibilities, and collaborations) indicate the attributes of the design that may be adjusted to enable the pattern to accommodate a variety of problems.
Frameworks • A frameworkis not an architectural pattern, but rather a skeleton with a collection of “plug points” (or hooks and slots) that enable it to be adapted to a specific problem domain. • Note that: • Design patterns are more abstract, less specialized and have smaller architectural elements than frameworks. • In an OO context, a framework is a collection of collaborating classes
Assessment of Design Notations • Design notations should • Support modularity • Be simple • Be easy to edit • Be machine readable • Maintainable • Enforce structure • Represent data • Goal of automatic verification • “code-to” ability
Design Post-Processing • Processing narratives for each module • Interface description for each module • Local/global data structures defined • All design restrictions/limitations noted • Conduct design review • Consider optimization