FUNCI ÓN EXPONENCIAL
80 likes | 272 Views
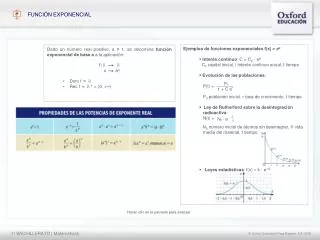
Ejemplos de funciones exponenciales f(x) = e x Interés continuo : C = C 0 · e ik C 0 capital inicial, i interés continuo anual, t tiempo Evolución de las poblaciones : P(t) = P 0 población inicial, r tasa de crecimiento, t tiempo

FUNCI ÓN EXPONENCIAL
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ejemplos de funciones exponenciales f(x) = ex • Interés continuo: C = C0 · eik • C0 capital inicial, i interés continuo anual, t tiempo • Evolución de las poblaciones: • P(t) = • P0 población inicial, r tasa de crecimiento, t tiempo • Ley de Rutherford sobre la desintegración • radioactiva: • N(t) = • N0 número inicial de átomos sin desintegrar, V vida • media del material, t tiempo • Leyes estadísticas: f(x) = k · e-x2 • Dado un número real positivo, a ≠ 1, se denomina función exponencial de base a a la aplicación: • f:RR • x ax • Dom f = R • Rec f = R+= (0, +∞) P0 r t 1 + C e e t . - N 0 V FUNCIÓN EXPONENCIAL
Propiedades de la función logarítmica • Dom f = R+ = (0, +∞) • Rec f = R • Es continua en su dominio • Para cualquier a > 0, loga 1 = 0 • Ejemplo: • o a > 1 • o 0 < a < 1 • Si tenemos y = ax se denomina logaritmo en base a de y: • x = loga y • Se denomina función logarítmica de base a, f(x)= loga x, a la función inversa de f(x) = ax : • f:R+R • x = ay y= loga x • Propiedades de los logaritmos • loga (xy) = loga x + loga y • loga • loga xm = m loga x • loga x = l og x - l og y y a a l og x m a x = m FUNCIÓN LOGARÍTMICA
La aplicación que asigna a cada número real x, el valor sen x es una función real de variable real y se denomina función seno: f(x) = sen x. f:RR x senx FUNCIÓN SENO • Propiedades de la función seno • Dom f = R • Rec f = [-1, 1] • Función acotada, |sen x| ≤ 1 • Continua • Propiedades de la función seno • Periódica de periodo 2π: • sen x = sen (x + k · 2π) • Función impar: • sen (-x) = -sen x
La aplicación que asigna a cada número real x, el valor cos x es una función real de variable real y se denomina función coseno: f(x) = cos x. f:RR x cosx FUNCIÓN COSENO • Propiedades de la función coseno • Dom f = R • Rec f = [-1, 1] • Función acotada, |cos x| ≤ 1 • Continua • Propiedades de la función coseno • Periódica de periodo 2π: • cos x = cos (x + k · 2π) • Función par: • cos (-x) = cos x
La función tangente se define como la función cociente: f(x) = y se expresa como f(x) = tg x. se n x cos x • Propiedades de la función tangente • Dom f = {x Є R | cos x ≠ 0} = R – {(2k + 1)· | k Є Z} • Rec f = R • Función discontinua • Función periódica, de periodo π: tg x = tg (x + π) • Función impar: tg (-x) = - tg x • Función estrictamente creciente en su dominio ∏ 2 FUNCIÓN TANGENTE
La función cotangente se define como la función cociente: f(x) = y se expresa como f(x) = cotg x. cos x se n x FUNCIÓN COTANGENTE • Propiedades de la función cotangente • Dom f = {x Є R | sen x ≠ 0} = R – {kπ | k Є Z} • Rec f = R • Función discontinua • Función periódica, de periodo π: cotg x = cotg (x + π) • Función impar: cotg (-x) = - cotg x • Función estrictamente decreciente en su dominio
La función arcocoseno hace corresponder a todo x Є [-1, 1] un valor y Є [0, π], tal que x = cos y: f:[-1, 1] [0, π] x y = arc cos x La función arcotangente hace corresponder a todo x Є R un valor y Є tal que x = tg y: f:[-1, 1] x y = arc tg x La función arcoseno hace corresponder a todo x Є [-1, 1] un valor y Є tal que x = sen y: f:[-1, 1] x y = arc sen x π π , - [ ] π π 2 2 , - [ ] 2 2 π π π π , - [ ] , - [ ] 2 2 2 2 FUNCIONES TRIGONOMÉTRICAS INVERSAS