Topologies
280 likes | 487 Views
Topologies. The structure of the network Physical topology Actual layout of the media Logical topology How the hosts access the media. Physical Topologies. Bus Uses a single backbone cable All hosts connect directly to backbone Ring

Topologies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Topologies • The structure of the network • Physical topology • Actual layout of the media • Logical topology • How the hosts access the media
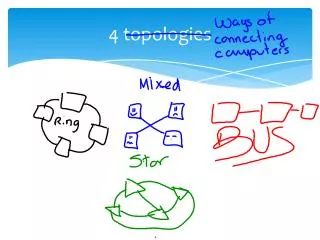
Physical Topologies • Bus • Uses a single backbone cable • All hosts connect directly to backbone • Ring • Connects each host to the next, and the last to the first • Physical ring of cable
Physical Topologies • Star • Connects all cables to a central point of concentration • Usually a hub or switch at center • Extended Star • Links stars by linking hubs or switches
Physical Topologies • Hierarchical • Similar to extended star • Links star LANs to a computer that controls network traffic • Mesh • Each host is connected to all other hosts • No breaks, ever!
Logical Topologies • Broadcast • Each host sends its data to all other hosts • First come, first served to use the network • Ethernet • Token Passing • Controls access by passing token • Host can send when it has the token
LAN Devices • Devices that connect to a LAN are called hosts • Hosts are not part of any layer • Operate at all layers • Symbols not standardized • Bear a resemblance to device
Network Interface Cards • Network adapter • printed circuit board or PCMCIA board • Adapts the host device to the network medium • Each has a unique MAC address • Media Access Control • No standard symbol • Implied on each host
Transceivers • Converts one type of signal or connector to another • AUI to RJ-45 on router • Attachment Unit Interface • Layer 1 • only looks at bits • Found on routers
Media • Carries a flow of information • Bits and bytes • Layer 1 • Media selection is based on: • Cable length • Cost • Ease of installation • Total number of computers on the media
Repeaters • Regenerate and retime signals at the bit level • Allows data to travel further • Single-port “in” • Single-port “out” • Layer 1 • bits
5-4-3 Rule for Repeaters • Five Repeater Rule • You can connect 5 segments with 4 repeaters, but only 3 cable segments can have hosts on them
Hubs • Regenerate & retime network signals • done at bit level for many hosts • “Multi-port Repeater” • Create a central connection point • Increases reliability • Layer 1
Active Hubs • Use energy from a power supply to regenerate signals
Passive Hubs • Simply split signal to multiple users • Like a Y cable • Do not regenerate bits • Do not extend cable length • Only allow two or more hosts to connect to same cable segment
Intelligent Hubs • Console ports • Can be programmed to manage network traffic
Dumb Hubs • Take an incoming network signal and repeat it to every port
Hubs in other topologies • Token Ring • MAU • Media Access Unit • FDDI • MAU is called a concentrator • All Layer 1
Bridges • Layer 2 device • Connects two LAN segments • Filters traffic based on MAC address • local traffic is kept local • other traffic is directed out
Switches • Layer 2 device • “Multi-port bridge” • Decisions based on MAC addresses • Switch data out of the port where the receiving host is connected
Switches • Looks outwardly like a hub • Makes data transmission more efficient • Combines connectivity of hub with the traffic regulation of a bridge on each port
Routers • Layer 3 • Can make decisions based on groups/ classes of addresses • Can connect different layer 2 technologies • Ethernet, FDDI, Token-Ring
Routers • Backbone of the Internet • Examines incoming packets, switches to correct outgoing port • Most important regulating devices on large networks
Clouds • Suggests another network (perhaps Internet) • Does not supply details • Really a collection of devices • Layer 1-7
Segments • Common path for data transmission • Each time a device is used to extend cable length or manage data flow, a new segment is created
Segments • Function of a segment is to act as an efficient local LAN that is part of a larger network • Segment, as applied to LANs, is completely different from the Layer 4 PDU known as a segment