Manufacturing execution system (MES)- Process and Batch
0 likes | 2 Views
Discover how Process and Batch Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) optimize real-time production, enhance quality control, ensure traceability, and integrate seamlessly with ERP systems to drive efficiency, compliance, and data-driven decision-making in process industries.<br>
Share Presentation
Embed Code
Link

Manufacturing execution system (MES)- Process and Batch
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Transforming Process Manufacturing: How MES Drives Real-Time Efficiency and Quality In today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape, Process and Batch Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) play a vital role in driving efficiency, consistency, and quality. Designed specifically for process-oriented industries such as chemicals, pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and specialty manufacturing, MES bridges the gap between the shop floor operations and enterprise-level business systems. A process and batch MES is a software-based solution that monitors, controls, and optimizes production processes in real time. It ensures that every production step— from raw material handling to final packaging—operates seamlessly and adheres to defined standards and regulations. What is a Process and Batch MES? A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) for process and batch manufacturing is designed to handle continuous and batch-based production environments, where precision, traceability, and compliance are paramount. Unlike discrete manufacturing, where individual items are assembled, process manufacturing involves formulations, recipes, or blending operations that require meticulous control and consistency. MES acts as the central nervous system of the plant, coordinating production activities, monitoring performance, and delivering actionable insights for optimization. Core Functions of Process and Batch MES A modern MES offers a comprehensive suite of functionalities tailored for process manufacturing environments. Some of its key features include: 1. Real-Time Data Collection MES captures data from machines, sensors, and production lines in real time. This includes temperature, pressure, batch timing, and material flow—ensuring accurate monitoring and instant response to process variations. 2. Process Monitoring and Control Operators and supervisors can visualize live production data to ensure each process step follows the defined parameters. Automated alerts notify users of deviations, allowing quick corrective action and minimizing downtime. 3. Quality Control MES ensures that every batch produced meets quality standards and regulatory requirements. Integrated quality checks during production reduce waste, rework, and non-conformance.
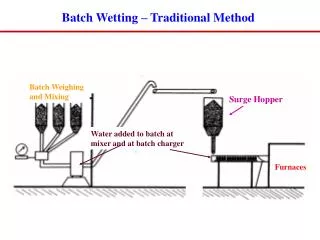
4. Inventory and Resource Management From raw materials to finished goods, MES tracks inventory levels and resource utilization in real time. This minimizes stockouts, overstocking, and material wastage. 5. Workflow and Recipe Management Process and batch MES streamline workflows by managing recipes, formulations, and standard operating procedures (SOPs). Any recipe modification or versioning is controlled and documented for full traceability. 6. Weighing and Dispensing Accurate weighing and dispensing modules ensure that ingredients are measured and mixed precisely as per defined recipes, maintaining product quality and consistency. 7. Traceability MES provides end-to-end traceability by tracking raw materials, intermediate products, and final batches. This helps manufacturers trace any issue back to its source—vital for audits and recalls. 8. Reporting and Analytics Real-time dashboards and historical reports give decision-makers complete visibility into production performance. Key metrics such as OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness), downtime, and yield help identify improvement areas. Compare products used inManufacturing Execution System-Process and Batch Integration with ERP and Control Systems A defining capability of modern MES is its seamless integration with Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems and production process control systems. •ERP Integration: MES connects with ERP to synchronize business and production data—such as work orders, material requirements, and batch records—ensuring both systems stay updated. •Control System Integration: MES interfaces with PLCs, SCADA, and DCS systems on the shop floor for automated data collection and process control. This two-way integration delivers end-to-end visibility—from top-level business planning to real-time production execution—allowing manufacturers to respond quickly to changing demands or production issues. Benefits of Implementing Process and Batch MES Implementing MES brings measurable advantages to process manufacturers. Below are the key benefits:
1. Real-Time Visibility Manufacturers gain a live view of the entire production process, including machine performance, resource availability, and product quality. 2. Optimized Work Scheduling MES dynamically adjusts production schedules based on real-time data, ensuring efficient use of machines, materials, and manpower. 3. Improved Equipment Efficiency By monitoring downtime, cycle times, and performance indicators, MES helps identify bottlenecks and improve equipment utilization. 4. Regulatory Compliance Industries such as pharmaceuticals and food require strict adherence to regulations like FDA or GMP. MES provides electronic batch records and audit trails to support compliance. 5. Enhanced Traceability Every material and process step is logged, enabling full traceability for quality assurance, customer confidence, and regulatory audits. 6. Better Decision-Making With accurate, real-time data, managers can make informed, data-driven decisions that enhance productivity and reduce operational risks. 7. Cost and Waste Reduction MES minimizes material losses, prevents batch failures, and ensures optimal resource use—translating to lower costs and higher profitability. Real-Time Data Empowering Smart Manufacturing In today’s era of Industry 4.0, where digital transformation is reshaping manufacturing, MES plays a pivotal role in creating smart factories. By connecting machines, systems, and people, it enables a data-driven ecosystem that continuously learns and improves. Through IoT, AI, and analytics integration, MES can predict equipment failures, optimize recipes, and automatically adjust production parameters. This intelligent control not only improves quality but also supports sustainable manufacturing goals through energy efficiency and waste minimization. Conclusion
A Process and Batch Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is more than just a software tool—it’s the foundation of a modern, efficient, and compliant manufacturing environment. By offering real-time visibility, ensuring process consistency, and enabling integration across business and control systems, MES empowers manufacturers to make smarter, faster, and more informed decisions. As industries continue to evolve, investing in a robust MES solution will remain a key enabler for achieving operational excellence, regulatory compliance, and sustainable growth in the competitive world of process manufacturing.