CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
670 likes | 942 Views
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. Kristina C. Erasmo , M.D. Function. Transport – oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, waste products Immune defense. CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. Cardiovascular system Heart 2 systems of blood vessels: Systemic circulation Pulmonary circulation Lymph vascular system.

CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Kristina C. Erasmo, M.D.
Function • Transport – oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, hormones, waste products • Immune defense
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM • Cardiovascular system • Heart • 2 systems of blood vessels: • Systemic circulation • Pulmonary circulation • Lymph vascular system
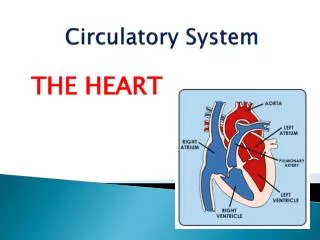
Heart • Muscular pump that propels blood to the arteries of both systemic and pulmonary circulation • Systemic circulation – brings blood from the heart to the rest of the body then back to the heart • Pulmonary circulation – brings blood from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart
Heart • Located in the central mediastinum of the thoracic cavity • Four chambers: • Left ventricle – systemic circulation • Right ventricle – pulmonary • Left atrium • Right atrium
Pericardium • Connective tissue sac covering the heart • Outer sac (fibrous pericardium) • Inner sac (serous pericardium) • Parietal pericardium • Visceral pericardium • Pericardial cavity – with fluid
Pericardium • Fibrous and parietal pericardia – dense CT (collagen and elastic fibers, fibroblasts, other CT elements) • Inner aspect of parietal pericardium – simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) • Visceral pericardium a.k.a. epicardium
Histologic Layers of Heart Wall • Epicardium • Myocardium • Endocardium
Epicardium • a.k.a. visceral pericardium • Outermost layer of heart wall • Lining epithelium of external surface: mesothelium
Myocardium • Thickest (thickness varies for different parts) • Thickest: left ventricle • Thinnest: atria • Mainly cardiac muscle fibers
Purkinje Fibers • Modified cardiac muscle cells • Initiate and conduct the electrical impulse that controls the contraction of the heart • Form the impulse-conducting system of the heart • Larger, contain more glycogen than ordinary cardiac muscle cells
Myocardium • Atrialnatriuretic peptide (ANP) – polypeptide hormone secreted by cardiac muscle cells in atria and interventricular septum • Causes natriuresis– excretion of sodium by the kidneys
Endocardium • Thinnest • Lining epithelium: endothelium • Continuous with innermost layer of the great blood vessels • Lines all internal surfaces of heart
Endocardium • Subendothelial layer – loose CT • External to subendothelial layer – dense CT, thickest portion of endocardium
Blood Vascular System • Refers to the system of blood vessels within which blood circulates • 3 types of blood vessels: • Arteries • Veins • Capillaries
Blood Vascular System • Arteries – carry blood from the heart to the capillaries • Veins – carry blood from the capillaries to the heart
Endothelium • Lining of the luminal surface of all blood vessels • Functions: • Lining blood vessels to facilitate blood flow • Secretes components of underlying CT
Endothelium • Functions: • Secrete prostacyclin – inhibits platelet aggregation, promotes vasodilation • Nitric oxide and endothelin I – vasodilator • Von Willebrand factor – blood coagulation
VasaVasorum • Network of small blood vessels that supply large blood vessels • Veins: present in the tunica adventitia and media • Arteries: confined to adventitia
Capillaries • Smallest blood vessels (5-10 um) • Connect arterioles and venules • Function: Allow exchange of gases and materials between blood and surrounding tissue
Capillaries • Wall consists of single layer of endothelial cells and its associated basal lamina • Surrounding connective tissue elements
Pericytes • Slender, elongated, perivascular cells that usually accompany capillaries • Look like fibroblasts • Not part of the endothelium • Contain tropomyosin • Function: contractile cells that influence the luminal size of capillaries
Types of Capillaries • Continuous (Type I) • Fenestrated (Type II) • Sinusoids
Continuous Capillary • Found in muscles, lungs, CNS, skin • The endothelial cell and the basal lamina do not form openings (which would allow substances to pass the capillary wall without passing through both the endothelial cell and the basal lamina)
Fenestrated Capillary • Mucous membranes of GIT, renal glomerulus, pancreas, some endocrine glands • Endothelial cell body forms small openings (fenestrations) which allow components of the blood and interstitial fluid to bypass the endothelial cells
Sinusoids • a.k.a. discontinuous capillaries or sinusoidal capillaries • Formed by fenestrated endothelial cells, (which may not even form a complete layer of cells) • Basal lamina is also incomplete • Found in liver, spleen, red bone marrow (free exchange of substances or even cells between bloodstream and organ is advantageous)
Histologic Layers of Arteries and Veins • Tunica adventitia • Tunica media • Tunica intima
Tunica Adventitia • Outermost coat of arteries and veins • Chiefly made up of connective tissue with cells and fibers arranged longitudinally
Tunica Media • Middle coat of arteries and veins • Concentrically arranged smooth muscle fibers • Interspersed between the muscle cells are connective tissue elements (collagen and elastic fibers)
Tunica Media • In large arteries: • External elastic lamina/membrane – outer layer of elastin which demarcates the tunica media from the tunica adventitia
Tunica Intima • Innermost coat of arteries and veins • Consists of a layer of endothelium that rest on a basal lamina • Subendothelial layer of loose CT • In arteries: • Internal elastic lamina/membrane – demarcates tunica intima from tunica media
Arteries • Classification: • Small (arteriole) • Medium (muscular or distributing) • Large (elastic or conducting) • Decrease in size but increase in number as they go farther from the heart
Arterioles • Smallest arteries (40 – 400 um) • Tunica intima: only endothelium, no IEL or subendothelial CT • Tunica media: no EEL • Tunica adventitia: loose CT