MOTION
350 likes | 510 Views
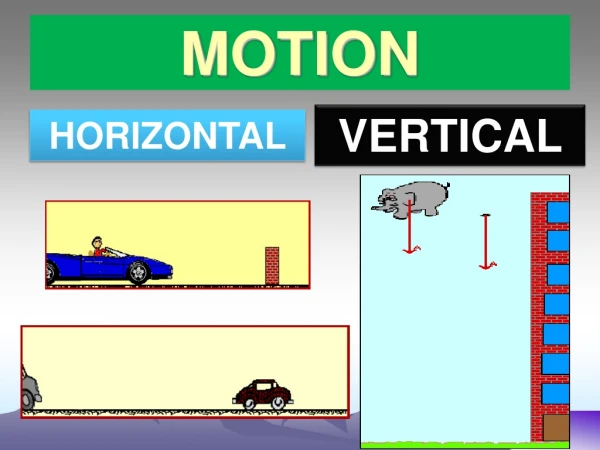
MOTION. MOTION. A change in the relative position of an object when compared to a reference point. Motion-. What is Motion?. Reference Point-. The object that appears to stay in one place. Distance & Displacement. The length of the route you travel. Displacement-.

MOTION
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MOTION A change in the relative position of an object when compared to a reference point. Motion- What is Motion?
Reference Point- The object that appears to stay in one place
Distance & Displacement The length of the route you travel Displacement- Distance from the starting point and the direction in which you traveled (as the crow flies) Distance-
Distance & Displacement 500m E N S W 200m 538.5m Distance= 700m Displacement= 538.5m SW
Speed- d t Distance Time v = Speed= The distance covered by a moving object per unit of time.
What is Bob’s speed ? 6m 3 sec. Distance = v x t Time = d / v 6m 3s d t 2m/s v = = =
What is Bob’s speed ? E 15 km 3 hr. 15km 3hr d t 5km/h EAST v = = =
What is the distance ? 20 km/h 3 hr. d = v x t d = 20 x 3 d = 60 km
d t v = Average Speed-The total distance divided by the total time actual speed average speed Distance Distance Time Time
Average Speed d t v = 5 sec. 15 m d t 15 5 v = 3 m/s v = v =
Velocity-The speed and DIRECTION of a moving object Speed is not velocity 100 km/h West vs. 100 km/h East No direction Yes direction
Acceleration-A change inthe velocity (speed or direction) of a moving object Even when slowing down or turning a corner
Acceleration= a= = Vf – Vi V t t Change in velocity time Vf = final Velocity Vi = initial Velocity = change
Bob’s New Car From 0 36 km/h In 12 s E 3 km/h/s a= = 36 km/h 12 s Vf – Vi t 36 km/h – 0 km/h 12 s =
Gravity Gravity pulls objects to the center of the Earth at 9.8 m/s/s -slowed by air resistance
Gravity pulls objects to the center of the Earth at 9.8 m/s/s Gravity 9.8 m/s 1 s 19.6 m/s 2 s Speed Time 29.4 m/s 3 s 39.2 m/s 4 s Accelerated by 9.8 m/s every second that it falls
Object will reach Terminal speed Ex. People = 190 km/h
As Bob walks down the street at 5 km/h, A tiger jumps out!! Bob then runs 40 km/h in 7 seconds. What is his acceleration? Sample problem .
Vf = 40 km/h Vi = 5 km/h t = 7 s a = Sample solution Vf-vi t 40-5 7 35 km/h 7s . 5 km/h/s
Bob’s van goes from 0 km/h to 8 km/h in 20 seconds. What is its acceleration Sample Problem .
Vf = 8 km/h Vi = 0 km/h t = 20 s a = Sample Solution . Vf-vi t 8-0 20 8 km/h 20s .4 km/h/s
AAAAAGH!! Bob runs for his life, reaching 42 km/h in just 3 seconds. What is his acceleration? Sample Problem .
Vf = 42 km/h Vi = 0 km/h t = 3 s a = Sample Solution . Vf-vi t 42-0 3 42 km/h 3s 14 km/h/s
Mass- Momentum The amount of matter in an object Ex. kilogram Mass and Inertia
SAME – velocity and acceleration Momentum 5kg 10 m/s East 500kg 10 m/s East vs. What is different about the motion of objects that have different masses? Different? MASS
Inertia- Mass = inertia The tendency of an object to resist a change in its motion. Mass = harder to move Ex. Seat belts
Momentum- Velocity = momentum Ex. Walking vs. running A measure of how difficult it is to stop a moving object Mass = momentum Ex. Bike vs. train
Momentum = P = m x v Velocity = both speed & direction Mass x Velocity
P = m x v What is the momentum of the . P = 1.5 kg m/s W P = .3 kg x 5 m/s W 5 m/s W .3 kg
P = m x v What is the momentum of the U.F.O.? . P = 200,000 kg km/h N P = 1000 kg x 200 km/h N 200 km/h N 1000 kg
States that the total momentum of objects that collide with each other doesn’t change. Conservation of Momentum Ex. Billiards , croquet Ex. X 1
Conservation of Momentum Momentum of the cue ball is equal to the end momentum. X Ex. 1
Outside forces acting on objects Using Momentum Conservation 9.8 m/s/s 2. FRICTION - a force that opposes motion 1. GRAVITY
When Objects Collide They: Ex. Bowling 2. Collide and stick together 1. Bounce off each other Ex. Football tackle