Heartworms
300 likes | 610 Views
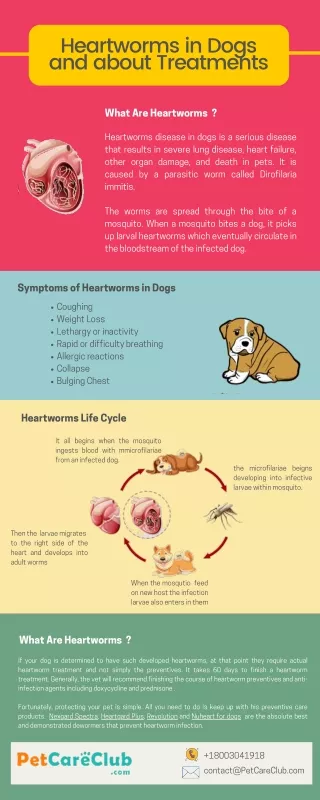
Heartworms. Dirofilaria immitis. The dog is the primary host of Dirofilaria immitis . Other Hosts

Heartworms
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Other Hosts Cats are sporadic hosts, 4% in Louisiana surveys. Most are occult, but there can be an acute seasonal pulmonary disease. The fox and coyote are possible reservoirs. The ferret and sea lion are highly susceptible. Man can develop “coin lesions” with an occult infection of L4-L5 only. D. tenuis, a subcutaneous filarid of raccoons, causes skin nodules in humans.
Vectors Thirty mosquito spp. have been reported as vectors. Culex quincifasciatus is the main vector in Louisiana. Aedes albopictus (asian tiger mosquito) is now of equal importance in the transmission of D. immitis. There is a 10-14 day development period in the mosquito in warm weather. At >57ºF microfilariae (mf) develop in the malphigian tubules of the mosquito, and at >65 ºF can develop and molt from L1-L3.
Life Cycle Microfilariae of an infected dog are picked up by a mosquito upon feeding.
Life Cycle Microfilaria molt from the L1 stage to the L3 stage within the mosquito.
Mf become ‘sausage stage’ and molt in malphigian tubules. L3 escape to hemocoel fluids.
Life Cycle L3 is deposited in the hemolymph via the proboscis upon another meal by the mosquito, then penetrate via puncture wound.
Life Cycle At 10-14 days after infection, L3 molts to L4 in the SQ tissues. By 60-70 days, L4 will molt to L5 within the muscle fascia.
Life Cycle At 3-4 months, the worms enter the heart as L5, still at a small size of 1-3 cm.
Life Cycle 5-8 months is the prepatent period. After this time, microfilaria will be present in the blood with the presence of male and female worms.
Adults are 10-30 cm. Normally they are 15 cm with a corkscrew tail. Adults live about 5 years in the dog and less than 2 years in the cat. Microfilaria live 1-2 years in the dog with no microfilaricide treatment.
Dogs: Chronic Thromboembolic disease results. Glomerulonephiritis, DIC, Pulmonary Infiltrates with Eosinophilia, Post-Cava Syndrome are less common. Cats: Acute Pulmonary Asthmatic disease may result
Microfilariae can be detected via direct smear (an underestimated screening test), microhematocrit, Knott’s test, or filter test methods.
Upon examination of microfilariae, a distinction must be made between infection of Dirofilaria immitis, or the non-pathogenic Dipetalonema reconditum.
To distinguish between Dirofilaria and Dipetalonema, the above factors must be considered upon examination.
DirofilariaDipetalonema Length 286-340um 246-293um (by knott’s) Width 6.0-7.2um 4.5-5.8um Anterior tapered blunt Posterior straight 30% hooked Body straight often curved No./ml numerous(1-10,000) less numerous (1-1,000) Movement undulate in situ move across field R(G) cells* 1-2-1 pattern 1-3 pattern *Rectal or genital cells are near posterior of microfilariae.
Treatment Adulticidal drugs: Organic arsenicals that affect rapidly multiplying digestive cells. Worms starve to death in 7-10 days, at which time they embolize to the lungs for up to 4 weeks. If this occurs, control clinical pulmonary embolism with diminishing anti-inflammatory doses of corticosteroids. Can use Caparsolate or Immiticide. Microfilaricide: 3-4 weeks post adulticide treatment is safe for microfilaria treatment. Drugs to use are Ivermectin, Milbemycin, or Diethylcarbamazine HCL.
Heartworm Prevention Ivermectin and Milbemycin Pharmacology Macrocyclic lactone structures Produced by same genera of soil dwelling organisms Affect similar spectrum of parasitic organisms Share similar mode of action Structural modification affect biological profiles
Heartworm Prevention Interceptor
Heartworm Prevention RevolutionTM (selamectin) First topically applied endectocide First topical heartworm preventative Broad-spectrum activity against endo- and ectoparasites A novel semi-synthetic avermectin Low volume, easy to apply, topical formulation Quick drying/cosmetically acceptable Packed in color-coded, multidose tubes Water fast two hours after application
Revolution Spectrum of Protection Dog Cat Adult fleas + + Flea eggs + + Heartworm + + Ear mites + + Sarcoptic mites + Tick (D. variabilis) + Hookworm (A. tubaeforme) + Roundworm (T.cati) +