Krashen’s Input Hypothesis
190 likes | 427 Views
Krashen’s Input Hypothesis. PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010 Language & Literacy Education Faculty of Education Universiti Malaya KL. Group Members. Tan Chung Szuan PET 080017. Choo Yin Yin PET 080002. Loo Ke Sin PET 080005.

Krashen’s Input Hypothesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Krashen’s Input Hypothesis PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010 Language & Literacy Education Faculty of Education Universiti Malaya KL
Group Members Tan Chung Szuan PET 080017 Choo Yin Yin PET 080002 LooKe Sin PET 080005 Sharon Pang PET 080015 PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Content PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
What is input and output? PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Five Hypotheses 1. Acquisition-Learning Hypothesis PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
“Fluency in second language performance is due to what we have acquired, not what we have learned. ” Krashen Conscious Subconscious learning acquisition are NOT able to exist at the same time (mutually exclusive) PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
2. Monitor Hypothesis Only involved in learning, x acquisition Device for editing & making corrections Krashen, “such explicit intentionally learning should be avoided.” Should only be applied after fluency is established PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
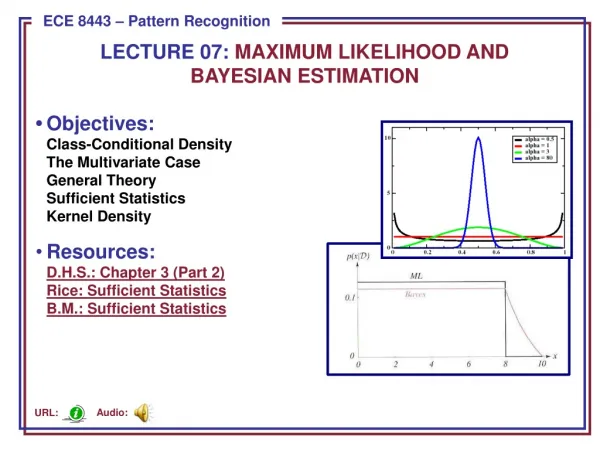
3. Natural Order Hypothesis By following the earlier morpheme order studies of Dulay and Burt… Krashen claimed that: we acquire language in a predictable or “natural” order PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
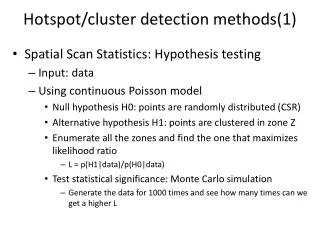
4. Input Hypothesis Krashen: Comprehensible the only true foundation input = of SLA Comprehensive input: understanding of input language, that contains ‘a bit beyond’ the current level of competence. (i + 1) Speech will ‘emerge’ once acquirer has built up enough comprehensible input PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
5. Affective Filter Hypothesis Krashen: the best acquisition will occur when we have low anxiety and defensive-free low “affective filter” (in Krashen’s terms) PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Evaluations of the five hypotheses 1st criticism: Krashen McLaughlin (psychologist) it is difficult for us to identify the conscious or subconscious distinctions, in language acquistion. • Rather fuzzy distinction between subconscious (acquisition) and conscious (learning) PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Evaluations of the five hypotheses 2nd criticism: Krashen Gregg Learning & acquisition can both be beneficial depends on the learner’s own styles and strategies • Learning is not as important as acquisition PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Evaluations of the five hypotheses 3rd criticism: Krashen Gregg & White We are unable to define i and 1 • Claimed that the input one understands MUST contains i + 1, that is the comprehensive input PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Evaluations of the five hypotheses 4th criticism: Krashen Criticism Speech will indeed emerge for bright learners BUT no significant information on Krashen’s theories about learners whose speech does not ‘emerge’ • Speech will ‘emerge’ once acquirer has built up enough comprehensible input PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
The Output Hypothesis • Introduced by Merill Swain (1985) • Output important role in SLA • She denied Krashen’s claims a person could learn second language without speaking at all. • Her studies in Canada : English-speaking students learn all subjects in French but not having to reply in French did not achieve full productive competence in French PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Three major functions of Output in SLA 1. Get learners to recognize their linguistic weaknesses 2. A way to try out / test one’s language 3. For the learner to… think deeper on language PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Conclusion Related to CALL • It includes input and output 4 skills Our Group’s View • Input go hand in hand with output • They achieve the most efficiency when both of them work together PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL
Source: Brown, H. Douglas. 2007. Principles of Language Learning and Teaching, 5th Edition. White Plains, NY: Pearson Education. Chapter 10 Created for: PBET 2113 Participants (TESL) Semester 2, AY 2009-2010 Department of Language & Literacy Faculty of Education University of Malaya KL Created by: Tan Chung Szuan, LooKee Sin, Choo Yin Yin and Sharon Pan Xie Mei Facilitator: Jessie Grace U. Rubrico, PhD PBET 2113 Group 7b (TESL) Semester 2 AY 2009-2010, Department of Language & Literacy Education, Faculty of Education, Universiti Malaya KL