Chapter 7 III. Cell Boundaries
240 likes | 354 Views
Explore the cell boundaries, from membranes to walls, regulating the passage of materials in and out of cells. Understand diffusion, osmosis, and active transport mechanisms essential to cellular functions.

Chapter 7 III. Cell Boundaries
E N D
Presentation Transcript
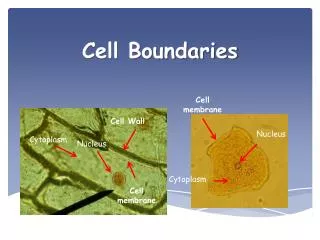
All cells have a _____________________________and some have a cell wall Cell membrane
Interest Grabber Section 7-3 • How is a window screen similar to a cell membrane? Read on to find out. • 1. What are some things that can pass through a window screen? • 2. What are some things that cannot pass through a window screen? Why is it important to keep these things from moving through the screen? • 3. The cell is surrounded by a cell membrane, which regulates what enters and leaves the cell. Why is it important to regulate what moves into and out of a cell? Go to Section:
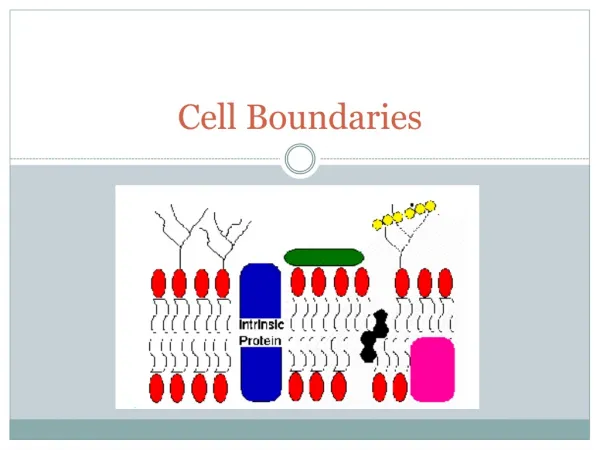
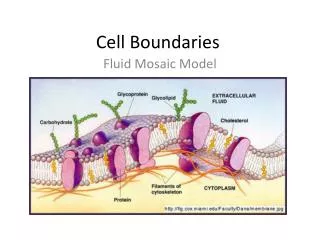
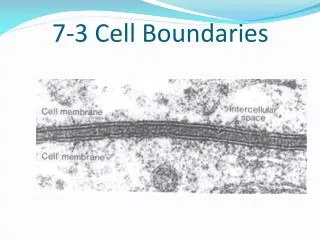
A. Cell Membrane • Regulates what enters and leaves the cell and also provides _____________________________. • Almost all cell membranes are made of a double layered sheet called a ___________________________-flexible,yet strong barrier • Cell membranes usually have a protein molecule imbedded in the bilayer w/ carbohydrate molecules attached • Called a _________________model • Some of the proteins form channels or pumps to move material across the membranes • Some of the carbs act as ____________________tags Fluid mosaic Phospholipid bilayer Protection and support Chemical id tags
Carbohydrate chains Proteins Cell membrane Protein channel Lipid bilayer Figure 7-15 The Structure of the Cell Membrane Section 7-3 Outside of cell Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Go to Section:
B. Cell Walls • In plants,algae,fungi, and many prokaryotes • Lie _______________the cell membrane • Usually porous enough to let water,O2,CO2 and certain other substances to pass through easily • Main function is support and protection • Usually made of fibers of ____________________-produced in cell and secreted to surface • Mostly _____________________-tough carb fibers cellulose Carbohydrate and protein outside
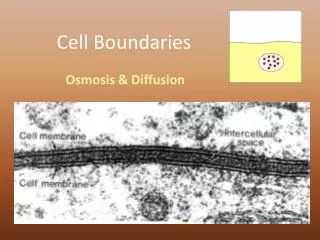
C.Diffusion Through Cell Boundaries • Every cell is in a liquid environment • Cell membrane regulates the movement of cell materials from one side to the other
1.Measuring concentration • Cytoplasm is a solution of various substances in water • _____________of a solution is the mass of solute in given volume of solution---ie. Mass/volume…..If you have 15 g salt in 3 mL water,what is the concentration?------_______….If you have 24 g salt in 2mL water you would have 12 g/mL salt….Which solution is more concentrated?______________ 12 g/mL 5g/mL concentration
2. Diffusion • In a solution the particles move constantly,spreading out randomly….tending to move where more concentrated to an area less concentrated…This is called __________________. • ____________________= concentration of a solute is the same throughout a system • does not require energy because random movement • if equilibrium is reached,particles keep moving across the membrane,still balancing concentration isotonic
Figure 7-17 Osmosis Section 7-3 Water molecules Higher Concentration of Water Cell membrane Lower Concentration of Water Sugar molecules Go to Section:
D. Osmosis • Some molecules are too large or too strongly charged to make it across the lipid bilayer----thus impermeable to it • Most membranes are selectively permeable • _____________________is the diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane • water moves easily and will move to balance the concentration of a solute,water moving from area of higher to lesser conc. For the WATER • ____________________-same strength of a solute on both sides of a cell membrane isotonic osmosis
more concentrated side of solute is ____________________ • less concentrated side is____________________ • Osmosis exerts a pressure known as ____________________________on the hypertonic side of a membrane….This could results in a cell bursting • Bursting not so much a problem in larger organisms….tend to be in isotonic environments • Osmotic pressure may not allow a plant or bacterial cell to burst , but could weaken the cell wall Osmotic pressure hypotonic hypertonic
E.Facilitated Diffusion • Some molecules,like glucose ,diffuse quickly across due to ________________________ • These allow only certain molecules to pass • Since it is diffusion it does not require energy and still goes from area of higher to lower concentration Protein channels
F.Active Transport--- • _______________________________________________________________________________ • Requires much energy • Usually carried out by proteins or pumps found in the membrane Moves materials across a concentration gradient,or difference
1. Molecular Transport • Small molecules and ions carried by proteins that act like energy requiring pumps • Ca ,K,and Na ions are carried
Endocytosis and Exocytosis • Transports larger molecules and even clumps of matter • ________________________is the process of taking material inward by enfolding,or pockets • In endocytosis ,the pocket breaks loose from the cell membrane and forms a vacuole…large molecules,food and even whole cells can be taken in this way endocytosis
2 examples of endocytosis are • ___________________-extensions of cytoplasm surround a particle and package it in a food vacuole,then the cell engulfs it ---This is how amoebas eat-----is a form of active transport • _______________-Cells use this to take up liquids in the environment—tiny pockets filled w/ liquid form along the cell membrane and pinch off to form vacuoles phagocytosis pinocytosis
___________________________--releases large amounts from the cell by pinching off or a contractile vacuole as in paramecium---also active transport exocytosis
Figure7-20 Active Transport Section 7-3 Molecule to be carried Low Concentration Cell Membrane High Concentration Molecule being carried Low Concentration Cell Membrane High Concentration Energy Energy Go to Section: