MySQL Joins
0 likes | 10 Views
MySQL Joins are used to combine rows from two or more tables based on related columns. They help retrieve meaningful data by connecting tables through primary and foreign keys. Common join types include INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JOIN, and FULL JOIN. Understanding MySQL Joins is essential for effective relational database management and writing complex SQL queries.

MySQL Joins
E N D
Presentation Transcript
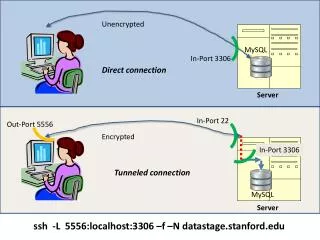
MySQL Joins Explained: Inner, Left, Right, Cross, Self, Natural, EquiJoin Introduction Joins in MySQL are used for combining rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. They allow you to import data from multiple tables using a single query statement in MySQL. This is essential for normalized database structures where data is distributed across different tables to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. MySQL is an open-source platform for managing databases using Structured Query Language, a language used for writing a query in MySQL. Joins play a very important role in MySQL for combining the data from different tables. This article will give you a description of different joins in MySQL. Given below is the list of purposes of MySQL JOINs: Purpose of MySQL JOINs Combine related data: The primary purpose of joins in MySQL is to link the related data from different tables that have logical relationships (eg, records of customers purchasing more than Rs. 1500 from different shopping malls). Efficient data retrieval: Structured query language in MySQL allows you to retrieve data from different tables using a single query instead of performing multiple separate queries and then combining the results in your applications.
Support normalized database design: Joins plays an important role in MySQL to minimize redundancy and maintain data consistency stored. Data is organized into rows and columns in a structured format in a database. Data analysis: There are different mathematical functions performed in the database using queries like COUNT, SUM, AVG, and GROUP BY clauses for comprehensive data analysis across related datasets. Types of Joins Given below is the list of different types of joins used in MySQL with their description. 1.INNER JOIN This joins return only the rows that have common data among the different tables. You can think of an inner join as an intersection of different tables. Given below is an example of an inner join in MySQL. Example: You are provided with two tables as given below. Table 1: Students student_id 1 2 3 4 name Ashok Rahul Kunal Ruby course_id 201 202 203 204 Table 2: Courses course_id 201 202 208 301 course_name Data Science Machine Learning Java Programming Mathematics In this question, you are asked to write a MySQL query that returns the name and course_name, which have a common course_id. Query: Given below MySQL query is for performing the above task
SELECT Students.name, Courses.course_name FROM Students INNER JOIN Courses ON Students.course_id = Courses.course_id; Output: The output for the above query is given below name Ashok Rahul 2.LEFT JOIN LEFT JOIN returns all rows from the left table and common rows from the right table. If there is no common data in the right table, the left table will be returned, and null values will be returned for the right table. You can think of the left table as taking everything from the left table and whatever matches from the right table. Given below is an example of a left join in MySQL. Example: We use the same data that we use in an inner join and perform a left join operation. Query: Given below is the MySQL query for performing the left join operation. SELECT Students.name, Courses.course_name FROM Students LEFT JOIN Courses ON Students.course_id = Courses.course_id; Output: The above MySQL will give the output as given below. name Ashok Rahul Kunal Ruby 3.RIGHT JOIN RIGHT JOIN returns all rows from the right table and common rows from the left table. If no match is found in the left table, null values will be returned for those rows. It is like the mirror image of LEFT JOIN. You can think of RIGHT JOIN as take course_name Data Science Machine Learning course_name Data Science Machine Learning NULL NULL
everything from the right table and matching rows of the left table. Given below is an example of a right join in MySQL. Example: We use the same data that we have used in an inner join to perform the right join operation. Query: Given below is the MySQL query for performing the right join operation. SELECT Students.name, Courses.course_name FROM Students RIGHT JOIN Courses ON Students.course_id = Courses.course_id; Output: The above MySQL query will give the output as shown below. name Ashok Rahul NULL NULL 4.CROSS JOIN CROSS JOIN in MySQL returns the Cartesian product of the tables on which cross the join operation has to be performed. A Cartesian product produces a new set containing all possible ordered pairs from two or more given table where the first column comes from the first table and the second column comes from the second table. Also, CROSS JOINis used to generate all possible combinations (e.g., pairing students with courses, employees with shifts, etc. ). Every row from the first table is combined with every row from the second table. You can think of CROSS JOIN as pairing everyting in the first table with everything in the second table. Example: You are provided with two tables as given below. Table 1: Students student_id 1 2 Table 2: Subjects course_name Data Science Machine Learning Java Programming Mathematics name Harry Jagdish
subject_id 201 203 206 In this question, a CROSS JOIN has to be performed on two tables and return the resultant table. Query: Given below is the MySQL query for performing the CROSS JOIN operation. SELECT Students.name, Subjects.subject_name FROM Students CROSS JOIN Subjects; subject_name Physics Chemistry Biology Output: name subject_name Harry Physics Harry Chemistry Harry Biology Jagdish Physics Jagdish Chemistry Jagdish Biology 5.SELF JOIN A SELF JOIN is a JOIN in MySQL in which joining operations are performed within the same table. It is used when there is a relationship within the same table instead of fetching the data from two or more different tables. You can think of CROSS JOIN in MySQL as building the relationship among different rows within the same table. Given below is an example of a self-join in MySQL. Example: You are provided with a table name Employees as given below. Table: Employees emp_id 1 2 3 Suraj emp_name Priya Sameer manager_id NULL 1 1
4 Praveen 2 In this question, you are asked to write the MySQL query for performing a self-join. Join operation in MySQL returning the manager’s name assigned to employees. Query: Given below MySQL query is for performing the above task using self-join. SELECT e1.emp_name AS Employee, e2.emp_name AS Manager FROM Employees e1 JOIN Employees e2 ON e1.manager_id = e2.emp_id; Output: The above MySQL query will return the manager names assigned to employees as shown in the table below. Employee Sameer Suraj Praveen Sameer 6.NATURAL JOIN A NATURAL JOIN is a type of Join in MySQL used to combine columns with the same name and compatible data types automatically in different tables. A NATURAL JOIN is performed automatically by the database engine. You can think of this join as joining two tables wherever column names match. Given below is an example of a natural join in MySQL. Example: You are provided with two tables as shown below. Table 1: Students student_id 1 2 3 Amir Table 2: Courses course_id course_name Manager Priya Priya name Kuldeep Alia course_id 201 202 203 201 Computer Science 202 Data Science
204 Mathematics In this question, you need to return the name and course_name having the common course_id using natural join. Query: Given below is the MySQL query for performing the above task. SELECT Students.name, Courses.course_name FROM Students NATURAL JOIN Courses; Output: The above MySQL query will return the output table as shown below. name Kuldeep Alia 7.Equi Joins An Equi Join is a specific type of inner join in SQL where different tables are combined based on an equality condition (=) among columns. All Equi Joins are Inner Joins, but not all Inner Joins are Equi Joins. You can think of Equi Joins as joining two tables where one column equals another column. Example: You are provided with two tables as shown below. Table 1:Students student_id 1 2 3 Anamika Table 2: Courses course_id 203 204 207 In this question, you need to write the MySQL query for returning the name and course_name having the common course_id. course_name Computer Science Data Science name Rohan Rishi course_id 203 204 205 course_name Physics Chemistry English
Output: The above MySQL query will give the output table as shown below. name Rohan Rishi Conclusion Joins in MySQL play an important role in relational databases, allowing you to retrieve information from different tables and represent that data in a structured format. Mastering joins is essential for those working with databases. Joins are the core concept in MySQL, and once you understand the joins, you will be able to write powerful queries in MySQL that transform raw data into a structured format. This article describes joins in detail, along with their examples. To find more such educational articles, you can visit the Tpoint Tech Website, where you can find various articles in programming and other technology as well with interview questions and an online compiler for practise programming and gaining valuable information. course_name Physics Chemistry