PSTN and VoIP
200 likes | 406 Views
PSTN and VoIP. Chapter 1. PSTN-Public Switched Telephone Network. Ring Down Circuit-Direct connection between two phones with no signaling. Original phone system invented by Bell Pick up phone and talk –No ringing. Switched Telephone.

PSTN and VoIP
E N D
Presentation Transcript
PSTN and VoIP Chapter 1
PSTN-Public Switched Telephone Network • Ring Down Circuit-Direct connection between two phones with no signaling. Original phone system invented by Bell • Pick up phone and talk –No ringing
Switched Telephone • Original switch was a telephone operator who manually connected the two voice paths. • Now switching is electronic
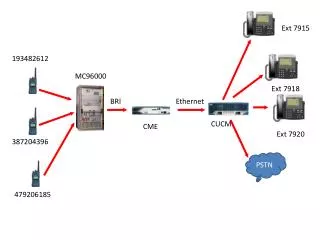
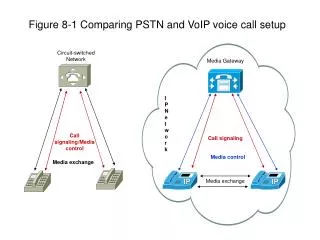
Calling Pennsylvania 6 5000 • The telephone number identified a specific pair of wires • Circuit switched to complete a connection • VoIP phone numbers no longer tied to a specific set of wires but to a TCP/IP address. • Packet switched network
Analog • Original telephone signal was Analog –continuous voice wave. • Analog uses amplifiers resulting in accumulated noise caused by amplifying the signal and the noise.
Digital • Digital signals use a repeater which amplifies and cleans the signal. • Repeater does NOT amplify noise
Pulse Code Modulation • To convert an analog voice wave to digital we use PCM. • Filter the signal to eliminate frequencies over 4000 Hz • Sample the signal at 8000 Hz • Convert to digital – 8 bits • Nyquist criteria –Must sample at greater than twice the modulating frequency
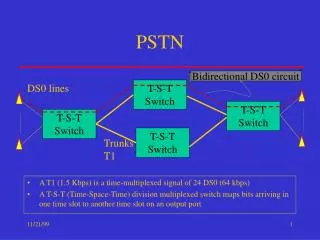
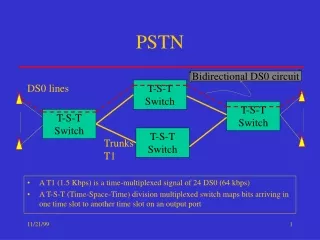
Local Loop • Local Loop – Home telephone to central office switch • Trunk – path between central office switches • Switches connect trunks
Signaling • User to Network Signaling – End user to PSTN • DTMF – Dual Tone Multi Frequency Each digit is represented by TWO frequencies to eliminate errors
Network to Network Signaling • Switches communicate with each other • Uses SS7 • T1 lines over twisted pair • T3 line over coax • T3 over microwave
SS7 • Signaling System 7 is out of band signaling. • SS7 is a method of sending messages between switches for basic call control. • Reduced post dialing delay • Increased call completion • Connection to the IN (Intelligent Network)
Drawbacks to PSTN • Data has overtaken voice as the primary traffic on networks built for voice • PSTN cannot create and deploy features quickly enough • Data/Voice/Video cannot converge on PSTN • Voice architecture not flexible enough to carry data
Real Time Protocol • RTP is used to carry voice data • RTP runs on UDP • RTP streams – RTP packet flows • TCP/IP – TCP causes retransmission of packet. • Not possible or desirable with RTP/UDP • RTP uses timestamps instead
Jitter • Jitter – variation of interpacket arrival time or the difference between when a packet is supposed to arrive and when it is actually received
PSTN Numbering Plans • Shortage of phone numbers • Must use all ten digits in most areas • Overlay- One area has multiple area codes • Existing area code has another “overlayed”
H.323 • ITU-T specification for transmitting audio, data and video across an IP network • Translates between audio, video and data transmission formats
MGCP • Media Gateway Control Protocol • Soft Switch • Control endpoints • Entire IP network acts as a virtual switch • P 28
Session Initiation Protocol • SIP – An Application layer protocol for creating, modifying and terminating sessions with one or more participants