Have you ever been frustrated with slow internet speeds, dropped connections, or buffering videos? If so, you’re not alone. Many people question the differences between Ethernet and Wi-Fi, especially when deciding how to set up a reliable network at home or in the office. Understanding the specifics of Wi-Fi versus wireless internet, wired versus wireless networks, and different connection types can greatly improve speed, reliability, and overall user experience.
Whether you’re working from home, gaming online, streaming movies, or managing smart home devices, choosing the right connection is important. This guide will explain the key differences, benefits, and drawbacks of Wi-Fi and Ethernet, helping you make informed choices for your network.
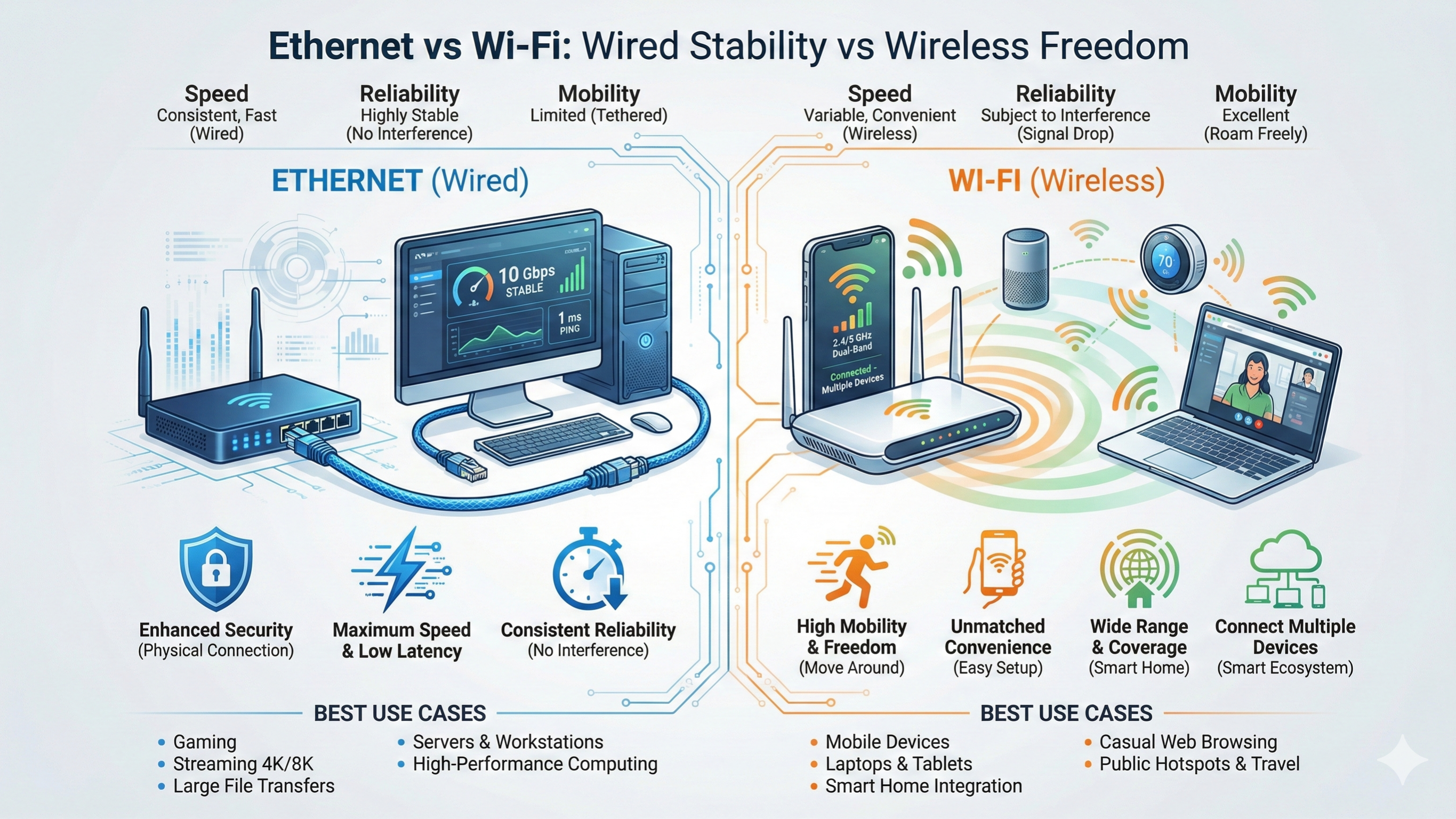
What Is Ethernet?
Ethernet is the traditional wired connection method, linking your device to a router or switch with a cable. It has been the backbone of networking for decades due to its reliability and high performance. Ethernet connections are commonly used in homes, offices, and data centers where stable, high-speed internet is essential.
Why Ethernet Stands Out:
- Consistent Speeds: Ethernet offers stable download and upload speeds unaffected by distance or interference within the cable limit.
- Low Latency: Perfect for online gaming, video conferencing, and other real-time applications.
- Security: Less vulnerable to hacking compared to wireless connections.
- High Bandwidth: Handles multiple high-demand tasks simultaneously without lag.
Drawbacks of Ethernet:
- Limited mobility: you're tethered to a cable.
- Requires physical installation, which can be tricky in large spaces.
- Cable clutter can become an issue with multiple devices.
What Is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that lets devices connect to the internet or a local network through radio signals. Modern Wi-Fi standards, like Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6, offer faster speeds, greater range, and the ability to connect multiple devices at once.
Advantages of Wi-Fi:
- Mobility: Connect devices anywhere within the router’s range.
- Convenience: No cables, less clutter, and easy setup. Multi-device
- Support: Connect laptops, phones, smart TVs, and IoT devices at the same time.
- Modern Speeds: High-speed wireless standards can rival wired connections under optimal conditions.
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi:
- Performance can fluctuate due to distance, walls, or interference.
- Slightly higher latency than wired connections.
- Security depends on strong passwords and encryption protocols like WPA3.
Key Differences Between Ethernet and Wi-Fi
Connection: Ethernet uses a wired connection, meaning your device plugs directly into the router for a dedicated link. Wi-Fi is wireless, allowing devices to connect through radio signals without cables.
Speed: Ethernet offers high and stable speeds, consistently delivering near-maximum performance. Wi-Fi provides medium to high speeds, but performance can vary based on distance, obstacles, or interference.
Latency: Ethernet maintains very low latency, which is crucial for real-time activities like gaming or video calls. Wi-Fi has moderate latency, which may fluctuate based on signal strength or congestion.
Mobility: Ethernet’s wired setup limits movement since devices must remain near the cable. Wi-Fi provides high mobility, allowing you to use devices freely around your home or workspace.
Reliability: Ethernet is known for excellent reliability, delivering consistent connectivity. Wi-Fi can be less predictable and may be influenced by interference from walls, devices, or neighboring networks.
Setup: Ethernet requires cables and physical connections, which can make installation more effortful. Wi-Fi setup is straightforward and router-based, making it easy for multiple devices to connect quickly.
Best Use: Ethernet is ideal for gaming, video editing, streaming, and large file transfers where stability is important. Wi-Fi is best for mobile devices, casual browsing, smart home gadgets, and everyday use where convenience is key.
Wired vs Wireless Network: What You Should Know
When deciding between wired vs wireless network, it helps to consider how you use your devices and the layout of your space.
- Performance Matters: Ethernet offers consistent speeds and low latency, while Wi-Fi may vary due to interference, walls, or distance.
- Device Mobility: Wi-Fi allows devices like laptops and smartphones to move freely. Ethernet keeps desktops or gaming consoles stationary but maximizes performance.
- Number of Devices: High-density households or offices benefit from a hybrid setup; Ethernet for essential devices and Wi-Fi for mobile or casual-use devices.
- Security Considerations: Wired connections are inherently more secure. Wi-Fi needs strong encryption and updated passwords to maintain safety.
- Ease of Installation: Wi-Fi is simple and quick to set up. Ethernet might require running cables through walls or using switches for multiple devices.
Choosing the Right Internet Connection Type
Choosing the right types of internet connections depends on usage, location, and device requirements:
- Ethernet for Critical Devices: Desktops, smart TVs, gaming consoles, and workstations benefit from a wired connection for stability and low latency.
- Wi-Fi for Convenience and Mobility: Laptops, tablets, smartphones, and IoT devices thrive with wireless connections.
- Wireless Internet for Remote or Rural Areas: LTE, 5G, or fixed wireless internet ensures connectivity where cable or fiber options are unavailable.
Many homes and offices use a hybrid setup, combining Ethernet for high-demand devices and Wi-Fi for all other devices. This approach balances speed, reliability, and convenience.
Tips to Optimize Your Network
- Router Placement: Place Wi-Fi routers centrally to reduce dead zones and improve coverage.
- Use Quality Cables: CAT6 or CAT7 Ethernet cables provide faster speeds and better reliability.
- Update Firmware: Keep your router firmware up to date for security and performance.
- Reduce Interference: Keep routers away from microwaves, cordless phones, or thick walls.
- Separate Networks: Use different networks for high-demand and casual devices to maintain speed.
Conclusion
Choosing between Ethernet and Wi-Fi depends on your priorities: speed, stability, mobility, number of devices, and security. Ethernet is best for users who need reliable, high-speed, low-latency connections for work, gaming, or media streaming. Wi-Fi provides flexibility, convenience, and mobility for multiple devices in a home or office. Understanding Wi-Fi versus wireless internet, wired versus wireless networks, and other internet connection types helps you make informed decisions, ensuring smooth, uninterrupted connectivity for all your devices.
For most users, a hybrid network, combining Ethernet and Wi-Fi, provides the best balance of performance and flexibility, making your internet experience faster, safer, and more reliable.
FAQs About Wi-Fi vs Ethernet
1. Is Ethernet faster than Wi-Fi?
Yes. Ethernet generally offers faster and more stable speeds because it uses a direct wired connection. It also has lower latency, making it ideal for tasks that require real-time responsiveness.
2. Can I use Wi-Fi and Ethernet at the same time?
Yes, you can use both at once without issues. Many homes rely on Ethernet for stationary devices like PCs or consoles, while mobile devices connect through Wi-Fi. This combination helps balance speed and convenience.
3. Which connection is better for online gaming?
Ethernet is the better choice for gaming because of its low latency and consistent performance. Unlike Wi-Fi, it isn’t affected by signal interference or distance. This results in smoother and more reliable gameplay.
4. Can Wi-Fi completely replace wired connections?
For everyday browsing and streaming, Wi-Fi can replace wired setups easily. However, Ethernet still outperforms it for high-demand tasks like large file transfers or competitive gaming. A wired connection ensures maximum stability.
5. What is the best setup for multiple devices at home?
A hybrid setup works best for most households. Use Ethernet for devices that require strong, stable connections and Wi-Fi for mobile or casual-use gadgets. This keeps everything running smoothly and efficiently.