Ampere’s Law
280 likes | 725 Views
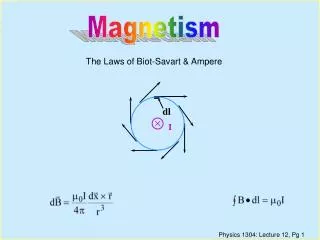
Ampere’s Law. Ampere’s Law. Write Ampere’s law. Rewrite Ampere’s law using the cosine in the dot product. Rewrite Ampere’s law (one more time) in terms of the component of B parallel to the path, B // . Ampere’s Law.

Ampere’s Law
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Ampere’s Law • Write Ampere’s law. • Rewrite Ampere’s law using the cosine in the dot product. • Rewrite Ampere’s law (one more time) in terms of the component of B parallel to the path, B//.
Ampere’s Law • Discuss the meaning of this (these) equation in your group. Write in your own words what this equation tells you. • Why is this integral called a path integral or line integral? • What does the little circle on the integral sign mean? Take any closed loop and sum up the component of the magnetic field parallel or tangent to the path of the loop, then this is proportional to the current inside the closed path. The integral is in two or three dimensions (space) so we must define a line- path- to integrate. Integral is around a closed path.
Ampere’s Law • Rewrite Ampere’s law when the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field do not change along the path.
Ampere’s Law • Below is a diagram of a constant magnetic field pointing to the right. We will use Ampere’s law to show that in a constant magnetic field the current is zero through any Amperian loop. Discuss different paths in your group. Draw two or three different closed paths using a dash line for the path.
Ampere’s Law • Recall from Calculus II that • Choose a path that will make the integral easy to do and show that the current through the path is zero. Why? Why?
Ampere’s Law • Next we need to see if the magnitude is constant on the path. Can you use symmetry to show that the magnitude and direction are constant on the path. Discuss this in your group. Explain.
dl B Ampere’s Law • Next we need to see if the magnitude is constant on the path. Can you use symmetry to show that the magnitude and direction are constant on the path. Discuss this in your group. Explain. What is cosq?
B dl Ampere’s Law Magnetic field for a toroid Draw an Ampereian closed path
r r a Ampere’s Law Magnetic field inside a conductor carrying a current Inside Outside Same as before
Ampere’s Law MRI or NMR
Ampere’s Law Magnetic Material Diamagnetic Paramagnetic Ferromagnetic
Ampere’s Law Application: Magnetic recording