Federal Cloud Computing Training
500 likes | 1.19k Views
Federal Cloud Computing Training. August 12, 2009. Agenda. Introduction Cloud Computing Definition Technical Overview Cost and Energy Benefits Federal Cloud Computing PMO Update Federal Cloud Computing Governance. Introduction.

Federal Cloud Computing Training
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Federal Cloud Computing Training August 12, 2009
Agenda Introduction Cloud Computing Definition Technical Overview Cost and Energy Benefits Federal Cloud Computing PMO Update Federal Cloud Computing Governance
Administration Priorities for Infrastructure Modernization and Cloud Computing The Federal technology environment requires a fundamental reexamination of investments in technology infrastructure.” “The Infrastructure Modernization Program will be taking on new challenges and responsibilities. Pilot projects will be implemented to offer an opportunity to utilize more fully and broadly departmental and agency architectures to identify enterprise -wide common services and solutions with a new emphasis on could computing. “ “The Federal Government will transform its Information Technology Infrastructure by virtualizing data centers, consolidating data centers and operations, and ultimately adopting a cloud-computing business model.” FY2010 Federal Budget Analytical Perspectives Cross Cutting Programs http://www.whitehouse.gov/omb/budget/fy2010/assets/crosscutting.pdf
The Fierce Urgency of Now • Federal government is fundamentally changing the way it operates. • We are confronted with system-wide challenges ranging from the economy, the environment, to health care, etc. • Our public infrastructure is not performing adequately and there are operational and public safety risks. • Such challenges have forced the Federal government to take a front and center role in working across the public, private, and academic sectors to solve massively complex and cross-disciplinary, interdependent problems. • From an operational perspective, all systems operate today via human interactions with technology and with IT infrastructure as the foundational grid from which those interactions and transactions are enabled. • Increasingly, more demands will be made of Federal government, for handling, managing, and overseeing transactions (e.g. Recovery.gov, Ethics.gov, Data.gov, etc.). • As a steward and provider of services to citizens, what we provision requires 21st century infrastructure, know-how, and innovation. 5
We Need to Think Differently • Real drivers for change in IT and IT infrastructure are not solely the need for higher performance or cost savings but the macro-level system-wide challenges that technology can help solve. • In a tight economy though, the real issue or challenge in IT is between the availability of money, perceived value, and the needs of IT infrastructure (especially data centers). • Problem is that as the demand for and the needs for modern IT infrastructure grow, the “discretionary cash” may not be there. • This pushes CFOs, CAOs, CIOs, CTOs, CHCOS to think differently about IT infrastructure investments and ask the fundamental questions of who, what, where, when , and how? • It forces us to think less about equipment purchases and more about services. • It pushes us to think more creatively about addressing these complex problems holistically with our community of CFOs, CAOs, CIOs, CTOs, CHCOs. How can we change the existing infrastructure in place? • We need to rally around the problem and solve the problem together. • We need to move from the status-quo and deliver required capabilities which will prime the pump for the transactions and services required by the people, businesses, and industries of the nation. 6
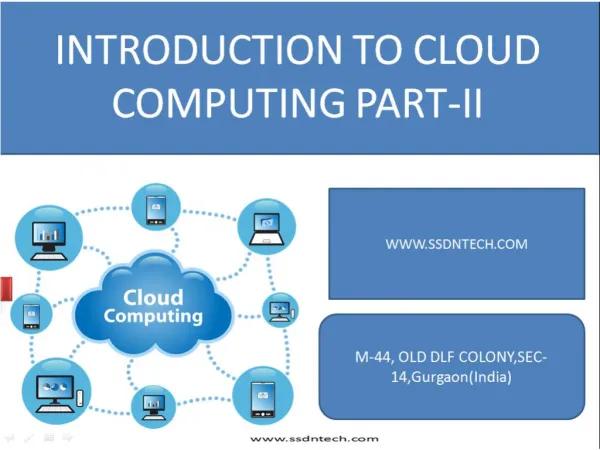
What is Cloud ComputingThe NIST Definition Cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. This cloud model promotes availability and is composed of five essential characteristics, three delivery models, and four deployment models”. NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, Draft version 14 http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/SNS/cloud-computing/index.html
What is Cloud ComputingThe NIST Definition (continued) • Deployment Models • Private Cloud • Community Cloud • Public Cloud • Hybrid Cloud • Delivery Models • Software as a Service (SaaS) • Platform as a Service (PaaS) • Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) • Five Characteristics: • On Demand Service • Ubiquitous Network Access • Location Independent Resource Pooling • Rapid Elasticity • Measured Service
What is Cloud Computing?Three Main Types of Services • Software as a Service (SaaS): Software deployment model whereby a provider licenses an application to customers for use as a service on demand • Platform as a service (PaaS): Optimized IT and developer tools offered through Platform as a Service (PaaS) for Database and Testing Environments • Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): On-demand, highly scalable Computing, Storage and Hosting Services • SaaS Examples: • Gov-Apps, Internet Services • Blogging/Surveys/Twitter, Social Networking • Information/Knowledge Sharing (Wiki) • Communication (e-mail), Collaboration (e-meeting) • Productivity Tools (office) • Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) • PaaS Examples: • Application Development, Data, Workflow, etc. • Security Services (Single Sign-On, Authentication, etc.) • Database Management • Directory Services • IaaS Examples: • Mainframes, Servers, Storage • IT Facilities/Hosting Services
The Different Types of Cloud Services Are Geared For Different Purposes SaaS PaaS IaaS
PRIVATE CLOUD Operated solely for an organization. Deployment Model Overview COMMUNITY CLOUD Shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns HYBRID CLOUD Composition of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability PUBLIC CLOUD Made available to the general public or a large industry group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services.
Selecting the Right Deployment Model Public / Outsourced Government Cloud Sourcing Models High Private Cloud Outsourced: Publically available Cloud Computing services offered through commercial sources that are dedicated and separate from the Public both physically and logically and must to remain within the U.S. borders to support heighted data security and privacy requirements. Access to these services are provided through a dedicated Government Intranet and is not accessible from the Public Internet. Private Government Cloud : The cloud infrastructure is operated solely for an organization. It may be managed by the organization or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise. Government Dedicated Intranet Private Outsourced Cloud Private Government Cloud Trust (Security and Data Privacy) Community Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is shared by several organizations and supports a specific community that has shared concerns (e.g., mission, security requirements, policy, and compliance considerations). It may be managed by the organizations or a third party and may exist on premise or off premise. Hybrid Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is a composition of two or more clouds (private, community, or public) that remain unique entities but are bound together by standardized or proprietary technology that enables data and application portability (e.g., cloud bursting). Public Cloud: The cloud infrastructure is made available to the general public or a large industry group and is owned by an organization selling cloud services. Community Cloud Public Cloud Hybrid Government Cloud Public Internet Low
Sample Services Per Deployment Model H Outsourced Private Cloud Internal Private Cloud Core Mission Applications Citizen Engagement (e.g. Virtual Town Hall) Business Services Applications Application Development &Testing Complexity & Cost Office Automation and Productivity Tools Data Dissemination (e.g. Data.gov) Internal Agency Web Portals Communications (Wikis, Blogs, Web Sites) Public Cloud Public-Private Cloud L H Security
Key Benefits • Significant Cost Reduction - Computing available at a fraction of the cost, eliminate upfront capital expenditures and dramatically reduce administrative burden on IT resources • Increased Flexibility - on-demand computing across technologies, business solutions and large ecosystems of providers, reducing time to implement new solutions from months to days • Elastic Scalability - scale up or down instantaneously based on actual consumption and pay for only what is used • Rich Business Tools - Unlock tools and capabilities offered within the industry that significantly increase time to market and offer rich functionality • Tap Free Market Innovation - expose Government Data and Applications to enable a 3rd Party open-source development community
Key Indicators for Cloud Computing Value Consider the benefits of Cloud Computing in a proposal when you see: Software or hardware migrations and upgrades (Email Migration) Projects that need to be deployed rapidly (Wikis, Blogs) Large capital infrastructure costs and low data sensitivity (Data Centers) Projects that need to scale massively up or down with demand (Tax season) Projects that require a great deal of Government IT infrastructure management New development for public or low data sensitivity projects (Web Presence) 19
Grab Bag of Cloud Related Terms may indicate a cloud solution 20
Deploying Cloud ServicesGovernment Considerations Government Considerations Security Cloud Delivery Models Interoperability & Portability • Software as a Service (SaaS) • Wikis, Blogs • CRM, Case Management, etc. • Office Productivity Systems Security Data Privacy Protection Compliance with FISMA (Federal Information Security Management Act) Public Cloud Private Cloud Hybrid Cloud Community Cloud Vendor Lock-in Integrating Multiple Clouds and Systems Moving Data & Apps In and Out of Clouds • Platform as a Service (PaaS) • Databases • Application Development & Testing Tools • Virtual Environments Cloud Services • Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) • Virtual Machines • Storage • Application hosting
Government Cloud Framework Customer / Account Mgmt User Tools User Profile Mgmt Software as a Service (SaaS) / Applications Application Integration User/ Admin Portal Reporting & Analytics Citizen Engagement Gov Productivity Gov Enterprise Apps Wikis / Blogs Email / IM Business Svcs Apps Order Mgmt Social Networking Virtual Desktop Core Mission Apps API’s Analytic Tools Agency Website Hosting Office Automation Legacy Apps (Mainframes) Trouble Mgmt Data Mgmt Workflow Engine Platform as a Service (PaaS) Reporting Cloud Services Database Testing Tools Developer Tools EAI Billing / Invoice Tracking Knowledge Mgmt DBMS Directory Services Mobile Device Integration Product Catalog Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) Data Migration Tools Storage Virtual Machines Web Servers Server Hosting CDN ETL Service Mgmt & Provisioning Service Provisioning SLA Mgmt Inventory Mgmt CoS/QoS Mgmt Utilization Monitoring App Perf Monitoring DR / Backup Operations Mgmt Security & Data Privacy Core Foundational Capabilities Authentication & Authorization Auditing & Accounting Data/Network Security Data Privacy Certification & Compliance Data Center Facilities Hosting Centers Routers / Firewalls LAN/WAN Internet Access
Technical Evolutionary Path • Complex Infrastructure Sprawl • IT Asset and Data Center Growth • Outdated Legacy System Tools • Inconsistent Processes • Soaring IT & Energy Costs • PhysicalConsolidation • Consolidate IT Assets and Data Centers • Standardize and Centralize Management • Streamline Processes, incorporating best practices (i.e. ITIL) • Energy Savings – Phase out inefficient hardware • Virtualization • Virtualize infrastructure, resulting in increased system utilization • Unify virtual & physical management • Promote resource sharing across the organization • Energy Savings – maximize effective usage. • Cloud • Service Oriented Architecture • On-demand provisioning of IT resources; Elastic scaling up and down • Dynamic Service Management • Energy Savings via automated workload distribution
Market Overview • SaaS Providers • Run on top of underlying cloud infrastructure platforms • CRM, ERP, VoIP, BI, supply chain • PaaS Providers • ERP,DB,XML files, flat files,web services, on-demand apps, SaaS hoster, API’s, • load balancing, DNS configuration, storage • IaaS Providers • Proxy for buying servers, software, data center space or network equipment • Pay for memory, bandwidth, storage consumed
Government Agencies are Already Experimenting with Cloud Services
A Sample of What Government Agencies Are Doing in Cloud Services
What will ultimately be delivered to users? Email, messaging apps, productivity tools = Software as a Service (SaaS) • Use cloud-based applications to enable improved productivity, cost reduction, and ubiquity of services • Example: web-based email solutions, allowing functionality such as web folders
Strategic Plan Cloud Computing Planning:Selecting Services Defines Organizational Goals and Mission Objectives Enterprise Architecture • Defines results-driven plan to achieve the Strategic Plan • EA should be services oriented – focusing on service reuse and information sharing • Should be FEA compliant to enable cross-agency analysis. Business SOA Service Component Data Technology SOI Performance Architecture Governance Architecture Management Governance Bodies Investment Management
IT Project Evaluation Criteria andCloud Computing Offers a Better Option IT Evaluation Criteria Cloud Computing Offers a Better Option
Lower Operational Costs Cloud Computing On Premise Development
Energy Savings Example • Current Data Center Statistics • The Government possesses data centers housing over 150,000 servers • Data centers used 61 billion kWh of electricity in 2006, representing 1.5% of all U.S. electricity consumption and double the amount consumed in 2000 • Based on current trends, energy consumed by data centers will continue to grow by 12% per year • The average utilization rate for servers ranges from 5% to 15%. • Many agencies are paying the energy costs to run data centers at 100% capacity. • Potential Savings • An EPA report to Congress estimated that if state-of-the-art technology were adopted then energy efficiency could be improved by as much as 70%. • Saving a modest 10%of total energy use would amount to energy savings of 10.7 billion kilowatt-hours per year -- an amount equivalent to the electricity consumed by one million US households and valued at about $740 million. State of the Art Technology = Virtualized Storage Services obtained through Cloud Computing
Phased Approach to Implementing Cloud Services Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Target Apps Light-weight collaboration & productivity tools and basic infrastructure / platform Rich productivity tools, enhanced platform capabilities Enterprise Applications in the cloud and integration services Target Availability Nov/Dec 2009 2Q 2010 4Q 2010 Cloud Delivery Models Commercially Available Public Clouds Public and Outsourced Private Clouds Private and Hybrid Clouds Procurement Strategy Advantage, BPA Smart-Buy, BPA, Directed RFP Smart-Buy, BPA, Directed RFP Security Low and Medium Impact FISMA Security Low , Medium an d High Impact FISMA Security Low-Impact FISMA Security
Phased Approach to Deploying Cloud Services Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 (Low Security, commercially available applications / services for Public Cloud models ) (Enhanced Security Options, Some Customized services for the Government and support for Public, Private and Hybrid Models) (High Security Options, Interoperability standards and Support for Hybrid and Community Models) Gov Productivity – Office Automation Gov Enterprise Apps Software as a Service Commercial SaaS Products via Storefront Gov Productivity - Email Citizen Engagement – Participatory Legislation Citizen Engagement - Wikis, Blogs &Town-Halls Data as a Service Directory as a Services Platform as a Service Content Mgmt Services Database as a Service App Development & Test Environments and Tools Storage as a Service Infrastructure as a Service Web Hosting Services Storage Computation (CPU) Time
IaaS RFQ RFQ IaaS Services • RFQ Released for IaaS on July 31st • Focus Low-Impact Security • Requirements Based on NIST Definition for Cloud Storage Virtual Machines Server Hosting • Online Web Based Storage • Store Files & Data Objects • Online VMs / Computing • Multiple CPU & OS Types • Online Server Hosting • DNS and CDN Capabilities On-demand Self Service Online, self service provisioning capabilities for services Ubiquitous Network Access Accessible via the Internet with a sufficiently robust architecture Location Independent Resource Pooling Massively scalable services, independent of location of resources NIST Definition for Cloud Services Rapid Elasticity Scale up or down dynamically based on consumption and/or request Measured Service Utilization and consumption GUI dashboard and electronic interfaces
Cloud Storefront Simplify the customer experience – web application “storefront” • Agencies identify their infrastructure and web application requirements using a menu-type screen • Payment is by credit card or requisition • Delivery of a secure environment supported by the selected applications • Cloud Storefront: • Web based user interface for acquiring Cloud Services • Front-end user interface based on simple commercial Cloud models • Provides access to service agreements negotiated by GSA for free Social Media • One-stop shop site for agencies to request services, make selection from several vendor options, resulting in auto-provisioned fully functional services
Additional PMO Activities Refining the Federal Cloud Computing Concept of Operations and Transition Strategy Plan Market Research Agency Cloud Computing Initiative Research/ Knowledge Sharing Development of a Federal-wide C&A Process
Cloud Computing Deployment is Possible Only Through Effective Planning • Driven By: • Strategic Goals • Mission Objectives • Business Need
Putting Effective IT Planning into Practice IT Operations EA Do not use Enterprise Architecture as a compliance or reporting exercise. Use it as a management tool to achieve true business transformation. Build a bridge between EA and IT Operations, fostering continuous collaboration. Use EA analysis to drive the Capital Planning process by making specific investment recommendations that will result in cost savings and performance improvements.
Federal Cloud Computing Governance Structure CIO Council • Strategic Objective Definition • Overall Guidance • Adjudication PMO (GSA) Cloud Computing Executive Steering Committee (ESC) • Day to Day Management of the Federal Cloud Computing Initiative • Development of required deliverables • Provide Technical Guidance and Subject Matter Expertise • Strategic Direction • Priority Setting • Issue Resolution • Approval Cloud Computing Advisory Council (AC) • Provide Collaborate Federal Agency Input and Feedback for Cloud Computing Initiatives/Deliverables • Support the PMO and Cloud Copmuting Subcommittee with Federal Subject Matter Expertise • Approve Cloud Computing deliverables for submission to the Cloud Computing ESC • Cross-Functional Collaboration