FRACTIONS
90 likes | 112 Views
Learn the basics of fractions, from numerators to denominators, how to compare, add, subtract, multiply, and divide fractions effectively. Master equivalent fractions and simplify calculations with practical examples.

FRACTIONS
E N D
Presentation Transcript
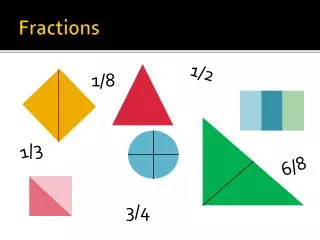
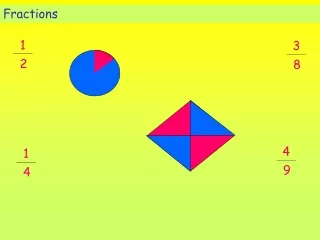
FRACTIONS Fractions consist of two numbers. The top number is called the numerator. The bottom number is called the denominator. numerator denominator • The NUMERATOR tells how many fractional pieces there are. The fraction 3/8 indicates that there are three pieces. • The DENOMINATOR of a fraction tells how many pieces an object was divided into. The fraction 3/8 indicates that the whole object was divided into 8 pieces.
Comparing Fractions with Different Denominators • If the numerators of two fractions are the same, the fraction with the smaller denominator is the larger fraction. For example: 5/8 is larger than 5/16 because each fraction says there are five pieces but if an object is divided into 8 pieces, each piece will be larger than if the object were divided into 16 pieces. • But if the numerators are not the same,you must obtain equivalent fractions with the same denominator to compair them.
Equivalent Fractions • Equivalent fractions are fractions that have the same value or represent the same part of an object. Examples:If a pie is cut into two pieces, each piece is also one-half of the pie. If a pie is cut into 4 pieces, then two pieces represent the same amount of pie that 1/2 did. We say that 1/2 is equivalent to 2/4. • To obtain equivalent fractions you just have tu multiply numerator and denominator by the same number or divide both by a factor of them. • To determine if two Fractions are equivalent you must compare this two products. the numerator of the fist fraction multiply by the demoniator of the second. and numerator of the second fraction by the demoniator of the first. If this two products are iquals, these two fractions are equivalents.
Adding Fractions with the Same Denominator To add (or subtract) two fractions with the same denominator, add the numerators and place that sum over the common denominator.
Adding(or Subtracting) Fractions with Different Denominators • Find the Least Common Denominator (LCD) of the fractions • Rename the fractions to have the LCD • Add the numerators of the fractions • Simplify the Fraction Example: Find the Sum of 2/9 and 3/12 • Rename the fractions to use the Least Common Denominator (2/9=8/36, 3/12=9/36) • The result is 2/9 +3/12 =8/36 + 9/36 • Add the numerators and put the sum over the LCD 2/9 and 3/12= 17/36 • Simplify the fraction if possible. In this case it is not possible
Multiplying Fractions • Multiply the numerators of the fractions • Multiply the denominators of the fractions • Place the product of the numerators over the product of the denominators • Simplify the Fraction • Example:
Dividing Fractions by Fractions • Invert (i.e. turn over) the denominator fraction and multiply the fractions • Multiply the numerators of the fractions • Multiply the denominators of the fractions • Place the product of the numerators over the product of the denominators • Simplify the Fraction • Example:
What must we do first? First: The Parenthesis Second: The Products and the Divisions. Starting from the left if there are more than one. (Example: ) Third: Adds and Subtractions