Unveiling the Cell's Command Center: The Nucleus and Its Intricacies
140 likes | 220 Views
Discover the nucleus, the powerhouse of the cell housing genetic material, nucleoli, nuclear envelope, and genes, pivotal in cell activity. Delve into genomics and the Human Genome Project. Uncover the significance of nuclear structures, such as the nucleus's role, its composition, and variations in cells.

Unveiling the Cell's Command Center: The Nucleus and Its Intricacies
E N D
Presentation Transcript
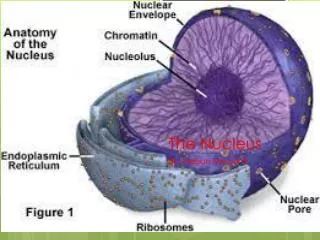
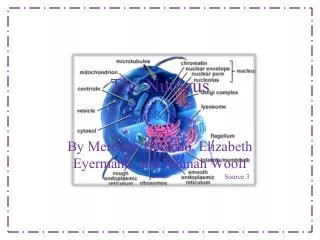
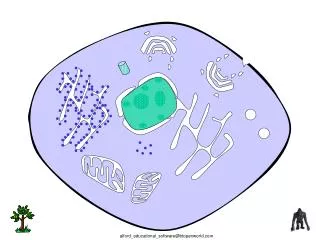
Spherical or Oval Structure • Usually most predominant structure in a cell • Most cells have a single nucleus • Mature RBCs – no nuclesu • Skeletal Muscle – multinucleated
Nuclear Envelope • Double Membrane • Lipid Bilayers • Separates the Nucleus from the Cytoplasm • Outer membrane is continuous with the Rough ER
Nuclear Pores • Openings in the nuclear envelope • Control movement of substances between the nucleus and cytoplasm
Nucleoli • Cluster of protein, DNA and RNA • Found within the nucleus • Site of ribosome production • Cells that produce large amounts of protein have very predominant nucleoli
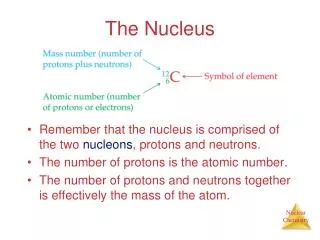
Genes • Heredity Units • Control cell structure and direct cell activity • Arranged in single file on chromosomes • Humans cells have 46 chromosomes • Appear as thin threads called chromatin when the cell isn’t dividing
Genome • The total genetic information carried in a cell or organism • Genomics – the study of the genome and the biological functions of the organism
Human Genome Project • Began in 1990 in an effort to sequence all 3.2 billion (BILLION!) nucleotides of the human genome.
Checkpoint • Describe the function of the nucleus • What are the structures that compose the nucleus? • Do all cells have a single nucleus?