Optimization of ICP Using K-D Tree
240 likes | 478 Views
Optimization of ICP Using K-D Tree. Baochun Bai Instructor: Prof. Boulanger. Outline. An Introduction to ICP Algorithm Steps KD-Tree Method to compute rotation and translation matrix Results. Overview of ICP Algorithm. A popular algorithm to register a data shape to a model shape

Optimization of ICP Using K-D Tree
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Optimization of ICP Using K-D Tree Baochun Bai Instructor: Prof. Boulanger
Outline • An Introduction to ICP • Algorithm Steps • KD-Tree • Method to compute rotation and translation matrix • Results
Overview of ICP Algorithm • A popular algorithm to register a data shape to a model shape • Data shape point set P{pi} with Np points • Model shape point set X{xi} with Nx points • Find the optimal rotation R and translation matrix T to transform P to X • Minimize the mean square error
Algorithm Steps of ICP • Initialize P0 = P, R0 = I, T0 = (0, 0, 0) • For each iteration k, • Find the closest points Yk = C(Pk, X) based on Euclidean distance • Compute the registration and find rotation matrix Rk and translation matrix Tk • Apply the registration, Pk+1 = Rk(Pk) + Tk • Stop if mean square error is less than a threshold
Nearest Neighbor Search Algorithms • Performance bottleneck of the algorithm • Straightforward Approach • Sequential Search • O(NpNx), Np <= Nx, O(N2) • K-D Tree • A binary search tree • O(logN)
K-D Tree • A balanced binary search tree for k-dimensional data • Root node: entire space • Leaf node: a mutually exclusive subspace • Intermediate node: key to partition the space, key is one of k dimensions
Algorithm to Compute Rotation and Translation Matrix • Compute the cross-covariance matrix of P and X • Compute the 4x4 symmetric matrix Q
Algorithm to Compute Rotation and Translation Matrix • Get the unit eigenvector qR of Q, which is corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue of Q • Compute the rotation matrix R from qR • Compute the translation matrix T based on R • T = ux - Rup
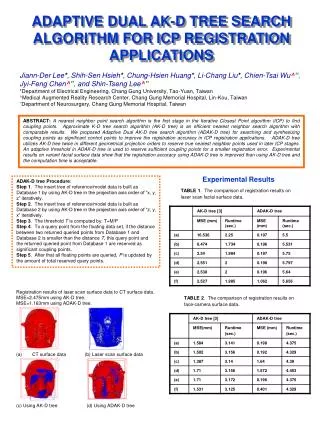
Results • Running Time • Bunny Model • 31000 points • 601MHZ, 128Mb Memory