Exploring Areas of Polygons: Trapezoids, Triangles, and Regular Shapes
130 likes | 253 Views
This resource covers multiple exercises focused on calculating the areas of various geometric shapes, including trapezoids, equilateral triangles, isosceles trapezoids, and rhombuses. It also introduces the concept of regular polygons and their properties, such as apothems and perimeter, using real-life applications like kaleidoscopes to visualize these shapes inscribed within circles. A step-by-step approach to solve problems, including determining heights, perimeters, and areas based on given dimensions, is featured for both learners and educators.

Exploring Areas of Polygons: Trapezoids, Triangles, and Regular Shapes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
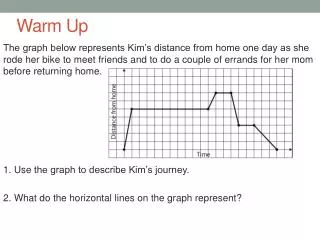
WARM UP • Find the area of a trapezoid with bases 8 and 11 and a height of 7.5. • Find the area of an equilateral triangle with sides 8ft. • An isosceles trapezoid has bases 12 and 28. The area is 300. Find the height and the perimeter. • Find the area of a rhombus with a 120o angle and sides of 6 cm.
Section 11.4 AREAS of REGULAR POLYGONS
Regular Polygons • Think of a kaleidoscope. • The body of a kaleidoscope is a tube and therefore the images always look inscribed in a circle. • You can inscribe any regular polygon into a circle.
What is a regular polygon? • A regular polygon is a polygon with all equal sides and angles.
Inscribe a Regular Polygon into a Circle 90o 45o Center Radius Central Angle Apothem 60o
APOTHEM • The apothem is the perpendicular distance from the center of the polygon to the side. APOTHEM
AREA of a REGULAR POLYGON • Area = one half of the apothem and the perimeter. A= ½ ap Perimeter AREA Apothem
SIMPLE • Find the area a regular octagon with side 5 and apothem 3. 5 5 5 A= ½ ap 5 5 A= ½ (3)p A= ½ (3)(40) 3 5 5 P = 5(8) A= 60 5 P = 40
MEDIUM 1) Find the area of a regular hexagon with apothem 9 and side length of A= ½ ap A= ½ (9)p 9
TOUGH 3) Find the area an equilateral triangle with radius 16. A= ½ ap 60o A= ½ (8)p 16 60o 8 60o 30o
REAL TOUGH 4) Find the area a regular hexagon with a side of A= ½ ap 30o 60o 120o
PRACTICE • Page 442 • # 2 - 8 • Classroom Exercises • Draw Diagrams