Influence of Climate on Soil Formation Processes in Different Landscapes
200 likes | 222 Views
Explore how climate affects the transformations of organic matter, clay, and ions in soil, leading to variations in depth, composition, and structure. Discover the impact of vegetation and topography on soil development in diverse environments.

Influence of Climate on Soil Formation Processes in Different Landscapes
E N D
Presentation Transcript
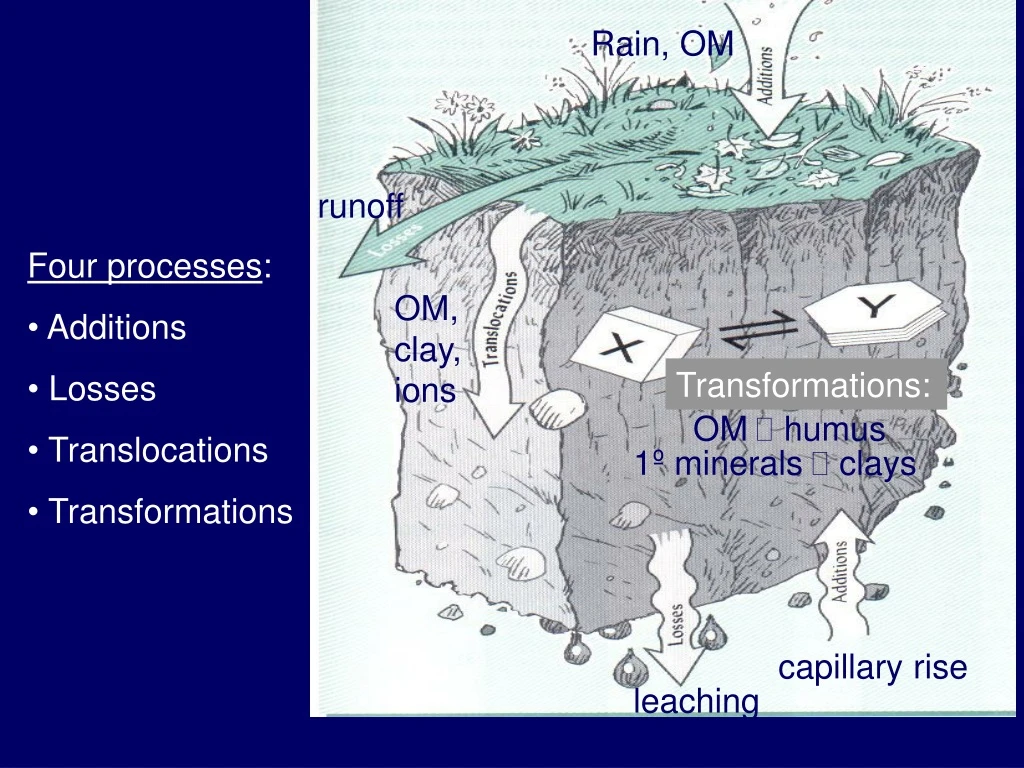
Rain, OM runoff OM humus 1º minerals clays capillary rise leaching • Four processes: • Additions • Losses • Translocations • Transformations OM, clay, ions Transformations:
Influence of climate on Carbonate Layer Depth Depth i.e., near surface
A A Bw R 40cm 60cm Cr limestone wet climate Effect of Climate on Soil Formation limestone dry climate note depths of these profiles
ppt T
Organisms / Climate influences on soil formation Feb 18, 2002
Effect of Vegetation on SOM High High Low Rapid Rapid Slow No Seasonal Yes SOM = soil organic matter
Temperate Deciduous Forest Grassland Organic matter Organic layer Leached zone Weathered PM Blocky structure CaCO3 Clays, oxides Unweathered bedrock Unweathered loess Time Time Effect of Vegetation on Development Soil Samples!
Temperate Deciduous Forest Organic layer Leached zone Weathered PM Clays, oxides Unweathered bedrock Time Effect of Vegetation on Development Ultisol Sample!
Grassland Organic matter Blocky structure CaCO3 Unweathered loess Time Effect of Vegetation on Development Meadow Soil Sample!
Topography as an Influence on Soil Formation • Relief • Aspect • Elevation (steep vs. flat) (N,S,E,W) (link to climate, organisms) Trinity Alps Wilderness Area Northern California
Landscape positions Footslope Toeslope Figure 2.13 Brady & Weil
Effect of topography on soil formation Summit Backslope Toeslope
1.5 lowest 5.5 highest 4.0 3.0 4.5 6 lowest 25 highest 15 10 18 si c l Most clay si c l Most clay si l l si l Effect of Topography on Soils E. Colorado; grassland; limestone pH 7.0 7.2
A A A Bw E C 1m >1m 15m Bt C C Mature Young Parent material Very mature Effect of time on soil development C
A 10cm A Bt1 80cm C Bt2 C Modern floodplain Higher terraces Time • both formed in alluvium from mixed sources • similar topography
Effect of Time on Soils Primary: quartz, feldspar, etc. Secondary: smectites, illite, etc. low high low high
Factors That Retard Soil Development • Low rainfall and RH • Cold temperatures • High water table • Parent materials that are mostly quartz • Very high clay content • Presence of substances toxic to plants • Very steep slopes erosion • Disturbance frequency – e.g. fire
Soil Orders Study Guide Saved as a separate file on-line