2-1 Patterns and Inductive Reasoning
170 likes | 357 Views
2-1 Patterns and Inductive Reasoning. Learning Goals 1. To be able to define and use inductive reasoning to form conjectures. If you go to a restaurant several times and the food tastes good, what could you conclude about the food when you go again?.

2-1 Patterns and Inductive Reasoning
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Learning Goals1. To be able to define and use inductive reasoning to form conjectures.
If you go to a restaurant several times and the food tastes good, what could you conclude about the food when you go again?
If you go to a restaurant several times and the food tastes good, what could you conclude about the food when you go again? The food will taste good.
CounterexampleAn example that shows the conjecture is false.
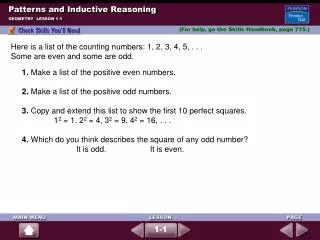
Given: x ● x = 9 Write a conjecture. (remember, a conjecture is an educated guess)
Given: x ● x = 9 Conjecture: x must equal 3
Given: x ● x = 9 Conjecture: x must equal 3 Is the conjecture true or false?
Given: x ● x = 9 Conjecture: x must equal 3 False
Given: x ● x = 9 Conjecture: x must equal 3 Is the conjecture true or false? x could = -3
Example 2Based on the given information, is the conjecture true or false.If false, give a counterexample.
Given: Solomon is a person.Conjecture: Solomon is a woman.FalseCounterexample:
Given: Solomon is a person.Conjecture: Solomon is a woman.FalseCounterexample: Solomon could be a man.