HERANÇA MITOCONDRIAL
391 likes | 1.51k Views
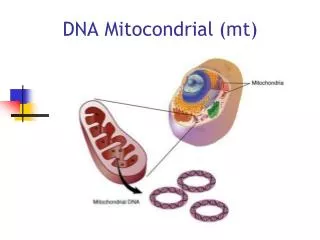
HERANÇA MITOCONDRIAL. A MITOCONDRIA. Glicose Responsável pela energia celular Possui seu próprio DNA mtDNA Local de várias rotas metabólicas. Espaço intermembranas. Matriz: diversas proteínas e ciclo de Krebs e o mtDNA. Membrana interna: CRM. Membrana externa. crista.

HERANÇA MITOCONDRIAL
E N D
Presentation Transcript
A MITOCONDRIA • Glicose • Responsável pela energia celular • Possui seu próprio DNA mtDNA • Local de várias rotas metabólicas Espaço intermembranas Matriz:diversas proteínas e ciclo de Krebs e o mtDNA Membrana interna:CRM Membrana externa crista
A herança materna: Cada célula humana contém 100 mitocôndrias e cada uma contém 2 a 10 cópias de mtDNA
AS DOENÇAS MITOCONDRIAIS Patologias de expressão clínica heterogênea caracterizadas por uma disfunção na produção de energia CERÉBRO MÚSCULO CORAÇÃO MULTISSISTÊMICAS
ENCEFALOPATIA CONVULSÕES RETINITE PIGMENTAR DEMÊNCIA DEPRESSÃO ATAXIA ENXAQUECA AVC SURDEZ NEUROSSENSORIAL CARDIOMIOPATIA HIPERTRÓFICA OU DILATADA DEFEITO DE CONDUÇÃO CARDÍACO ALT. TIREÓIDE DIABETE MELITUS BAIXA ESTATURA ALTERAÇÕES NA FIBRA MUSCULAR FRAQUEZA FADIGA INTOLERÂNCIA AO EXERCÍCIO NEUROPATIA PERIFÉRICA INSUF. HEPATICA TUBULOPATIA RENAL INSUF. MEDULA ÓSSEA MIOPATIA
Neuropatia óptica hereditária de Leber (LHON) • Rápida perda da visão de campo central • Morte do nervo óptico • Início na 3ª década • Disritmia cardíaca
MERRF-Epilepsia Mioclônica com Fibras Rotas Vermelhas (RRF) • Epilepsia • Demência • Ataxia ( mov. muscular descoordenado) • miopatia
MELAS- Miopatia, Encefalopatia, Acidose Lática e Episódios de Acidente Vascular Cerebral
1 – 2%dos portadores de diabetes mellitus apresentam a mutação MELAS
KSS - Síndrome de Kearns Sayre • oftalmoplegia (paralisia dos músculos do olho) • demência e ataques • alterações cardíacas