Maximal Isometric Strength Differences in Quadriceps of MS Patients
10 likes | 135 Views
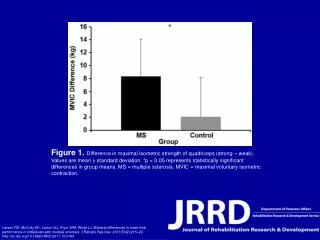
This study investigates the differences in maximal isometric strength of the quadriceps between strong and weak individuals living with multiple sclerosis (MS). Results, presented as mean ± standard deviation, indicate statistically significant differences in group means (p < 0.05). The findings emphasize the importance of understanding bilateral differences in lower limb performance in individuals with MS, providing insights for rehabilitation strategies. The research was published in the Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development and explores the implications of muscle strength on mobility in MS patients.

Maximal Isometric Strength Differences in Quadriceps of MS Patients
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Figure 1. Difference in maximal isometric strength of quadriceps (strong – weak). Values are mean ± standard deviation. *p < 0.05 represents statistically significant differences in group means. MS = multiple sclerosis, MVIC = maximal voluntary isometric contraction. Larson RD, McCully KK, Larson DJ, Pryor WM, White LJ. Bilateral differences in lower-limb performance in individuals with multiple sclerosis. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2013;50(2):215–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1682/JRRD.2011.10.0189