Federalism A
300 likes | 321 Views
Federalism A. Seating Arrangement. Find your desk based on the card you were given. U.S. Constitution Quiz. Tell how long it took you to complete the Constitution Packet. Today we will …. Agenda: Quiz Comparative Constitutions Designing a Gov questionnaire Federalism Defined

Federalism A
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Seating Arrangement Find your desk based on the card you were given.
U.S. Constitution Quiz Tell how long it took you to complete the Constitution Packet
Today we will …. Agenda: • Quiz • Comparative Constitutions • Designing a Gov questionnaire • Federalism Defined • Comparative Systems • Supreme Course Briefs Objectives: • Compare Constitutional principles of the AP6. • Distinguish between federal enumerated, federal implied, state reserved and powers denied to both in the U.S. Federal system. • Identify tension inherent in federalism as illustrated in SC cases.
Clarifications… • Direct representation is done by the people through elections to enact their will. Indirect representation is where the people's will is interpreted by elected officials and they vote the way they feel the people wish. • Habeus corpus - Latin for "that you have the body." A writ of habeas corpus is used to bring a prisoner or other detainee before the court to determine if the person's imprisonment or detention is lawful. • U.S. Senate: Reference Home > Frequently Asked Questions about a New Congress
Federalism The Grasshopper and Ant explain federalism - YouTube What is it? What must the Federal government provide for the people and the states? (enumerated & implied) What powers are reserved to the states? What are guarantees that states have to give to other states? What powers are denied to both?
What is Federalism? Federalism is a political system where local units of government, as well as the national government, can all make final decisions with respect to some governmental action
Original Division of Power Power was divided between Nation & states … • Enumerated Powers (exercised by National government) & Supremacy Clause • Reserved Powers for states • Provisions giving states role in the composition of the National government • Powers Denied to Both
Federal Government Guarantees • “republican form of government” • Protection against foreign invasion • Protection against domestic insurrection, if requested
Positive and Negative Aspects of Federalism Positive Negative States block action Prevent progress Upset national plans/ policy Protect powerful local interests Cater to self-interest of “hack” politicians Perpetuate racism • Governmental strength, political flexibility, individual liberty is protected • Regions can begin progressive policies - may gain national support • Larger political unit - less likely to be dominated by a single political faction
Enumerated & Implied Powers of the Fed • Enumerated • Article I, Section 8 17 specific grants of power • Implied • “Necessary & Proper” Clause • Power “to make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States or in any department or officer thereof.” • Ex: Military draft, minimum wage
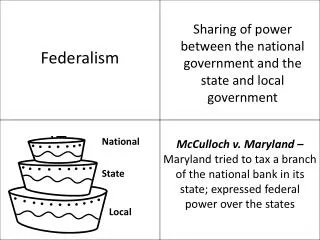
The Supremacy Clause Where is it ?? TheConstitution is the supreme law of the land. If a state law or constitution contradicts a constitutional federal law, state judges are required to uphold the federal law & overturn the state law. McCulloch v Maryland & Gibbons v Ogden
Principle of Nullification • States have the right to declare null and void a federal law that they believe violated the Constitution • Virginia Kentucky Resolutions • Civil War ended idea of nullification. Some scholars claim Civil War was fought for state’s rights.
Check for Understanding • Look back through your notes, which federal powers do you view as a for federalism? • Which powers/principles do you view as for federalism?
Powers Denied to the States To Abridge Individual Rights To Coin Money To Enter into Treaties w/ Foreign Nations To Interfere w/ “obligations of contracts” To Levy Taxes on Imports & Exports To Engage in War
How should states deal with each other? • Full Faith and Credit • Privileges and immunities??? • Extradition (Article IV, Sec. 2)
States’ Role in National Government Apportionment of the House of Representatives & # of Reps State Legislatures’ draw House Districts Equal Senate representation Electoral College Ratification of proposed Amendments
Powers Reserved to the States 10th Amendment: “the powers not delegated to the United States … are reserved to the states respectively, or to the people.” • Property & Contract Law • Criminal Law • Marriage & Divorce • Provision of Education, Highways, & Social Welfare • Organization & Power of Local Governments • Concurrent Power to Tax & Spend
Powers Denied to Both To Deny “Full Faith & Credit” To Deny “Privileges & Immunities” To Refuse “Interstate Rendition” To Enforce Bills of Attainder To Pass Ex Post Facto Laws To Suspend Habeas Corpus Grant titles of nobility
Check for Understanding • Look back through your notes, which federal powers do you view as a for federalism? • Which powers/principles do you view as for federalism?
Federal vs. Unitary Federal Unitary Iran UK China • Mexico • Russia • Nigeria
Federal v Unitary System • What are the benefits and challenges of a federal versus a unitary government? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OsAU_nO7s2Q
Unitary: High level of centralization • Benefit: Uniformity in laws • Weakness: disregard local differences/ needs • Federalism: Medium level of centralization • Benefit? • Weakness?
China - Unitary • The majority of power is in the party, which controls the National government. • Gov. was originally based on the idea of Democratic Centralism, but becoming more federal in recent years • To increase accountability of local leaders • Legitimacy • SEZ: Special Economic Zones opened to foreign investment • 22 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, 4 centrally administrated municipalities and 2 special admin regions (Hong Kong and Macao)
Russia: Asymmetrical Federalism • Federal-Some regions are stronger than others, so power is Devolved Unequally across the Country (asymmetric federalism). • Central government chooses regional governors, governors choose representatives in the upper house • Current regime contains 89 regions/ republics • 6 levels of autonomy
Supreme Court Cases Check for Understanding • What provisions of the Constitution has the federal government used to increase it’s power?
Federalism CLOSURE • 3: Limits on government in the Constitution • 2: Powers the Federal government has. • 1: Question or Comment. • Federalism B Questions • Federalism in Legislation - review laws to prepare for activity next block • Next Block: Quiz on Federalism A & B