Development of Multichannel Adaptive Information Systems for Enhanced User Experiences
320 likes | 433 Views
This project focuses on the development of Multichannel Adaptive Information Systems (MAIS) aimed at improving e-service access and enhancing user adaptability across various platforms. Key objectives include creating methods, models, and architectures that facilitate mobile, web, and client-server service provisioning while considering device capabilities, network conditions, and user context. Ongoing research explores adaptive orchestration, service quality negotiation, and reflective architecture to achieve better service delivery, specifically in sectors such as tourism, e-learning, and risk management.

Development of Multichannel Adaptive Information Systems for Enhanced User Experiences
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MAIS Project:Multichannel Adaptive Information Systems Barbara Pernici, Politecnico di Milano
Outline • Multichannel Adaptive IS • MAIS goals • MAIS Architecture • Research problems • Results and ongoing research
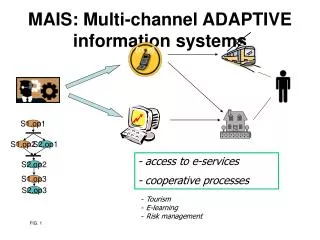
MAIS: Multi-channel ADAPTIVE information systems S1.op1 S1.op2 S2.op1 S2.op2 S1.op3 S2.op3 - access to e-services - cooperative processes • Tourism • E-learning • Risk management
MAIS goals • Develop methods, models, and architectures for multichannel adaptive information systems • Multichannel • Mobile information systems • Service provisioning: web, e-mail, sms, client-server • Heterogeneity, dynamic evolution of channels • Device characteristics • Network connections • Adaptation to context • User model • Service provisioning • Channel of invocation, QoS • Hardware: low power consumption processors, VSBD CHANNEL MODEL, USER MODEL
MAIS general architecture Adaptation E-Service rules composition E-service composition platform E-service registry Definitions of Interaction enabling platform Quality levels Adaptive channel Context Manager Context description User access E-service providers i M a c User and serviceprofile, recommender E-service retrieval, negotiation, and composition Reflective architecture Network and device adaptivity, very small databases
Research focus ADAPTIVITY • Adaptive orchestration of e-services • Reflexive architecture for context-aware services • Adaptive networks • Low power consumption processors • Methods and tools for multichannel interface design and integration • Application areas: e-learning, tourism, emergency teams
Service-oriented paradigm Query Publish Interact Registry Discovery Agency ServiceSpecification ServiceSpecification ServiceRequestor ServiceProvider Service Request Response Requirements Requirements
MAIS Service request model Profile 1..n User 1..n Profile Preference 1 Activity Generic Expertise Role Preference Request 1 USER MODEL 1..n requests 1..n EService Actor 1..n 1..n 1..n Quality t n Level e r r n i u s c i is in Channel Context 1 1..n 1 1..n 1..n Application 1..n 1 1..n 1..n Channel Context Time Zone Protocol 1..n 1 1 Network 1 1 1..n 1..n Device Location Property Network 1..n Interface 1..n 1..n 1..n 0..n 0..n 1 1 Geo CPU Memory Display Town Position 1..n 1..n 1..n 0..n 0..n Input Operating Application Device System District Country
Service invocation S1.op1 S1.op2 S2.op1 S2.op2 S1.op3 S2.op3 Services PROCESS op1 S1 op2 op3 op1 S2 op2 Abstract and concrete e-services op3
Registry: MAIS E-service ontology Abstract Service level E-Service Ontology QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS QoS
Research problems • Dynamic selection of services • On the basis of • quality parameters • user request and user profile • Context • When • Preselection • For each process instance • For each operation • Negotiation (quality levels, price) • Substitution • Dynamic process evolution
MAIS services orchestration MAIS functional architecture
MAIS adaptive e-service architecture E-Service Composition Platform Orchestration Chooses the best e-service according to user request Invokes the choosen service Architectural strategies MAIS reflective architecture
General Architecture Interaction Enabling Platform chooses the best n-ple for service delivering determines QoS levels acceptable for the user translates logical constraints in technological ones merges service/user/context constraints
General Architecture Reflective Platform Works on a given n-ple Receives as input the acceptable QoS levels with their constraints Monitors the channel during service provisioning Attempts a channel adaptation trying to change the real values
MAIS reflective architecture – classes (2) F. Tisato et al., Univ. Milano Bicocca
Knowledge vs. Guess F. Tisato et al., Univ. Milano Bicocca
Quality in Multi-channel ADAPTIVE information systems QoS Accepted quality threshold t Quality dimensions? (225 in MAIS documents…) PoliMI, Univ. Milano Bicocca, Univ. Roma 1
QoS classification based on negotiation perspective QoS Provider side – non negotiable Negotiable Internal resources quality dimensions Quality dimensions related to external resources Provider side negotiable User side negotiable Each provider community defines its Quality dimensions and levels Technical characteristics User profile
The MAIS quality model Service Provider • VideoOnDemand • Service Community • QoSspec = • <framerate, [5fps..40fps]> • <colordepth, [2bit..24 bit]> • <resolution, [320×200; 800×600; 1024×768]> • Quality rules • FR * CD * RES = K * BD MAIS quality model Users Network Provider Device Provider Video On Demand Services Object network device • QoSobj = <framerate, [5fps..30fps]> • <colordepth, [2bit..24 bit]> • <resolution, [320×200; 800×600]> • FR * CD * RES = K * BD • QoE = <framerate, [5fps..20fps]> • <colordepth, [2bit..16 bit]> • <resolution, [800×600]>
Service user environment • Multichannel provisioning (WebML to M3L, WML, HTML) • Interface generation (access to information) • Special usage contexts • Text simplification • Bliss language • Vocal interaction Polimi, Engineering, CEFRIEL, ISUFI-Lecce, IFAC-CNR, Roma 1, Roma 3, Engineering
Application domain: e-learning HOC Lab, Politecnico di Milano
Application domain: E-learning BLISS PCS Translation Symbolic language Complex text Gulpease index By hand Text simplifier Sentence complexity analyzer Classifies into Simple text Input text Word by word Text simplifier Syntactic based Shallow parser Very simple text Disability lab, Politecnico di Milano
Application domain: Risk management Mobile camp Ad hoc network Central administration PoliMi and CEFRIEL
References • MAIS web site: http://www.mais-project.it • Contact: barbara.pernici@polimi.it IFIP TC8 Conference on Mobile Information Systems Oslo, September 15-17, 2004
MAIS Project • Multichannel adaptive IS • Italian Research Project (2002-2005) • Partners: • 6 universities • Politecnico di Milano (coordinator) • University Milano Bicocca • University of Roma La Sapeinza • University of Roma Tre • University of Lecce – ISUFI • University of Brescia • 2 research centers • CEFRIEL • IFAC-CNR • 2 companies • ST Microelectronics • Engineering
Quality model: Objects and actors Communities define quality dimensions Service providers Network providers Users Device providers Services networks devices
Multichannel provisioning Code generation
Other research areas: MAIS adaptive procssors • Parallelism in VLIW processors • Jump prediction in VLIW • Security processing • Wireless protocols power consumption Hardware design group, PoliMI, ST Microelectronics
Other research areas: VSDB design • For small devices • Storages technologies • View design • View concretization Bolchini, Tanca, Schreiber, PoliMI