Ecosystem Productivity
180 likes | 888 Views
Learn about primary productivity, factors influencing it, trophic levels, biomass, and energy flow within ecosystems. Understand how human activities disrupt food chains and webs. Practice calculations and grasp ecological concepts.

Ecosystem Productivity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Students will be able to… • Discuss trophic levels and energy flow in ecosystems
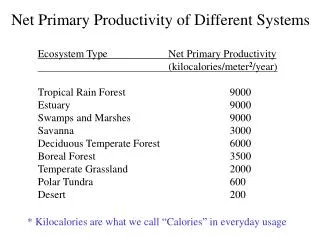
Primary Productivity • The rate at which producers capture & store energy in their tissues • Gross = total • Net = after respiration • The most productive ecosystems in the world • Estuaries, swamps, marshes, tropical rain forest, and temperate forests
Factors Influencing Primary Productivity • Climate & nutrients • Morphology & Size of organism • Rainfall • Temperature • Season • Soil (mineral & nutrient availability)
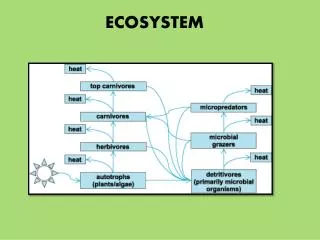
Pathways of Energy Flow • Energy from primary productivity can flow through 2 categories of food webs • Grazing food webs • Producer Primary consumer Secondary consumer tertiary consumer… • Detrital food webs • Energy flows from producers to detrivores & decomposers
How do people disrupt the flow of food chains and webs? • Clearing habitat for urban/industrial/farm development • Introducing (accidentally or intentionally) invasive, nonnative organisms, and chemicals from industry and agriculture • Plastic waste in ocean gets consumed by fish which in turn get consumed by baby seabirds, baby seabirds cannot pass or digest the plastic so they die.
Trophic Levels • Feeding levels with respect to primary source of energy • Producers & consumers each occupy a different trophic level • Energy is lost at each level • Only 10% move on (ecological rule of thumb)
Can there be more than 4 trophic levels in an ecosystem? • Yes • but this doesn’t occur often (more than five trophic levels would be even more uncommon) because of the amount of energy that is lost by the time the tertiary consumer is reached.
Biomass • The total weight of all living organisms • Biomass at each trophic level biomass pyramid 1.5 Biomass pyramid (grams/m2) Top carnivores 11 Primary carnivores 37 Herbivores 809 Detrivores/ decomposers Producers 5
Why does energy and biomass decrease at higher trophic levels? • Only 10% is used • The rest is given off as heat • Body activity 1.5 Biomass pyramid (grams/m2) Top carnivores 11 Primary carnivores 37 Herbivores 809 Detrivores/ decomposers Producers 5
Here is the question? • Assume that there are 5,000,000,000 leaves with a mass of 0.2 grams each, making up a biomass of 1,000,000,000 grams at the producers level. Calculate the number of cat(s) that could be supported by the food chain leaves caterpillar robin cat if: • 1 caterpillar has a mass of 0.5 grams • 1 robin has a mass of 75 grams • 1 cat has a mass of 2,900 grams
Assignment • Energy Flow Worksheet and Math Problems
Ticket out The Door • What is Primary productivity? • How can humans affect food webs? • What are Trophic levels? • Why do trophic levels loose energy?