Memory and Information Processing
110 likes | 297 Views
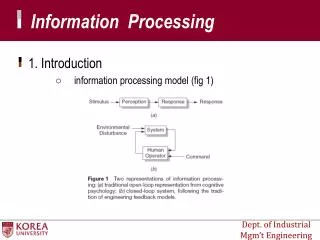
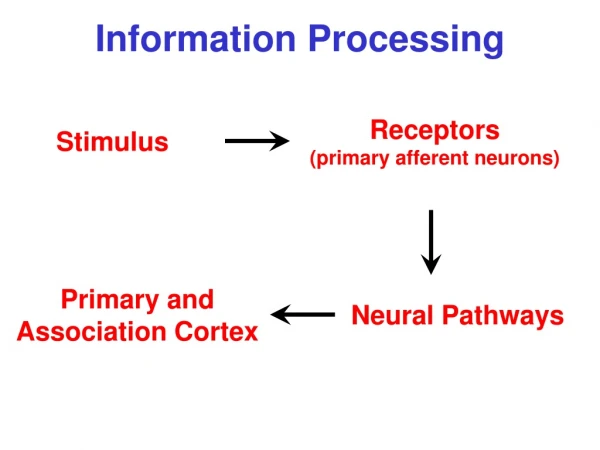
Memory and Information Processing . Psychology . Sensory Registers. Entry points for raw information from the senses Information stays a short time and then processed or lost Visual and auditory studied most Visual Registers Visual Image (Icon)

Memory and Information Processing
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Memory and Information Processing Psychology
Sensory Registers • Entry points for raw information from the senses • Information stays a short time and then processed or lost • Visual and auditory studied most • Visual Registers • Visual Image (Icon) • Visual information erased in ¼ of second and replaced with new information • Auditory Registers • Auditory Image (Echo) • Fades more slowly than icon • Need to remember first of sentences after hearing last word
Initial Processing • Cannot be aware of all information coming into registers • Attention • Process of selective looking, smelling, tasting, hearing, feeling • Gives meaning to the information • Theories of Attention • Filter Theory (Donald Broadbent – 1958) • Sort stimuli by physical properties (color, size, loudness) • Cocktail Party Phenomenon (Anne Treisman - 1964) • Paying attention to one person, but when hear your name across the room your attention changes
Short Term Memory • Working Memory • Briefly stores and processes selected info from the sensory registers • 2 Tasks of STM • Store raw info briefly and Work on that information • STM can hold as much info as you can repeat in 1.5 – 2 seconds • 1. B L C • 2. J S T V Y • 3. X T P R L C A • 4. G R N O Q Z X L T P • 5. B D G V A X N H J O K T • Chunking – grouping info into meaningful units for easier handling by the STM • 128963812093 • 1289 6381 2093
Why Do We Forget? • Decay Theory- time causes forgetting • Interference Theory- interference from other info causes forgetting • Can forget info in 20 seconds if we don’t rehearse
Remembering • Rote Rehearsal- repeating info over and over again • Elaborative Rehearsal- linking new info to familiar info in long term memory • Flashbulb memory – vivid memory of a certain event and the incidents surrounding it even after a long time has passed.
Long Term Memory • Everything we know • It is essentially permanent – Permanent memory • Semantic Memory • LTM that stores general facts and info • Episodic Memory • LTM that stores more specific info of a personal nature
Coding In Long Term Memory • Most info in LTM is coded in terms of memory – can be verbatim • Info from STM transferred to LTM by rehearsal • Explicit Memory – memory for info that was intentionally committed to memory • Implicit Memory – memory for info that was unintentionally committed to memory
Retrieval of Long Term Memory • Info lasts for a very long term • Tip of Tongue • ex. – Names of all the seven dwarfs • Best way to remember – quit thinking about it for a while • Mnemonics – techniques that make material easier to remember. • ex. – colors of the rainbow, spectrum - ROY G. BIV • SQ3R – Survey, Question, Read, Recite, Review- another technique used to help you remember information
Amnesia and Different Types of Forgetting • Retrograde amnesia – events just prior to an accident are forgotten • Milner’s syndrome – brain surgery, then after surgery could not remember new info, but could still remember info from before the surgery • Korsakoff’ssyndrome – chronic alcoholism leads to this type of amnesia (due to vitamin deficiency) • Infantile amnesia – inability to recall events before the age of two. • Alzheimer’s – neurological disorder that involves severe memory loss. • Hysterical amnesia – memory loss that has no known neurological cause • -ex.- waking up in a strange city with no recollection of anything, seen in movies/TV • Repression– when an experience doesn’t fit our view of the world or ourselves, we tend to unconsciously blot out the memory altogether.