Understanding Ulnar Nerve Anatomy and Disorders
540 likes | 696 Views
Learn about the origin, course, and distribution of the ulnar nerve. Explore common sites of compression and symptoms of ulnar nerve injury in the elbow, hand, and wrist. Discover the effects of ulnar nerve division and handlebar neuropathy.

Understanding Ulnar Nerve Anatomy and Disorders
E N D
Presentation Transcript
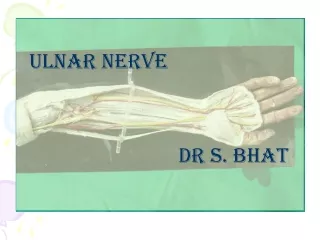
Ulnar nerve Dr s. bhat
Learning objectives • To know the origin, course and distribution of ulnar nerve. • To learn about common applied anatomy of ulnar nerve.
Ulnar nerve • Branch from medial cord of brachial plexus • Conveys fibers from C8 & T1 • Receives contribution from C7 through the median nerve for flexor corpi ulnaris
Course and relations: In the axilla : • Runs along the medial side of third part of the axillary artery in the interval between axillary artery and vein
In the arm: • Accompanies the medial side of brachial artery in the proximal half of the arm • Pierces the medial inter-muscular septa in the middle of the arm • Descends superficial to the medial head of the triceps
Appears in the interval between medial epicondyle & olecranon process • Lodges in a groove on the dorsal surface of the medial epicondyle, here we can palpate the nerve
In the forearm: • Enters the forearm between two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris • Descends along the medial side of the forearm, lying on the flexor digitorum profundus • Proximally nerve is covered by flexor corpi ulnaris
distally lies lateral to the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle and is covered only by skin & fascia • Upper third of forearm, the nerve is distinct from ulnar artery, but distally lies close to the medial side of the artery
In the hand: • Enters in to the hand by passing deep to the superficial part of flexor retinaculum (in Guyon’s canal) • Deep to the palmaris brevis divide into superficial and deep terminal branches
Branches: • No branches in axilla and arm Branches in forearm Motor branches to the:- • flexor carpi ulnaris • medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus (to the tendons of the little & ring fingers)
Cutaneous branches:- Dorsal branch: arises 5 cm proximal to the wrist -Supplies skin of the dorsal aspect of medial one and a half of the fingers, excluding terminal phalanges of ring & little fingers Palmar branch: supplies skin of the medial side of the palm
In hand: Superficial branch: • Supplies palmaris brevis and medial palmar skin • Divides into two palmar branches, which can be palpated against the hook of the hamate • Proper digital nerve supplies the medial side of the little finger • Common digital nerve divides into two proper digital nerves to supply adjacent sides of the little and ring finger
Deep terminal branch: • Accompanies the deep branch of the ulnar artery • Passes between abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi • Pierces the opponens digiti minimi and turns laterally lodging in a groove below the hook of the hamate • Supplies to the: hypothenar muscles, 3rd and 4th lumbricals, palmar & dorsal interossei & adductor pollicis .
Articular branchesto the:- -elbow -intercarpal -carpometacarpal joints Vascular branches to the:- -ulnar -palmar arteries
Applied anatomy • Common sites of compression of ulnar nerve • at the elbow • in the cubital tunnel • at the wrist joint • in the hand • The effects of injury depends on the site of lesion
Effects of ulnar nerve injury at the elbow • Damaged by • Fracture of medical epicondyle of humerus
Cubital tunnel syndrome: • Due to the compression of nerve behind the medial epicondyle • Clinical manifestations:- -on attempting to flex the wrist, the hand is abducted due to the unopposed action of the flexor carpi radialis -medial four fingers cannot be adducted and abducted due to the paralysis of palmar & dorsal interossei -Claw hand is a condition seen in ulnar nerve injury in which medial two fingers are extended at MP joints and flexed at IP joints
-Thumb cannot be adducted due to paralysis of adductor pollicis -wasting of hypothenar muscles -loss of sensation of the medial one and a half digits and medial side of the hand
Ulnar tunnel syndrome:- -it is an entrapment neuropathy of the ulnar nerve as it passes through the Guyon’s canal symptoms: -pain in the hand or forearm -sensory changes in the palmar aspects of the little and ring fingers -weakness or wasting of the intrinsic muscles of the hand -clawing posture of the hand in extreme cases
Ulnar nerve division at the wrist:- Symptoms: -paralysis of all intrinsic muscles of the hand except 1st & 2nd lumbricals -loss of flexion at MP joints and extension at IP joints -unopposed actions of extensors and flexors causes the hand to assume a clawed appearance -sensory loss over the medial one and a half fingers
Handlebar neuropathy Cause:- -occurs in people who ride long distances on bicycles -hand grip put pressure on the hooks of their hamates, which compresses the ulnar nerves Symptoms:- -sensory loss on the medial side of the hand -weakness of the intrinsic hand muscles
Tests for ulnar nerve lesion:- 1.Patient will not be able to hold a sheet of paper between index and middle fingers 2.Wartenberg’s sign: - patient will not be able to adduct and abduct the four digits, while placing the flat hand on a table
Questions • Origin, course, distribution and applied anatomy of ulnar nerve. • Ulnar nerve in hand.