
0 likes | 86 Views
Jaundice is a condition characterized by yellow discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to increased levels of bilirubin in circulation and tissue deposition. This article delves into the different types of jaundice, including prehepatic, hepatic, and posthepatic, outlining their respective causes such as hemolytic anemias, viral hepatitis, and cirrhosis. Various associated disorders like G6PD deficiency and leptospirosis are discussed, along with relevant clinical considerations and diagnostic approaches.

E N D
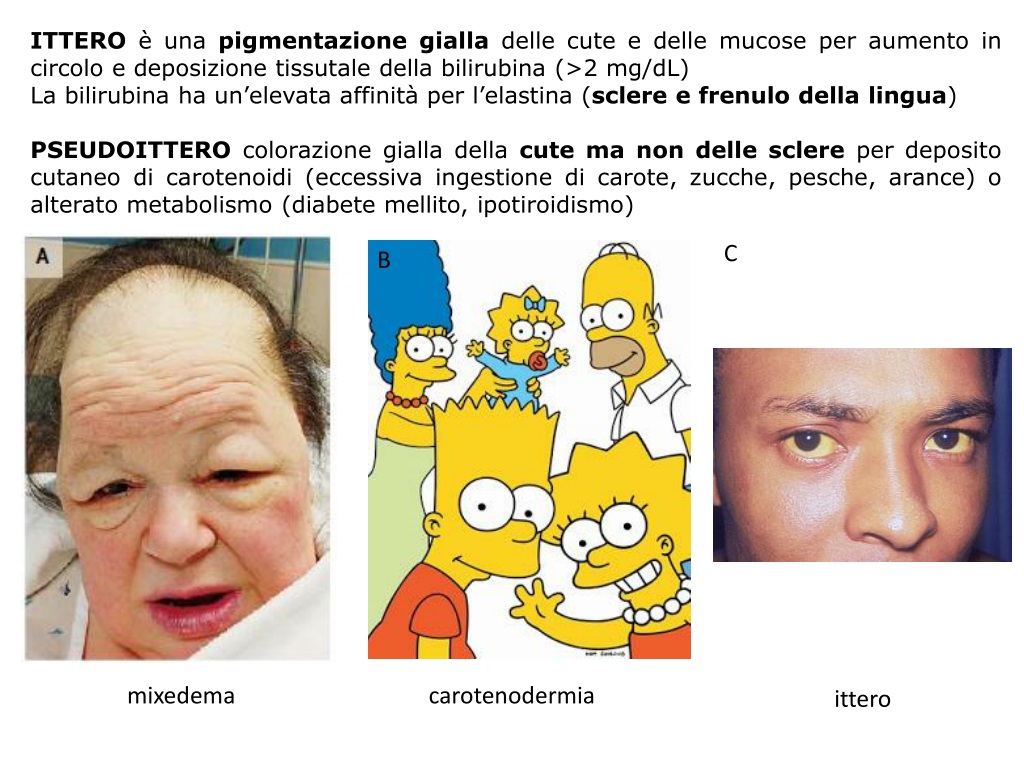
ITTERO è una pigmentazione gialla delle cute e delle mucose per aumento in circolo e deposizione tissutale della bilirubina (>2 mg/dL) La bilirubina ha un’elevata affinità per l’elastina (sclere e frenulo della lingua) PSEUDOITTERO colorazione gialla della cute ma non delle sclere per deposito cutaneo di carotenoidi (eccessiva ingestione di carote, zucche, pesche, arance) o alterato metabolismo (diabete mellito, ipotiroidismo) C B mixedema carotenodermia ittero
PREEPATICO (FLAVINICO) - ittero a BILIRUBINA NON CONIUGATA URINE ARANCIO FECI SCURE • Anemie emolitiche (cause intraglobulari o extraglobulari) • Riassorbimento di ematomi • Crigler-Najjar e Sindrome Gilbert EPATICO (RUBINICO) – ittero a BILIRUBINA MISTA URINE SCURE FECI IPOCOLICHE • Epatite virale (Epatite A, B, C, D, E; CMV, EBV, HSV)/batterica • Epatite alcolica • Epatite autoimmune • Epatite da farmaci e altri tossici • Malattia di Wilson (NEJM 368;14:1345-1351), emocromatosi e altre malattie congenite • Rotor e Dubin Johnston CIRROSI POSTEPATICO (VERDINICO) – ittero a BILIRUBINA CONIUGATA URINE IPERCROMICHE (COLOR MARSALA) FECI ACOLICHE • Colestasi intraepatica • Colestasi extraepatica
• • • • Modalità e epoca di comparsa Continuo o episodico? Fattori scatenanti? Disturbi associati? ANAMNESI PATOLOGICA PROSSIMA: ITTERO ANAMNESI FISIOLOGICA ANAMNESI PATOLOGICA REMOTA ANAMNESI FAMILIARE ESAME OBIETTIVO
DEFICIT di G6PD - FAVISMO M (X-linked recessivo) Africa, Medio-Oriente, Mediterraneo (Sardegna, Sicilia, Grecia) Difetto di enzima antiossidante G6PD Fattori scatenanti: di fave o esposizione sostanze ossidanti Anemia emolitica modesto (4-5 mg/dL) astenia, tachipnea, tachcardia, frequente celere, eiezione su tutti i focolai Urine arancio aumento di emoglobinuria; feci scure • • • Ingestione • a Vicia Fava con ittero • polso soffio da (cariche) urobiline per • e Beutler E. N Engl J Med 1991;324:169-174.
LEPTOSPIROSI - SINDROME di WEIL ITTERO - DISFUNZIONE RENALE - DIATESI EMORRAGICA ANAMNESI: Viaggio nei tropici ?, Canoa, windsurf, nuoto, sci d’acqua?, immersione imprevista in acque contaminate? andamento bifasico
EPATITE ACUTA VIRALE ANAMNESI - EPATITE B/C (parenterale) Tatuaggi/piercing? Interventi chirurgici/odontoiatrici/ trasfusioni/iniezioni/emodialisi? Uso di droghe per via endovenosa? ANAMNESI - EPATITE A (oro-fecale) Viaggi in aree ad alta endemia? Consumo di acqua e cibi contaminati? Frutti di mare? Epatite A: epatite acuta che va incontro a risoluzione, può essere subclinica nei bambini. epatite fulminante 1/1000 casi Epatite B e C: epatite acuta che nel 6% HBV e 75% HCV cronicizza con conseguente cirrosi nel 3% e nel 20% dei pazienti