Exploring Organism Diversity
200 likes | 249 Views
Learn about the five kingdoms of organisms, classification of animals and plants, including diverse features of prokaryotes, protoctists, fungi, plants, and animals. Explore vertebrates and invertebrates, including details on fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals. Discover the classification of flowering and non-flowering plants with examples of different plant groups.

Exploring Organism Diversity
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BIOLOGY Diversity of Organisms
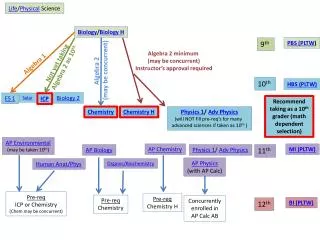
Diversity of Organisms • Today I want to talk about Diversity of Organisms. There are three main topics: • A) Five kingdoms of organisms • B) Classification of Animals • C) Classification of Plants
Five kingdoms of organisms 1 Prokaryotes • They include bacteria & blue-green algae. • They are very tiny and can seen with the high power of a light microscope. • They consist of a single cell but do not have any true nucleus ,mitochondria or chloroplasts. < Anthrax bacteria A flagellate >
Five kingdoms of organisms 2 Protoctists • They are tiny and can be seen with the low power of a microscope. • They consist of the single cell with a true nucleus but some are multicellular. • They live mainly in water or inside other organisms. < Amoeba Paramecium >
Five kingdoms of organisms 3 Fungi • They are made up of a single call or thread-like structures called hyphae. • They have cell wall and do not move.They have no chlorophyll and any roots, stems or leaves. • They are usually saprophytic or parasitic and live in soil ir inside other organisms. < Yeast Mushroom >
Five kingdoms of organisms 4 Plants • All plant cells have cell wall and green plant cells contain chlorophyll. • They make their own food by photosynthesis. • They do not move from place to place. < Plant Green plant>
Five kingdoms of organisms 5 Animals • They do not have any cell wall. • They cannot make their own food and must take in food. • Most of them can move from place to place.
Vertebrates A ) Fish • Their bodies are covered by silmy scales. • They have fins. • Their bodies are streamlined. • They breathe with gills. • They are poikilotherms.
Vertebrates B) Amphibians • They can live both on land and in water • They have wet, silmy skins but no scales. • They have 4 limbs when they are adult. • They are poikilotherms.
Vertebrates C) Reptiles • Many live on land. • They have skin covered by hard, dry scales. • They breathe with lungs. • They are mostly poikilotherms.
Vertebrates D) Birds • They have feathers. • Most can fly with wings but some cannot. • They have beaks. • They breathe with lungs. • They are homoiotherms.
Vertebrates E) Mammals • Their bodies are covered with hair. • Females have well-developed mammary glands for feeding their young. • They breathe with lungs. • They are homoiotherms.
Invertebrates • Most of them are small.
Flowering plants A) Monocotyledonous plants • They have only one seed leaf in the seed. Iris Rice
Flowering plants B) Dicotyledonous plants • They have two seed leaves in the seeds. • Their leaves have a network of veins. Water lily Broad bean
Non-flowering plants A) Mosses • They are small plants,but no roots. • They have chlorophyll but no vascular tissue. Polytrichum
Non-flowering plants B) Ferns • They are small plants with true roots, stems and leaves. • They have chlorophyll and vascular tissue. dryopteris
Non-flowering plants C) Gymnosperms • They have large plants with roots, stems, leaves and vascular tissue. • Most of them have needle-shaped leaves. Firs