Budget & Cost Control Telco
150 likes | 334 Views
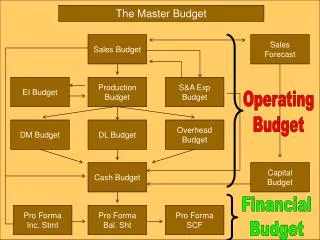
Budget & Cost Control Telco. IL MERCATO DELLE TELCO. 2. 4. 3. 1. 5. Hutchison Whampoa Limited.

Budget & Cost Control Telco
E N D
Presentation Transcript
IL MERCATO DELLE TELCO 2 4 3 1 5
Hutchison Whampoa Limited “In Hong Kong, HWL holds a majority interest in Hutchison Telecommunications Hong Kong Holdings (HTHKH). A listed company and an established integrated telecommunications operator, HTHKH provides leading-edge mobile services in Hong Kong and Macau under the 3 brand and advanced fixed-line services for local and international customers under the Hutchison Global Communications (HGC) brand”. “In global markets, Hutchison Asia Telecommunications (HAT) holds HWL’s interest in mobile operations in Indonesia, Vietnam and Sri Lanka, while 3 Group Europe operates businesses in Italy, the UK, Sweden, Denmark, Austria and Ireland”. http://hutchison-whampoa.com 2 Hong Kong - Macau 3 Indonesia - Vietnam - Sri Lanka 6 Italy - UK - Sweden - Denmark - Austria - Ireland
IL CONTROLLER Organization Activities Monitoring CEO CMO COO CFO Stanziamenti (Costo/Ricavo) Delta Analysis Reporting
P&L – Profit & Loss REVENUES Ricavi Lordi Fatturati ai Clienti Costi Diretti per i servizi di rete Direct Costs GROSS MARGIN Costi Operativi di Gestione OPEX CRC Costi di Acquisizione e Gestione della Clientela CAC EBITDA D & A Ammortamenti e Svalutazioni EBIT Interessi Finanziari e Tasse Interest & Tax NPAT
Dai Ricavi al Gross Margin REVENUES Customer Service Revenues Abbonamenti Credito Tel utilizzato Opzioni tariffarie Other Non Recurrent Revenues Ricavi da rivendita di traffico all’ingrosso ad operatori virtuali es. Direct Costs Costi di Rete Costo di Acquisto della Rete di altri Operatori Costi di Utilizzo della Rete Propria es. GROSS MARGIN Domanda di Beni e Servizi Prezzi di Vendita Costi Variabili di Produzione Leve del GM es.
Dal Gross Margin all’EBITDA OPEX General & Administrative Advertising & Promotion Budget Line Items IT Costs es. CRC & CAC Budget Line Items Customer Promotions & Loyalty Programs Subsidy Commissioning es. EBITDA Costi del Personale Costi di Vendita CRC & CAC Leve dell’EBITDA es.
IL BUDGET Il budget è uno strumento direzionale che serve per assicurare che la gestione aziendale si svolga coerentemente agli obiettivi identificati dal vertice aziendale. avente per oggetto le operazioni di gestione da compiere in un periodo amministrativo (normalmente di durata annuale); finalizzato al raggiungimento di obiettivi prestabiliti, che permettono a loro volta di conseguire obiettivi di lungo periodo; con una quantificazione delle risorse occorrenti. CARATTERISTICHE LA PROFONDITÀ Il budget concerne tutti gli aspetti della gestione aziendale. Gli aspetti economico-finanziari, gli aspetti infrastrutturali, e gli aspetti organizzativi. L’AMPIEZZA Il processo di budgeting coinvolge tutta l’impresa. Il budget deve guidare non solo il comportamento del vertice, ma anche quello delle varie unità organizzative della struttura aziendale. IL DETTAGLIO TEMPORALE Il budget si riferisce ad un anno di gestione, e presenta un dettaglio infra annuale, suddiviso in semestri, trimestri, bimestri o mesi. IL DETTAGLIO ECO - FIN L’insieme delle previsioni e delle scelte viene sintetizzato in termini “monetari” oltre che gestionali.
IL PROCESSO DI BUDGETING Organi apicali Definisce gli obiettivi strategici ed i risultati (es. EBIT) Gli obiettivi vengono scomposti per i vari Centri di Costo – vengono definite le nuove attività Unità Operative Centri di Costo CDG Form di Budget Verifica e consolida i dati Dettaglio attività per il nuovo anno Accetta il budget Rivede ed effettua gli eventuali tagli Procede alla definizione del P&L In questo contesto il controller svolge il ruolo di verifica della coerenza degli stanziamenti di risorse su attività routinarie rispetto allo storico degli anni precedenti, inoltre, verifica la coerenza della nuove richieste da parte dei centri di costo rispetto alle attività da svolgere, richiedendo le offerte da parte dei fornitori, attività similiari, dettaglio specifico delle operazioni da intraprendere.
La chiusura del Mese Definito l’EBIT Target, ogni mese viene effettuata una chiusura Gestionale. Vengono effettuate le classiche operazioni di chiusura annuale, quali competenziazione dei costi / ricavi con scritture di ratei / risconti, acc.to a fondo rischi, etc. Ogni mese viene verificato l’andamento della gestione rispetto agli obiettivi definiti. Vengono individuati i delta ed identificate le motivazioni tramite la “delta analysis” per esempio: DELTA Domanda GM DELTA Ricavi / Costi Unitari OPEX DELTA BLI CRC DELTA VOLUME (Volume BDG – Volume ACT) * Unitario BDG DELTA UNITARIO (Unitario BDG – Unitario ACT) * Volume ACT CAC EBIT
Dal Budget al Forecast Ogni 3 mesi viene effettuato un aggiornamento del budget, quindi dell’obiettivo di risultato, Ossia viene prodotto un forecast. ESTIMATE BUDGET JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC ACTUAL ESTIMATE F1 JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC F2 ACTUAL ESTIMATE JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC F3 ACTUAL ESTIMATE JAN FEB MAR APR MAY JUN JUL AUG SEP OCT NOV DEC