Chapter 5 Supply
260 likes | 464 Views
Chapter 5 Supply. Definition of Supply. Supply – the willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale. Law of Supply. Law of Supply – producers are willing to sell more of a good or service at a higher price.

Chapter 5 Supply
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Definition of Supply • Supply – the willingness and ability of producers to offer goods and services for sale.
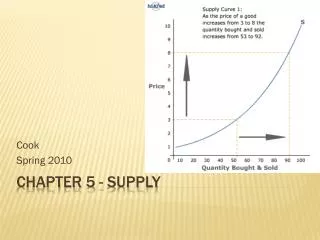
Law of Supply • Law of Supply – producers are willing to sell more of a good or service at a higher price. • If the price of a product falls producers will want to supply less of it. • This is a direct relationship.
Supply Schedule Shows the law of supplyin chart form. Individual Supply Schedule
Supply Curve Shows the supply schedule in a graph form.
Factors Affecting Supply • Input costs – the price of the resources used to make products • Labor Productivity – the amount of goods and services that a person can produce in a given time. • Technology – new discoveries in the production process means new manufacturing techniques.
Government Action (excise tax) – a tax on the production or sale of a specific good or service. • Producer Expectations – the expectation of a products price rising or falling will affect how much that producer is willing to produce.
Number of Producers – an increase in the number of producers of a certain product will increase demand.
Costs of Production • At my pizzeria I charge 12.00 for a large pizza. • It cost me (overhead, fixed + variable costs) 4.00 to make a large pizza. • What is my overhead?
Production Cost Schedules • Remember schedules in economics are charts. • Product Cost Schedule will show you the relationship between labor and production.
Terms to Know • Marginal Product – the change in total product that results from hiring one more worker. • Specialization – each worker being hired focuses on a particular part of production
Diminishing returns – each new worker can actually cause a decrease in marginal product
As an owner what are your costs? • Fixed costs – examples include mortgage, insurance, utilities • Variable costs – wages, more material or overhead if production goes up • Total costs – the sum of fixed and variable costs
Terms to Know • Marginal Costs – additional costs of producing one more item • Marginal Cost is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in total product.
How do we earn the highest profit • Since we can stand to lose money by producing at a rate that is not efficient, we have to calculate how much profit we can make before we start to produce
Simple Math!!! • Marginal revenue – the money made from the sale of each additional unit of output. Basically the price of an item. • Total revenue – a company’s income from selling its products. Total Revenue = P x Q • P = price / Q = quantity sold • Calculate by multiplying total product by marginal revenue
Simple Math!!! • Calculating profit – total revenue minus total cost • Profit = total revenue – total cost
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ • Profit Maximizing Output – level of production at which business realizes the greatest amount of profit. • Marginal Revenue = Marginal Costs • This is where you want to be and stay!!!!!!!!!
Elasticity of supply – a measure of how responsive producers are to price change. • If a change in price leads to a change in quantity supplied, the supply is elastic. • If a change in price leads to a very small change in quantity supplied, the supply is inelastic.
Factors of Elasticity • The ability of a company to change production to respond to price changes. • Given enough time most companies will make their supply more elastic by expanding or downsizing.