Electrochemistry
90 likes | 241 Views
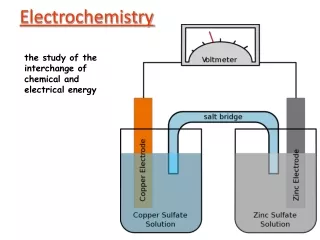
Electrochemistry. Chemistry 30 Unit 2. the transfer of electrons in chemical reactions. . Reduction operational definition : extraction of metals from the ore theoretical definition : gain of electrons

Electrochemistry
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Electrochemistry Chemistry 30 Unit 2 • the transfer of electrons in chemical reactions.
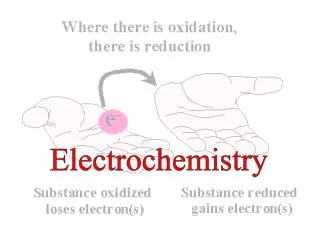
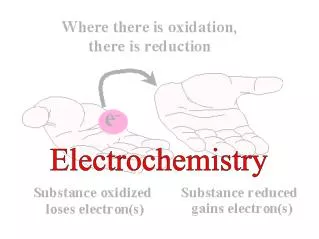
Reduction • operational definition: extraction of metals from the ore • theoretical definition: gain of electrons Reducing agent –species that causes reduction, and is an electron donor (it is oxidized)
Oxidation • operational definition : reaction with oxygen • theoretical definition: loss of electrons Oxidizing agent – is a species that causes oxidation by accepting electrons (it is reduced)
Memory Tips: • LEO (the lion) says GER (lose electrons and you are oxidized, gain electrons and you are reduced) • OIL RIG (oxidation is losing electrons, reduction is gaining electrons)
Oxidation States • A method of keeping track of the electrons that are transferred in a chemical reaction uses the oxidation states of an atom in an entity. • The apparent net electric charge that an atom would have if the electron pairs in a covalent bond belonged entirely to the more electronegative atom. • These are imaginary – they do not represent the actual charge on the atom
The oxidation number is the positive or negative number corresponding to the oxidation state.
Rules for Assigning Oxidation Numbers • Assign common oxidation number • The oxidation numbers of compounds must add to zero • Molecular compounds: oxidation # assigned to more electro negative is its regular ion charge • Polyatomic Ions: sum of the oxidation numbers must equal the charge of the ion