Weaning From Mechanical Ventillation
130 likes | 676 Views
Weaning From Mechanical Ventillation. By Sebastian Benavides PGY2. Objective. Identifying patients who are ready to wean from mechanical ventillation Via clinical criteria Identifying patient who are not ready for weaning Knowing the weaning parameters. Defining Weaning.

Weaning From Mechanical Ventillation
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Weaning From Mechanical Ventillation By Sebastian Benavides PGY2
Objective • Identifying patients who are ready to wean from mechanical ventillation • Via clinical criteria • Identifying patient who are not ready for weaning • Knowing the weaning parameters
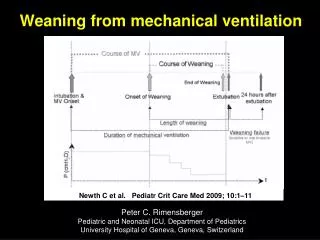
Defining Weaning • Progressive decrease in the amount of support a patient recieves from the ventilator • 2 step process • Patients who are ready to wean are identified using a two step predictors of weaning outcome • Weaning is then initiated
Weaning • Clinical Criteria: • Cause of respiratory failure improved • Patient is hemodynamic ally stable • Patient oxygenating well (SpO2>90% on FIO2<50%, PEEP< or = to 5) • Mental status: Awake and alert • Able to initiate inspiratory effort
Weaning • Parameters: • RSBI (RR/Vt)<105 • Mintue Ventilation <15L/min • Spontaneous Vt > or = 5ml/kg • Negative inspiratory force< or = to -30mm H2O
Initial Weaning • Set pressure support ventillation 1 hr prior to initiation of weaning: • FiO2 at 50% • PEEP: must be less than 8 • Pressure support should be weaned down to 5
Weaning • Prior to Extubation: • Confirm minimal FIO2 (less than or equal to 50%) and PEEP equal to 5 • Evaluate upper airway comlications • Check audible cuff leak (if concern for edema, stridor) • Check if cough and gag are present • Have equipment ready • NC/face mask/bipap • Suction secreations • Extubate!
Case • 62 year old male who weighs 70kg was intubated 3 days ago for hypercapnic respiratory failure • Patient is alert, cooperative on the ventilator over the past 6 hours • He is on poressure support ventilation with a tidal volume of 700ml, PS of 10 and an FIO2 of 50% • Upon assessing his weaning parameters, his RSBI is 70, minute ventillation is 10ml/min, his spontaneous tidal volume is 490ml nad NIF is -30mmH2O
Case • What would be the following appropriate plan of action? • Extubate patient to NC • Increase pressure support to 15 assess weaning parameters and extubate after 1 hour • Decrease pressure support to 5 assess weaning parameters and extubate after 1 hour • Increase FIO2 to 60% then extubate after assessing weaning parameters • Decrease FIO2 to 40% then extubate after assessing weaning parameters
Case • C is the correct answer
Case • Answer: reinitubate and resume mechanical ventilation
Summary • When weaning, remember that patients must meet clinical criteria. Use your judgment and ask yourself if this patient looks ready to be extubated • Know your weaning parameters • RSBI, Minute ventilation, Spontaneous tidal volume, NIF • Always have equipment ready once extubating as patient may fail extubation regardless if they meet all the weaning parameters and clinical criteria
Special Thanks • Whoever created slides prior to my adjustments • The ICU Book 3rd edition by Paul L. Marino • Angelina Amian (Excellent ICU fellow)